Abrasive substances are indispensable across a vast array of industrial applications—from precision manufacturing and automotive production to construction and metalworking. Their ability to shape, finish, and clean materials with unmatched efficiency makes them a cornerstone in supply chains worldwide. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the complexities of sourcing high-quality abrasives is vital to maintaining competitive advantage and operational excellence.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of abrasive substances, covering key categories such as natural and synthetic abrasives, their material properties, and the latest manufacturing and quality control standards. Buyers will gain insights into evaluating supplier reliability, cost factors, and market trends tailored to their regional context—whether navigating import regulations in Spain or optimizing procurement strategies in emerging African economies.
By addressing frequently asked questions and providing actionable tips on supplier selection, logistics, and cost management, this resource empowers buyers to make well-informed decisions that reduce risk and enhance value. With an authoritative and solution-oriented approach, the guide is designed to support procurement professionals in securing abrasive materials that meet rigorous performance standards while aligning with budgetary and sustainability goals.
Ultimately, mastering the global abrasive market landscape enables businesses to drive innovation, improve product quality, and sustain long-term growth in increasingly competitive international environments.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
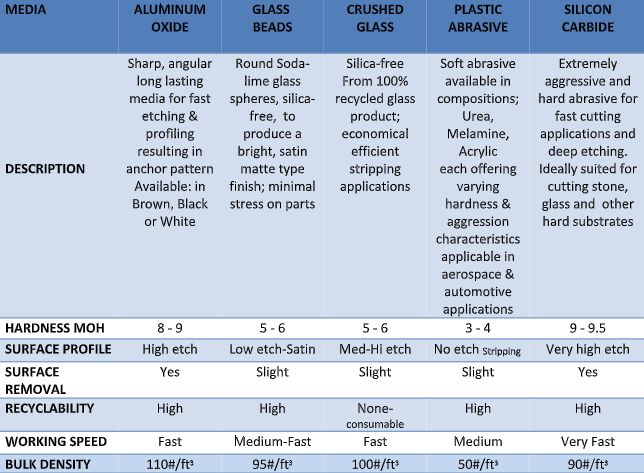
| Aluminum Oxide | Durable, sharp, available in various grit sizes | Metal fabrication, woodworking, automotive | Pros: Versatile, cost-effective; Cons: Not ideal for soft metals |
| Silicon Carbide | Extremely hard, sharp edges, chemically reactive | Glass, ceramics, stone cutting, electronics | Pros: High efficiency on hard materials; Cons: Brittle, dust hazard |
| Garnet | Natural, angular grains, environmentally friendly | Waterjet cutting, abrasive blasting, polishing | Pros: Eco-friendly, reusable; Cons: Higher cost, limited grit range |
| Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) | Synthetic, second hardest after diamond, heat resistant | Precision grinding, tool sharpening | Pros: Long life, withstands heat; Cons: High initial cost |
| Diamond | Hardest known abrasive, synthetic or natural | Cutting, grinding of hard materials like stone and carbide | Pros: Superior hardness, long-lasting; Cons: Expensive, requires specialized handling |
Aluminum Oxide
Aluminum oxide is a widely used abrasive due to its balance of hardness and cost-efficiency. It is ideal for applications involving metal fabrication, automotive parts, and woodworking. Its versatility makes it a staple for B2B buyers seeking reliable performance across various materials, especially ferrous metals. When purchasing, buyers should consider grit size variations and the abrasive’s bonding method to optimize for specific surface finishes and durability.
Silicon Carbide
Known for its sharpness and chemical reactivity, silicon carbide excels in working with hard, brittle materials such as glass, ceramics, and stone. It is favored in electronics manufacturing where precision and fine finishes are critical. However, its brittleness and dust generation require buyers to invest in proper handling and safety measures. This abrasive is best suited for industries needing aggressive cutting or grinding of non-metallic materials.
Garnet
Garnet abrasives are natural and environmentally friendly, making them attractive for companies prioritizing sustainability. They are commonly used in waterjet cutting and abrasive blasting, offering reusability that can reduce operational costs over time. Buyers should assess the cost-benefit trade-off between garnet’s higher upfront price and its long-term performance, especially in polishing and surface preparation tasks.
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)
CBN abrasives are synthetic and second only to diamond in hardness, with excellent heat resistance. These properties make CBN ideal for precision grinding and sharpening of hardened steels and superalloys. For B2B buyers, the high initial investment is offset by the abrasive’s longevity and performance in high-speed, high-temperature environments. It is a strategic choice for industries requiring consistent precision and durability.
Diamond
Diamond abrasives represent the pinnacle of hardness and cutting ability, suited for extremely hard materials like carbide, stone, and glass. Available in synthetic and natural forms, diamond abrasives are indispensable in high-precision cutting and grinding operations. Buyers must consider the premium cost and specialized equipment needed, but the extended lifespan and superior cutting efficiency often justify the investment for high-value manufacturing sectors.
Related Video: Types of Bonding (Ionic, Covalent, Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry Revision
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of abrasive substances | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Precision grinding and polishing of engine components | Enhances component durability and performance, reducing defects and recalls | Consistent grit size, high purity abrasives, and supplier reliability for just-in-time delivery |
| Metal Fabrication | Surface preparation and finishing of steel and aluminum | Improves weld quality and paint adhesion, increasing product lifespan | Abrasive hardness, compatibility with metal type, and cost-effective bulk purchasing options |
| Electronics Industry | Micro-abrasion for semiconductor wafers and circuit boards | Enables high precision and defect-free surfaces critical for device performance | Ultra-fine abrasives, contamination-free supply, and compliance with environmental standards |
| Construction & Mining | Cutting and grinding of concrete, stone, and minerals | Speeds up material processing, enhances structural integrity, and reduces downtime | Abrasive toughness, wear resistance, and availability of export-grade materials for large projects |
| Aerospace | Finishing of turbine blades and airframe components | Ensures aerodynamic efficiency and safety through smooth, defect-free surfaces | High-performance abrasives with consistent quality and adherence to strict aerospace standards |
Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive manufacturing, abrasive substances are crucial for precision grinding and polishing of engine components such as crankshafts, camshafts, and cylinder heads. These abrasives help achieve tight tolerances and smooth finishes that enhance engine efficiency and longevity. For international buyers, especially from regions like Europe and South America, sourcing abrasives with consistent grit size and high purity is essential to avoid defects that could lead to costly recalls. Reliable suppliers with robust logistics are preferred to support just-in-time manufacturing processes.
Metal Fabrication
The metal fabrication industry uses abrasives extensively for surface preparation, deburring, and finishing of steel and aluminum parts. Proper abrasive selection improves weld quality and paint adhesion, which directly impacts the durability and aesthetic appeal of the final product. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should prioritize abrasives that match the hardness of their metals and offer cost-effective bulk purchasing options to optimize operational expenses while maintaining quality.
Electronics Industry
Abrasive substances in the electronics sector are employed for micro-abrasion processes on semiconductor wafers and printed circuit boards. The demand for ultra-fine, contamination-free abrasives is high, as even microscopic impurities can compromise device performance. International buyers in technologically advanced markets such as Europe and South America must ensure suppliers comply with stringent environmental and quality standards, providing abrasives that support high precision and yield rates.
Construction & Mining
In construction and mining, abrasives are vital for cutting, grinding, and shaping concrete, stone, and mineral materials. High toughness and wear resistance are required to handle abrasive and heavy-duty materials efficiently. Buyers from regions with large infrastructure projects, including the Middle East and Africa, should focus on sourcing export-grade abrasives that guarantee durability and consistent supply to avoid project delays and cost overruns.
Aerospace
The aerospace sector demands abrasives for finishing turbine blades, airframe components, and other critical parts where surface smoothness affects aerodynamic performance and safety. Abrasives must meet rigorous quality standards and demonstrate consistent performance under strict regulatory oversight. European buyers, particularly in countries like Spain and Italy, often look for suppliers with certifications and proven track records to ensure compliance and minimize risk in their supply chains.
Related Video: Grit Blasting process Vs Sand Blasting process, Types of Grit Blasting abrasive materials
Aluminum oxide is one of the most widely used abrasive materials due to its excellent hardness and durability. It offers high temperature resistance up to approximately 1200°C and good chemical stability, making it suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Its corrosion resistance is moderate, which is generally sufficient for dry grinding and cutting operations.
Pros: Aluminum oxide is cost-effective and readily available, with a well-established manufacturing process. It is highly durable and versatile, suitable for grinding metals, ceramics, and plastics. The material’s consistent performance aligns well with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, facilitating compliance for buyers in Europe and other regulated markets.
Cons: Its performance can degrade when used with softer materials or in wet grinding environments due to potential chemical reactions. Manufacturing complexity is moderate but generally manageable for large-scale procurement.
Application Impact: Aluminum oxide is ideal for abrasive blasting, grinding wheels, and sandpaper, particularly when working with ferrous metals. It is less suitable for applications involving non-ferrous metals or softer substrates.
International Considerations: Buyers from Africa and South America should verify supplier adherence to ASTM or DIN standards to ensure quality consistency. In Europe (Spain, Italy) and the Middle East, regulatory compliance and environmental considerations around dust and particulate emissions are critical. Sourcing from suppliers with ISO certifications can streamline import and usage approvals.
Silicon carbide is known for its exceptional hardness and sharpness, with a temperature resistance around 1600°C. It exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, especially against acids and alkalis, making it suitable for abrasive applications in chemically aggressive environments.
Pros: It offers superior cutting efficiency and is ideal for grinding non-ferrous metals, glass, and ceramics. Silicon carbide’s sharp edges provide faster material removal rates, enhancing productivity. Its manufacturing process is more complex but yields a high-performance abrasive.
Cons: Silicon carbide is more brittle than aluminum oxide, which can lead to faster wear in certain applications. It is also generally more expensive, impacting cost-sensitive projects.
Application Impact: This material excels in precision grinding and finishing tasks where sharpness and chemical resistance are paramount. It is less effective for heavy-duty grinding of ferrous metals due to its brittleness.
International Considerations: For buyers in South America and Africa, cost and supply chain reliability are key; establishing relationships with trusted suppliers who meet ASTM or JIS standards is advisable. European and Middle Eastern buyers should consider environmental regulations related to particulate emissions and waste disposal, as silicon carbide dust can be hazardous.
Garnet is a natural abrasive mineral prized for its eco-friendly profile and moderate hardness. It offers good chemical stability and is effective in waterjet cutting and abrasive blasting, especially for softer materials and surface preparation.
Pros: Garnet is renewable and non-toxic, making it attractive for environmentally conscious buyers. It has good wear resistance and is relatively inexpensive compared to synthetic abrasives. Its natural origin reduces manufacturing complexity.
Cons: Variability in natural garnet quality can affect consistency. It has lower hardness compared to aluminum oxide and silicon carbide, limiting its use in heavy-duty grinding.
Application Impact: Garnet is ideal for surface preparation, paint removal, and waterjet cutting of softer materials such as wood, plastics, and composites. It is less suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications.
International Considerations: African and South American buyers benefit from local garnet sources, reducing logistics costs. European buyers, particularly in Spain and Italy, should ensure garnet complies with REACH regulations and other environmental standards. Middle Eastern buyers must consider import restrictions and quality certifications to avoid variability.
Ceramic alumina is a synthetic abrasive known for its extreme hardness and toughness, with excellent heat resistance up to 1400°C. It maintains sharp cutting edges longer than traditional abrasives, providing superior durability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pros: It delivers high performance in heavy-duty grinding and finishing applications, especially on hard metals and alloys. Ceramic alumina’s long lifespan reduces replacement frequency, lowering total operational costs despite higher initial pricing.
Cons: The manufacturing process is complex and costly, leading to a higher price point. It may be over-specified for less demanding applications, resulting in unnecessary expense.
Application Impact: Ceramic alumina is preferred for precision grinding of hardened steels and aerospace components. Its resistance to heat and wear makes it suitable for continuous high-pressure operations.
International Considerations: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize suppliers with certifications to ASTM F standards and ISO 9001 quality management systems. African and South American buyers need to evaluate cost-benefit trade-offs carefully, considering the longer lifecycle but higher upfront cost. Ensuring supplier transparency and traceability is critical for compliance and performance guarantees.
| Material | Typical Use Case for abrasive substances | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | Grinding wheels, sandpaper, abrasive blasting of metals | Versatile, durable, compliant with ASTM/DIN | Moderate corrosion resistance, less suited for soft materials | Low |
| Silicon Carbide | Precision grinding of non-ferrous metals, ceramics | High hardness, excellent chemical resistance | Brittle, higher cost | Medium |
| Garnet | Waterjet cutting, surface preparation, paint removal | Eco-friendly, renewable, low manufacturing complexity | Variable quality, lower hardness | Low |
| Ceramic Alumina | Heavy-duty grinding of hardened steels and alloys | Extreme hardness, long lifespan | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
The production of abrasive substances involves a series of precise and controlled stages to ensure consistency, performance, and safety. Understanding these stages allows B2B buyers to assess supplier capabilities and product suitability for their applications.
This initial stage involves selecting and processing raw materials such as natural minerals (e.g., garnet, emery) or synthetic abrasives (e.g., aluminum oxide, silicon carbide). Key activities include:
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The abrasive grains are then formed into usable products, which vary by application:
Techniques such as pressing, molding, and curing are precisely controlled to maintain structural integrity and abrasive effectiveness.
In some products, abrasive components are assembled with other parts:
Finishing enhances product usability and safety:
Quality assurance (QA) is critical to ensure abrasive substances meet stringent performance, safety, and regulatory requirements. B2B buyers should look for suppliers with robust QA systems aligned with international and industry-specific standards.
Quality control (QC) is typically segmented into three critical phases:
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QA is essential to mitigate risks associated with product failure or regulatory non-compliance.
Understanding regional regulatory nuances and certification requirements can streamline procurement and reduce compliance risks.
Additionally, cultural and logistical factors impact QC verification:
By prioritizing these aspects, international B2B buyers can secure high-quality abrasive substances that meet operational demands and regulatory standards across diverse markets.
Understanding the underlying cost structure is crucial for international buyers aiming to optimize procurement of abrasive substances. Key cost components include:
Several factors shape the final price points for abrasive substances, influencing buyer negotiation strategies:
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, managing cost and ensuring value requires nuanced approaches:
Prices for abrasive substances can vary significantly based on market conditions, raw material availability, supplier strategies, and geopolitical factors. The insights provided are indicative and should be validated through direct supplier engagement and market research tailored to specific sourcing needs and regions.
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology related to abrasive substances is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions in the international B2B market. This knowledge helps buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe optimize product performance, ensure compatibility with their manufacturing processes, and negotiate favorable trade terms.
1. Material Grade
The material grade indicates the quality and composition of the abrasive substance, such as aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or diamond. Higher grades generally offer better durability and cutting efficiency. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate grade is essential to balance cost with performance, ensuring the abrasive meets the demands of specific industrial applications like metal grinding or polishing.
2. Grain Size (Grit)
Grain size defines the coarseness or fineness of the abrasive particles, measured in microns or grit numbers. Coarser grains (lower grit numbers) remove material quickly but leave a rougher finish, while finer grains produce smoother surfaces. Understanding grain size helps buyers specify abrasives that align with production requirements, whether for heavy material removal or fine finishing.
3. Hardness
Hardness measures the abrasive’s resistance to wear and deformation. This property affects the lifespan of the abrasive product and its effectiveness on different materials. Buyers must consider hardness to ensure compatibility with the hardness of the workpiece, avoiding excessive wear or insufficient cutting action.
4. Bond Type
The bond type refers to the material that holds abrasive grains together, such as resin, vitrified (ceramic), or metal bonds. The choice of bond influences the abrasive’s strength, heat resistance, and flexibility. Selecting the correct bond type is critical for applications requiring specific durability or thermal properties, impacting operational efficiency and product longevity.
5. Tolerance and Shape Consistency
Tolerance relates to the dimensional accuracy and uniformity of abrasive particles or products. Consistent shape and size are vital for predictable performance and compatibility with automated machinery. For international buyers, verifying tolerance standards helps maintain quality control and reduces production downtime.
6. Porosity
Porosity indicates the presence of pores or voids within the abrasive material or product. Higher porosity can improve heat dissipation and reduce clogging, beneficial for certain grinding processes. Buyers should assess porosity levels based on the intended application to optimize abrasive efficiency and workpiece finish.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment which are then marketed by another company. In abrasives, OEM specifications often dictate the exact material grade, size, and bonding required. Buyers working with OEMs must ensure compliance with these detailed standards to secure contracts and maintain supply chain reliability.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term specifies the smallest quantity of abrasives a supplier is willing to sell per order. Understanding MOQ is critical for budget planning and inventory management, especially for buyers in emerging markets where storage or upfront capital might be limited. Negotiating MOQs can lead to better pricing or more flexible procurement terms.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal invitation sent by buyers to suppliers asking for price and delivery information on abrasive substances. It often includes detailed technical specifications. Mastery of the RFQ process enables buyers to compare suppliers effectively and secure the best value deals in a competitive global marketplace.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Common terms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Knowledge of Incoterms helps international buyers from regions such as Africa and South America minimize risks and clearly understand cost implications during import/export transactions.
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For abrasive substances, lead times can vary based on production complexity and shipping logistics. Accurate lead time expectations are essential for production scheduling and avoiding costly downtime.
Certification and Compliance
This refers to adherence to international quality and safety standards, such as ISO certifications or REACH compliance for chemical safety. Buyers prioritizing certified abrasives can reduce regulatory risks and ensure product consistency, which is particularly important in highly regulated markets like the European Union.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make strategic purchasing decisions, optimize supply chain management, and foster stronger supplier relationships in the abrasive substances market.
The global abrasive substances market is experiencing robust growth, driven by expanding industrial manufacturing, automotive production, and infrastructure development. For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing. Key growth drivers include increasing demand for precision machining, surface finishing, and the rise of advanced materials requiring specialized abrasives.
Regional Demand Patterns:
- Africa is witnessing growing infrastructure projects and mining activities, increasing demand for both conventional abrasives (like aluminum oxide) and super abrasives (such as synthetic diamond).
- South America benefits from expanding automotive and aerospace sectors, emphasizing high-quality abrasive materials for precision applications.
- The Middle East continues to invest heavily in construction and oil & gas industries, driving demand for durable abrasives tailored to harsh environments.
- Europe (Spain, Italy) maintains a mature market with a strong focus on innovation, quality, and sustainability, supporting a shift toward eco-friendly abrasive solutions.
Emerging B2B Tech & Sourcing Trends:
- Digital Procurement Platforms: Buyers increasingly leverage online marketplaces and AI-driven sourcing tools to optimize supplier selection, pricing transparency, and supply chain agility.
- Customization & Technical Collaboration: Leading suppliers offer tailored abrasive solutions, integrating R&D to meet specific industrial needs, such as coatings for enhanced durability or nanotechnology-enhanced abrasives.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Geopolitical uncertainties and pandemic-related disruptions have pushed buyers to diversify sourcing sources and maintain buffer inventories, particularly for critical abrasive materials like synthetic diamonds and ceramic abrasives.
- Sustainability Integration: Buyers prioritize suppliers with sustainable practices, including recycled abrasives and low-impact manufacturing, aligning with corporate social responsibility goals.
For B2B buyers, a strategic approach combining regional market insights, technology adoption, and supplier collaboration will be essential to harness competitive advantages in abrasive substance procurement.
Sustainability is rapidly becoming a non-negotiable factor in abrasive substances procurement. The environmental footprint of abrasive manufacturing includes energy-intensive processes, mining impacts, and waste generation. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly scrutinizing suppliers for adherence to sustainable and ethical practices.
Environmental Impact Considerations:
- Mining of raw materials like corundum, garnet, and synthetic diamonds can result in habitat disruption and water consumption challenges.
- Manufacturing processes often involve high energy usage and chemical treatments that may generate pollutants.
- End-of-life disposal of abrasive products must be managed to prevent environmental contamination.
Ethical Supply Chains:
- Buyers should demand transparency on sourcing origins to avoid conflict minerals and ensure fair labor practices, especially relevant in regions with complex mining sectors.
- Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), Responsible Mining Initiative (RMI), and third-party audits provide assurance of ethical compliance.
Green Certifications & Materials:
- Increasing availability of abrasives produced from recycled materials reduces dependency on virgin resources.
- Biodegradable and less toxic bonding agents are gaining traction, minimizing hazardous waste.
- Suppliers offering products with recognized green certifications or environmental product declarations (EPDs) enable buyers to meet internal sustainability targets and regulatory requirements.
Prioritizing sustainability not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation and aligns with evolving customer and regulatory expectations, making it a strategic imperative for abrasive substances procurement.
The abrasive substances sector has evolved significantly from traditional natural abrasives such as emery and garnet to advanced synthetic materials tailored for high-precision industrial applications. Historically, natural abrasives dominated until the early 20th century when synthetic abrasives like aluminum oxide and silicon carbide revolutionized the industry by offering consistent quality and enhanced performance.
In recent decades, the development of super abrasives—synthetic diamonds and cubic boron nitride (CBN)—has transformed sectors including automotive, aerospace, and electronics, enabling machining of hard materials with unmatched precision. This evolution reflects broader industrial trends towards higher efficiency, durability, and customization in manufacturing processes.
For B2B buyers, understanding this historical progression is essential to appreciate current sourcing complexities and to identify innovative suppliers capable of delivering cutting-edge abrasive solutions aligned with modern industrial demands.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
What customization options are typically available when ordering abrasive substances in bulk?
Many suppliers offer customization in grain size, abrasive material type (e.g., aluminum oxide, silicon carbide), bonding agents, and packaging formats to suit specific industrial applications. Buyers should clearly communicate their technical requirements, such as hardness, friability, and purity levels, to ensure product performance. Custom formulations might require additional lead time and minimum order quantities (MOQs), so negotiating these early is crucial. Request prototypes or small pilot batches to validate the customized product before scaling to full orders.
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for abrasive substances, and how can these be negotiated?
MOQs vary widely depending on supplier capacity and product complexity but generally range from a few metric tons to larger bulk shipments. Lead times typically span 3 to 8 weeks, factoring in production, quality checks, and export logistics. Buyers from regions like the Middle East or Europe can leverage long-term contracts or consolidate orders with other buyers to negotiate lower MOQs and faster turnaround. Establishing clear communication about forecasted volumes and flexible delivery schedules often helps suppliers optimize production planning, benefiting both parties.
Which payment terms and methods are considered best practice in international B2B abrasive substance transactions?
Secure payment methods such as Letters of Credit (LC) or escrow services are preferred to mitigate risk, especially for first-time transactions. Net terms (e.g., 30-60 days) may be negotiated with trusted suppliers, enhancing cash flow management. Suppliers in Europe and the Middle East often accept wire transfers (SWIFT) or trade finance instruments, while buyers in Africa or South America might face additional banking complexities; early coordination with financial institutions is advisable. Always confirm payment terms explicitly in contracts to avoid disputes.
What quality assurance certifications and testing should I require from abrasive substance suppliers?
Demand certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management, REACH compliance for chemical safety (particularly relevant in Europe), and product-specific standards such as ASTM or FEPA grades. Insist on batch-specific testing reports covering parameters like particle size distribution, hardness, and contamination levels. Independent laboratory verification can add confidence, especially for high-precision applications. Implementing incoming inspection protocols upon receipt helps identify discrepancies early and maintains consistent product quality.
How can I optimize logistics and shipping for abrasive substances across continents to minimize delays and costs?
Choosing suppliers with established export experience and strong logistics partnerships reduces risks of delays. Bulk shipments via sea freight are cost-effective but require advance planning due to longer transit times, especially when shipping from South America or Africa to Europe or the Middle East. Air freight suits urgent orders but is more expensive. Use consolidated shipments when possible and verify customs clearance requirements, including import duties and hazardous material regulations. Employ freight forwarders familiar with abrasive material classification to streamline documentation and compliance.
What strategies should I use to resolve disputes or quality issues with international abrasive substance suppliers?
Maintain clear, written contracts outlining product specifications, delivery schedules, payment terms, and dispute resolution mechanisms such as arbitration or mediation. Document all communications and inspections rigorously. If quality issues arise, request corrective action reports and consider involving third-party inspectors to verify claims. Building long-term supplier relationships based on transparency facilitates quicker, amicable resolutions. When necessary, engage trade associations or local chambers of commerce to mediate, especially in cross-cultural contexts.
How do regional regulations impact the import and use of abrasive substances in markets like Spain, Italy, or the Middle East?
Regional regulations can affect permissible chemical compositions, labeling, packaging, and environmental compliance. For instance, the EU enforces strict REACH and CLP regulations, requiring suppliers to provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and ensure substances do not contain restricted chemicals. Middle Eastern countries may have import licensing and certification requirements that vary significantly. Buyers should conduct thorough regulatory due diligence and collaborate with customs brokers and legal advisors to ensure compliance, avoiding costly delays or penalties. Staying updated on evolving standards is critical for uninterrupted supply chains.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of abrasive substances demands a nuanced understanding of market dynamics, supplier capabilities, and regional trade considerations. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, prioritizing supplier reliability, material quality, and cost-efficiency is critical to maintaining competitive manufacturing and operational processes. Leveraging local and global supplier networks can unlock opportunities for innovation and supply chain resilience.
Key takeaways include:
Looking ahead, the abrasive substances market is poised for transformation driven by technological advancements and shifting trade policies. Buyers who proactively embrace strategic sourcing frameworks will not only secure supply continuity but also foster innovation and sustainable growth. Companies in Spain, Italy, and other European hubs, alongside counterparts in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, are encouraged to deepen collaboration with trusted partners and invest in agile procurement strategies that anticipate future market shifts.
Seize this moment to refine your sourcing strategy—ensuring your operations remain robust, competitive, and forward-looking in an evolving global marketplace.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina