Alumina manufacturing stands at the heart of multiple high-value industries, powering sectors from aerospace and automotive to electronics and construction. As a critical intermediate in the production of aluminum metal, alumina’s quality, consistency, and supply reliability directly impact manufacturing efficiency and end-product performance. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the complexities of the global alumina market is essential to securing competitive advantages and fostering sustainable partnerships.
This comprehensive guide offers a deep dive into the multifaceted world of alumina manufacturing. It covers everything from the various types of alumina products and the raw materials used, to detailed insights into manufacturing processes and quality control standards. Buyers will gain clarity on how to evaluate suppliers based on technical capabilities, certifications, and compliance with environmental and safety regulations—key factors in regions like Brazil and the UAE where industrial standards and trade policies vary significantly.
Moreover, the guide provides actionable intelligence on cost structures, market trends, and supply chain dynamics, enabling buyers to make well-informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are navigating fluctuating global demand or seeking to optimize procurement strategies, this resource equips you with the knowledge to identify reliable manufacturers, negotiate effectively, and mitigate risks in international transactions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By leveraging this expert-driven analysis, B2B buyers can confidently engage with alumina suppliers worldwide, ensuring access to high-quality materials that meet stringent specifications and support long-term business growth across diverse markets.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bayer Process Alumina | Produced via digestion of bauxite in caustic soda; high purity | Aluminum smelting, refractory materials | Pros: High purity, consistent quality; Cons: Energy-intensive, requires high-grade bauxite |
| Calcined Alumina | Alumina heated to remove moisture and modify crystal structure | Ceramics, abrasives, electronics | Pros: Tailored properties for specific uses; Cons: Additional processing cost, energy use |
| Synthetic Alumina | Produced from chemical precursors, not bauxite; ultra-pure | Advanced ceramics, electronics, catalysts | Pros: Extremely high purity, customizable; Cons: Higher price, limited large-scale availability |
| Hydrate Alumina | Intermediate product from Bayer process before calcination | Chemical intermediates, specialty chemicals | Pros: Versatile feedstock, lower cost; Cons: Requires further processing, less stable for storage |
| Tabular Alumina | Manufactured by sintering alumina at high temperatures into dense granules | Refractories, kiln linings, foundry | Pros: High density, thermal stability; Cons: More expensive, niche applications |
Bayer Process Alumina is the most common form of alumina, extracted from bauxite ore through a chemical digestion process involving caustic soda. This method produces alumina with high purity, making it ideal for primary aluminum production and refractory manufacturing. For B2B buyers, especially in regions with access to quality bauxite like Africa and South America, the Bayer Process offers a reliable supply chain but demands consideration of energy costs and raw material quality.
Calcined Alumina results from heating hydrate alumina to remove moisture and alter its crystal structure, enhancing hardness and thermal resistance. This variation is crucial for industries such as ceramics, abrasives, and electronics. Buyers should assess the specific calcination parameters to ensure the alumina matches their application requirements, balancing cost implications of additional processing.
Synthetic Alumina is chemically synthesized rather than derived from bauxite, offering ultra-high purity and tailored particle sizes. This makes it suitable for advanced applications like electronics, catalysts, and high-performance ceramics. While synthetic alumina commands a premium price and may have limited large-scale availability, it is indispensable for buyers prioritizing purity and performance over volume.
Hydrate Alumina serves as an intermediate product in alumina manufacturing, commonly obtained from the Bayer process before calcination. It is used in specialty chemicals and as a versatile feedstock for further processing. For B2B buyers, hydrate alumina offers cost advantages but requires infrastructure for additional processing steps, making it more suitable for buyers with integrated manufacturing capabilities.
Tabular Alumina is produced by sintering alumina particles at high temperatures, resulting in dense, thermally stable granules. This type is preferred in refractory applications such as kiln linings and foundry molds due to its durability and heat resistance. Buyers should consider the higher cost and specialized nature of tabular alumina, ensuring it aligns with their technical specifications and operational demands.
Related Video: How to Make Alumina Ceramic Tubes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alumina manufacturing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Production | Raw material for smelting alumina to produce aluminum metal | Enables high-purity aluminum production, critical for automotive, aerospace, and packaging industries | Consistent quality and purity, reliable supply chain, compliance with environmental standards |
| Refractories | Manufacture of heat-resistant linings for furnaces and kilns | Enhances durability and thermal resistance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs | Thermal stability, chemical inertness, supplier certifications, and tailored formulations |
| Ceramics | Production of advanced ceramics for electrical and structural components | Provides mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and wear resistance | Particle size distribution, chemical composition, and compatibility with ceramic processing methods |
| Abrasives | Production of grinding wheels, sandpapers, and polishing agents | Improves efficiency in material removal and surface finishing | Grain size uniformity, hardness, and supplier reliability for continuous supply |
| Catalysts and Chemicals | Used as catalyst support and in chemical processes like water purification | Increases catalytic efficiency and environmental compliance | Purity levels, particle morphology, and supplier innovation capabilities |
Aluminum Production
Alumina manufacturing serves as the cornerstone raw material for producing aluminum metal through electrolytic smelting. For industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly in regions like Brazil and the UAE, securing high-purity alumina is essential to meet stringent quality standards in automotive and aerospace manufacturing. Buyers must focus on suppliers offering consistent chemical composition and robust logistics to avoid production interruptions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Refractories
In the refractory industry, alumina is critical for producing heat-resistant linings used in furnaces and kilns. These linings must withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments, making alumina’s thermal stability and chemical inertness invaluable. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that provide customized formulations and certifications verifying performance under high-temperature conditions, which is vital for sectors such as steelmaking and glass production prevalent in Europe and the Middle East.
Ceramics
Alumina’s role in advanced ceramics is pivotal for producing electrical insulators and structural components with exceptional mechanical strength and wear resistance. For international buyers, especially in developing industrial hubs in Africa and South America, understanding the required particle size distribution and chemical purity is crucial to ensure compatibility with ceramic processing technologies. Partnering with suppliers who offer technical support and tailored alumina grades can enhance product performance and reduce manufacturing defects.
Abrasives
The abrasives sector leverages alumina to manufacture grinding wheels, sandpapers, and polishing agents that demand uniform hardness and grain size for effective material removal and surface finishing. Buyers from emerging markets like Brazil and established industrial centers in Europe should evaluate supplier consistency and quality control measures to maintain production efficiency. Reliable sourcing ensures uninterrupted supply chains, critical for maintaining operational throughput in metalworking and automotive component manufacturing.
Catalysts and Chemicals
Alumina is extensively used as a catalyst support and in chemical applications such as water purification and petrochemical processing. Its high surface area and stability improve catalytic performance, enhancing process efficiency and environmental compliance. International B2B buyers must assess alumina purity and particle morphology to match specific catalytic requirements. Collaboration with innovative suppliers who offer customized alumina grades can provide competitive advantages in chemical manufacturing and environmental technology sectors.
Related Video: Sintering Process |An Essential Step of Alumina Ceramic Manufacturing
Key Properties:
Calcined alumina is characterized by high purity (typically >99.5% Al2O3), excellent thermal stability (up to 1750°C), and outstanding hardness. It offers excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against acidic and alkaline environments, and maintains mechanical strength under high pressure and temperature.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: High purity ensures superior end-product quality; excellent wear and corrosion resistance; well-established manufacturing processes.
- Cons: Production costs can be relatively high due to energy-intensive calcination; requires precise handling to avoid contamination; powder handling complexity can increase manufacturing overhead.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for producing high-performance refractory linings, ceramics, and abrasives where thermal and chemical resistance is critical. It is compatible with aggressive media, making it suitable for chemical processing industries prevalent in the Middle East and Europe.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers from Africa and South America should verify compliance with ASTM C799 and DIN EN standards to ensure material consistency. In regions like Brazil and UAE, sourcing from suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 quality management is preferred to meet stringent industrial requirements. Logistics and storage conditions are crucial to maintain powder integrity during transit.
Key Properties:
Tabular alumina is a dense, sintered form of alumina with a high melting point (~2050°C) and excellent abrasion resistance. It exhibits low porosity and high mechanical strength, making it suitable for demanding refractory applications.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Superior durability and thermal shock resistance; excellent for high-wear environments; stable performance under cyclic thermal loads.
- Cons: Higher production complexity and cost; heavier material weight can increase transportation expenses; limited flexibility in shaping compared to powders.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in high-temperature kiln linings, furnace components, and industrial crucibles. Its robustness suits industries in the Middle East and Europe where heavy-duty thermal applications are common, such as petrochemical and steel manufacturing.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers should ensure material certification aligns with DIN 66128 and ASTM C799 standards. For African and South American markets, availability and lead times can be a challenge, so establishing relationships with regional distributors is advisable. Compliance with environmental regulations, especially in Europe, must be confirmed.
Key Properties:
Reactive alumina features a high surface area and fine particle size, enhancing its chemical reactivity. It is widely used as a catalyst support and in adsorption applications due to its excellent surface properties and moderate thermal stability (~1200°C).
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: High chemical activity; versatile for catalyst manufacturing; relatively lower cost compared to tabular alumina.
- Cons: Lower thermal resistance limits use in extreme heat; more susceptible to moisture absorption; handling requires controlled environments to maintain quality.
Impact on Application:
Best suited for chemical and petrochemical industries focusing on catalyst production and purification processes. Its compatibility with acidic and basic media makes it attractive for buyers in the Middle East and South America, where refinery and chemical plants are expanding.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers must verify compliance with ASTM C110 and JIS R1601 standards. In regions like Brazil and UAE, ensuring supplier capability for custom particle sizing and surface treatments can provide competitive advantages. Packaging and shipment under inert atmospheres may be necessary to preserve product quality.
Key Properties:
This composite material combines tabular alumina with spinel (MgAl2O4) to enhance thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength. It maintains high melting points (~2100°C) and improved corrosion resistance against slag and molten metals.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Enhanced durability and lifespan in harsh environments; improved resistance to chemical attack; suitable for specialized refractory applications.
- Cons: Higher cost due to additive incorporation; more complex manufacturing process; limited availability in some markets.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for steelmaking and metallurgical industries requiring refractory materials with exceptional resistance to slag corrosion and thermal cycling. Particularly relevant for European and Middle Eastern buyers engaged in heavy industry sectors.
International B2B Considerations:
Compliance with ASTM C799 and EN ISO 9001 standards is critical. Buyers in Africa and South America should assess supplier capacity for consistent spinel dispersion and quality control. Import tariffs and customs regulations may affect total landed cost, so strategic sourcing and negotiation are essential.
| Material | Typical Use Case for alumina manufacturing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcined Alumina | High-purity refractory linings, abrasives, ceramics | High thermal stability and corrosion resistance | Energy-intensive production; handling complexity | High |
| Tabular Alumina | Kiln linings, furnace components, industrial crucibles | Superior durability and thermal shock resistance | Higher production complexity and weight | High |
| Reactive Alumina | Catalyst supports, adsorption media | High chemical reactivity and versatility | Lower thermal resistance; moisture sensitivity | Medium |
| Tabular Alumina with Spinel Additives | Specialized refractory for steelmaking and metallurgy | Enhanced thermal shock and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and limited availability | High |
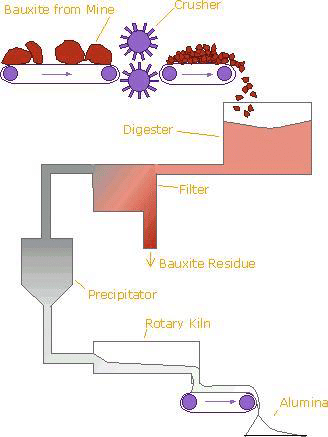
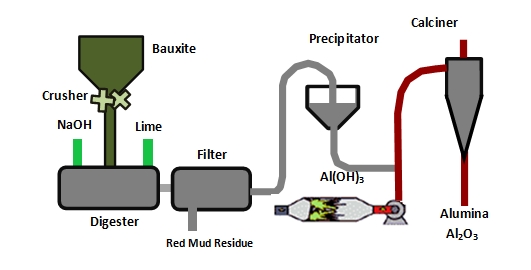
Alumina manufacturing is a complex industrial process involving multiple stages that transform raw materials, primarily bauxite, into high-purity alumina (Al₂O₃). For B2B buyers sourcing alumina globally, understanding the key manufacturing stages and quality checkpoints is crucial to ensure product consistency, performance, and compliance with international standards.
Main Stages of Alumina Manufacturing:
Raw Material Preparation
The process begins with the extraction and preparation of bauxite ore. This involves crushing, grinding, and washing to remove impurities such as silica, iron oxides, and clay. The prepared bauxite is then mixed with caustic soda (NaOH) in a digestion process to dissolve alumina into a sodium aluminate solution.
Clarification and Precipitation
The slurry undergoes clarification to separate the solid impurities (red mud) from the sodium aluminate solution. The clear liquor is then seeded with aluminum hydroxide crystals to initiate precipitation. This stage is critical to controlling particle size and purity of the alumina trihydrate formed.
Calcination (Thermal Processing)
The alumina trihydrate crystals are filtered, washed, and then heated in rotary kilns or fluidized bed calciners at temperatures around 1000–1100°C. Calcination removes water molecules, yielding anhydrous alumina powder with desired phase composition and particle characteristics.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Techniques and Equipment:
Robust quality assurance (QA) is non-negotiable for alumina suppliers, particularly for international B2B buyers who require consistent product quality to ensure downstream process stability and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Relevant International and Industry Standards:
Quality Control (QC) Checkpoints:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
Raw materials such as bauxite and caustic soda are tested for chemical composition and impurity levels. This prevents contamination and ensures consistent feedstock quality.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
Monitoring critical parameters during digestion, precipitation, and calcination stages, including temperature, pH, particle size, and moisture content. Real-time adjustments help maintain product specifications.
Final Quality Control (FQC):
Finished alumina is subjected to rigorous testing for purity (Al₂O₃ content), particle size distribution, bulk density, surface area, and impurity levels (iron, silica, sodium). Certificates of analysis (CoA) are generated for each batch.
Common Testing Methods:
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the robustness of supplier QC is critical to mitigate risks associated with substandard alumina. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
Africa: Many African buyers prioritize suppliers with transparent supply chains and ISO certification due to varying local regulatory enforcement. Emphasis on supplier consistency is critical where logistics and storage conditions can impact product quality.
South America (e.g., Brazil): Compliance with INMETRO and environmental standards is essential. Buyers often require extended documentation due to customs and import regulations. Local partnerships can facilitate smoother certification processes.
Middle East (e.g., UAE): Given the rapid industrial growth and stringent GSO standards, buyers should focus on suppliers with CE marking and API compliance, especially for oil and gas applications. Temperature resilience and packaging integrity are also critical due to harsh climate conditions.
Europe: European buyers demand strict adherence to ISO standards and often require REACH compliance for chemical products. Traceability and environmental impact disclosures are increasingly important in procurement decisions.
Summary:
For B2B buyers sourcing alumina internationally, a thorough understanding of manufacturing stages, quality control methodologies, and regional certification requirements is indispensable. By leveraging supplier audits, third-party inspections, and comprehensive documentation, buyers can secure high-quality alumina tailored to their industry needs, ensuring operational excellence and regulatory compliance across diverse markets.
When sourcing alumina, a clear grasp of the underlying cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
Pricing in alumina manufacturing is not static and is influenced by several factors beyond base costs:
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, adopting a strategic approach can optimize cost-efficiency and total value:
Prices for alumina manufacturing inputs and finished products are indicative and subject to frequent change due to commodity market fluctuations, geopolitical factors, and supplier-specific terms. Buyers should conduct up-to-date market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive and accurate pricing.
By thoroughly analyzing these cost and pricing factors, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that balance cost, quality, and supply chain reliability in the alumina manufacturing sector.
Understanding the core technical properties and trade terminology in alumina manufacturing is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions and negotiate effectively. This knowledge helps ensure product suitability, cost-efficiency, and smooth international transactions.
Material Grade
Alumina grades vary based on purity and intended application. Common grades include calcined alumina (used in refractories and abrasives) and chemical-grade alumina (high purity for catalysts and ceramics). Knowing the grade helps buyers match specifications with end-use requirements, avoiding costly mismatches.
Alumina Content (Purity)
Expressed as a percentage, alumina content typically ranges from 85% to over 99.5%. Higher purity alumina is essential for advanced ceramics and electronics, while lower purity grades suffice for construction or abrasive applications. Purity impacts performance, price, and compliance with industry standards.
Particle Size Distribution
Particle size affects processing behavior and final product quality. Fine powders are preferred for ceramics and catalysts, whereas coarser grades serve abrasive or refractory uses. Buyers should specify particle size tolerances to ensure compatibility with their manufacturing processes.
Moisture Content
Moisture affects storage stability and handling. Low moisture alumina is critical in applications sensitive to hydration, such as catalyst supports. Specifying moisture limits helps avoid product degradation and ensures consistent processing.
Bulk Density
Bulk density influences shipping costs and handling characteristics. Higher bulk density alumina reduces transportation expenses but may require specific storage conditions. Buyers should balance cost with operational needs when evaluating bulk density.
Tolerance Levels
This refers to allowable deviations in chemical composition and physical properties. Strict tolerances are vital for industries demanding high precision, such as aerospace or electronics. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers negotiate quality assurance terms.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or products used in another company’s end product. For alumina buyers, understanding whether the supplier caters to OEMs can indicate product quality standards and customization capabilities.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in one order. MOQ affects inventory planning and cash flow, especially for buyers in emerging markets. Negotiating MOQs can lead to better alignment with demand and reduce storage costs.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent by a buyer to suppliers to obtain pricing, delivery schedules, and terms. Crafting clear RFQs with detailed technical specifications ensures accurate quotes and minimizes misunderstandings.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight). Selecting the right Incoterm clarifies cost allocation and risk transfer, critical for cross-border transactions.
Lead Time
The period from order placement to delivery. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan production schedules and manage supply chain risks, particularly when sourcing from distant regions.
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
A document provided by the supplier detailing the product’s chemical and physical properties. Requesting a CoA ensures transparency and verifies that alumina meets agreed specifications.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies, ensure product quality, and foster stronger supplier relationships across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge ultimately supports better decision-making and competitive advantage in the alumina supply chain.
The global alumina manufacturing sector is experiencing dynamic growth fueled by increasing demand in aluminum production, driven primarily by the automotive, aerospace, construction, and packaging industries. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these market forces is critical to securing competitive sourcing agreements and managing supply chain risks effectively.
Key drivers include the rising adoption of lightweight aluminum in electric vehicles (EVs), which is boosting alumina consumption due to its role as a precursor to aluminum production. Additionally, infrastructure development projects in emerging economies, particularly in Brazil and across African nations, are increasing demand for aluminum products. The Middle East, with its expanding industrial zones and strategic ports, serves as a vital hub for alumina trade and distribution, offering logistical advantages for regional buyers.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends highlight a shift towards digital procurement platforms and enhanced supply chain transparency. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics and AI-driven forecasting tools to predict demand fluctuations and optimize inventory. This is particularly relevant for markets like the UAE, where digital transformation initiatives support more agile procurement processes. Furthermore, strategic partnerships and long-term contracts are gaining prominence to mitigate price volatility caused by fluctuating bauxite ore availability and energy costs, which directly impact alumina production costs.
Sourcing alumina from diverse geographic suppliers is also becoming a priority to reduce dependency on dominant producers and enhance supply chain resilience. African suppliers, such as those in Guinea and Mozambique, are gaining attention due to their rich bauxite reserves, while South American producers continue to expand capacity. European buyers, particularly those in manufacturing hubs, benefit from integrated supply chains that emphasize quality control and compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Sustainability has emerged as a pivotal concern in the alumina manufacturing sector, with international buyers increasingly prioritizing environmentally responsible sourcing. Alumina production is energy-intensive and traditionally associated with significant carbon emissions, water usage, and red mud waste generation. Buyers from regions with robust environmental regulations, like Europe, are demanding suppliers demonstrate adherence to sustainable practices to align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical, as alumina supply chains often intersect with regions facing social and governance challenges. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers uphold labor rights, community engagement, and transparency. Certifications such as the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) provide a credible framework for assessing sustainability performance, covering environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance standards.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials and processes—such as sourcing alumina produced using renewable energy or through low-emission refining techniques—can significantly enhance a buyer’s sustainability credentials. The adoption of circular economy principles, including alumina recycling and waste minimization, is gaining momentum. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Africa, investing in suppliers who prioritize water conservation and land rehabilitation not only mitigates environmental risks but also strengthens long-term supply security.
Ultimately, embedding sustainability into procurement decisions fosters stronger supplier relationships, reduces regulatory risks, and meets increasing end-customer expectations for ethically sourced aluminum products.
The alumina manufacturing industry has evolved substantially since the late 19th century, following the development of the Bayer process, which remains the dominant method for refining bauxite into alumina. Initially concentrated in a few regions with rich bauxite deposits, production has since globalized, with significant expansion in countries like Australia, China, and Brazil.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential as it explains current supply chain configurations and regional market strengths. Over the past two decades, technological advances have improved refining efficiency and environmental management, while geopolitical shifts have diversified production sources. Today’s buyers benefit from a more competitive market with multiple sourcing options, enabling strategic procurement that balances cost, quality, and sustainability considerations.
1. How can I effectively vet alumina manufacturers for international trade?
To vet alumina suppliers, prioritize manufacturers with verifiable certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and environmental compliance certificates relevant to alumina production. Request detailed company profiles, client references, and audited financial statements to assess reliability. Conduct virtual or on-site audits if feasible, focusing on production capacity and quality control processes. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensure the supplier understands export regulations and has experience shipping to your region to minimize customs and compliance risks.
2. Is customization of alumina products possible, and how should I approach it?
Yes, many alumina manufacturers offer customization in terms of particle size, purity levels, and moisture content to meet specific industrial needs. When approaching customization, clearly define your technical requirements and application goals upfront. Engage in detailed discussions about achievable specifications and potential cost implications. Request samples for testing before finalizing orders to ensure the customized product meets your operational standards, especially critical for industries like ceramics, refractories, or chemicals.
3. What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for alumina shipments internationally?
MOQs vary widely depending on the manufacturer’s capacity and the alumina grade but typically range from 10 to 50 metric tons per shipment. Lead times usually span 4 to 8 weeks, factoring in production, quality checks, and international shipping. For buyers in regions like the Middle East or South America, consider additional time for customs clearance. Negotiating flexible MOQs and staggered deliveries can help manage inventory and cash flow, particularly for smaller or emerging businesses.
4. Which payment terms are standard in international alumina procurement, and how can I mitigate payment risks?
Common payment terms include letters of credit (L/C), advance payments, or open account terms with credit insurance. Letters of credit offer strong protection by involving banks to guarantee payment upon fulfillment of contract terms. To mitigate risks, negotiate partial payments tied to production milestones or shipment confirmations. For buyers in emerging markets, working with suppliers open to escrow services or reputable trade finance providers can enhance transaction security.
5. What quality assurance certifications should I verify when sourcing alumina?
Ensure the supplier holds certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management, indicating robust production and sustainability practices. Certifications from recognized industry bodies such as the Aluminium Association or compliance with REACH (for European buyers) further validate product safety and regulatory adherence. Request detailed quality control reports and third-party lab test results to confirm alumina purity and consistency, critical for maintaining product integrity in your manufacturing processes.
6. How should I plan logistics and shipping to optimize cost and delivery reliability?
Partner with suppliers experienced in exporting alumina to your region, ensuring familiarity with local customs, import duties, and transportation infrastructure. Opt for consolidated shipments or multimodal transport (sea combined with rail or road) to reduce costs and transit times. Establish clear Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) upfront to define responsibilities. For buyers in landlocked regions or those with complex customs environments, engaging a reliable freight forwarder and customs broker is essential to avoid delays and unexpected fees.
7. What are best practices for handling disputes or quality issues with international alumina suppliers?
Address disputes proactively by documenting all communications, contracts, and quality certificates. Insist on including arbitration clauses in contracts referencing neutral international bodies (e.g., ICC arbitration) to streamline conflict resolution. In case of quality issues, promptly notify the supplier with evidence such as test reports and photographs. Engage third-party inspection agencies for impartial verification. Maintaining open communication channels and a collaborative approach often leads to faster resolutions and preserves long-term supplier relationships.
8. How can I stay compliant with international trade regulations when importing alumina?
Stay informed about import regulations, tariffs, and environmental standards applicable in your country and the supplier’s region. Verify that alumina shipments comply with hazardous material classifications and packaging standards, as alumina can be subject to specific handling rules. Use HS codes correctly for customs declarations to avoid delays. Collaborate with customs brokers and legal advisors familiar with trade agreements between your country and the supplier’s nation, particularly relevant for Africa, the Middle East, and Europe, where trade agreements can offer tariff advantages.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing in alumina manufacturing is essential for securing competitive advantages in a dynamic global market. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding supplier reliability, cost structures, and sustainability credentials is critical to optimizing procurement decisions. Prioritizing partnerships with producers who demonstrate consistent quality, innovative processing technologies, and transparent supply chains can significantly reduce risks and improve operational efficiency.
Key takeaways include:
- The importance of diversifying sourcing to mitigate geopolitical and logistical challenges.
- Leveraging regional market insights to negotiate better terms and foster long-term supplier relationships.
- Embracing sustainability standards as a differentiator that meets growing environmental regulations and customer expectations.
Looking ahead, international buyers should proactively engage with emerging alumina producers and invest in digital tools that enhance supply chain visibility. By adopting a strategic sourcing mindset, companies in Brazil, the UAE, and beyond can not only secure cost-effective materials but also drive innovation and resilience in their supply chains. The evolving landscape demands agility—now is the time to deepen market intelligence, strengthen supplier collaboration, and position your business for sustainable growth in the alumina sector.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina