Navigating the global market for alumina poisson ratio presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the significance of the alumina poisson ratio is crucial, as it directly impacts the mechanical properties of materials used across various industries, from aerospace to electronics. This comprehensive guide addresses key elements such as the types of alumina available, their specific applications, and how to effectively vet suppliers to ensure quality and reliability.
In addition, buyers will gain insights into cost considerations and the factors that influence pricing in different markets. By providing actionable strategies and expert analysis, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Whether you are sourcing alumina for advanced manufacturing processes or seeking to optimize material selection for research and development, understanding the nuances of the alumina poisson ratio will enhance your procurement strategy.
This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the global alumina market, ensuring that your sourcing decisions not only meet technical specifications but also contribute to your organization's overall success and competitiveness in the industry.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina A (High Purity) | High purity levels (>99.5%), low impurities | Electronics, aerospace, specialty ceramics | Pros: Excellent performance in high-tech applications. Cons: Higher cost. |
| Alumina B (Industrial) | Moderate purity (95-99%), suitable for general applications | Refractories, abrasives, and glass manufacturing | Pros: Cost-effective for bulk applications. Cons: Lower performance in specialized applications. |
| Alumina C (Calcined) | Calcined at high temperatures, enhanced mechanical strength | Structural ceramics, cutting tools | Pros: Improved durability and thermal resistance. Cons: More complex processing. |
| Alumina D (Activated) | High surface area, porous structure | Catalysts, adsorbents, water purification | Pros: Effective for chemical applications. Cons: Limited mechanical strength. |
| Alumina E (Nano) | Nano-sized particles, unique properties | Advanced materials, nanotechnology applications | Pros: Enhanced reactivity and strength. Cons: High production costs and handling challenges. |
High Purity Alumina (Alumina A) is characterized by its exceptional purity levels, typically exceeding 99.5%. This type is essential in sectors such as electronics and aerospace, where even minor impurities can lead to significant performance issues. When purchasing, buyers should consider the application requirements, as the higher cost is often justified by the enhanced performance and reliability in critical applications.
Industrial Alumina (Alumina B) offers a moderate purity range of 95-99%, making it suitable for a variety of general applications. This type is widely used in refractories, abrasives, and glass manufacturing. Buyers should weigh the cost-effectiveness of this alumina against their specific performance needs, as it may not meet the stringent requirements of specialized applications but offers a reliable solution for many standard uses.
Calcined Alumina (Alumina C) is subjected to high-temperature processing, resulting in improved mechanical strength and thermal resistance. This type is particularly valuable in structural ceramics and cutting tools. Buyers should consider the enhanced durability it offers, although the processing complexity may add to the overall cost. It's an ideal choice for applications that demand high strength and resilience.
Activated Alumina (Alumina D) features a porous structure with a high surface area, making it particularly effective as a catalyst or adsorbent. It's commonly used in water purification and other chemical processes. Buyers should note that while it excels in chemical applications, it does not possess the same mechanical strength as other types, which may limit its use in structural applications.
Nano Alumina (Alumina E) consists of nano-sized particles that impart unique properties, making it suitable for advanced materials and nanotechnology applications. Its enhanced reactivity and strength are significant advantages, but buyers must also consider the higher production costs and potential handling challenges associated with nano materials. This type is ideal for innovative applications that leverage its unique characteristics.
Related Video: Relation Between Y, K & σ!Relation Between Young's modulus(y),Bulk modulus,(k) and Poisson's ratio
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alumina poisson ratio | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Structural components in aircraft manufacturing | Enhances safety and performance through improved materials | Certification of materials and compliance with aviation standards |
| Electronics | Substrates for electronic components | Increases durability and thermal stability of devices | Supplier reliability and adherence to quality control standards |
| Construction | High-performance ceramics for building materials | Provides superior strength and durability | Local sourcing options and environmental impact considerations |
| Energy | Components in nuclear reactors and energy storage systems | Ensures safety and efficiency in energy production | Regulatory compliance and long-term material performance |
| Automotive | Brake systems and engine components | Improves vehicle safety and performance | Material sourcing consistency and adherence to automotive standards |
In the aerospace sector, the alumina poisson ratio is crucial for designing structural components that withstand extreme stress and temperature variations. By utilizing materials with an optimal poisson ratio, manufacturers can enhance the safety and performance of aircraft, ensuring they meet strict regulatory standards. International B2B buyers must ensure that suppliers can provide certified materials that comply with aviation industry regulations, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulations are stringent.
In electronics, the alumina poisson ratio is significant for substrates used in various components, including semiconductors and circuit boards. The right poisson ratio improves the durability and thermal stability of electronic devices, which is critical for performance and longevity. Buyers from Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing from reliable suppliers who adhere to quality control standards, ensuring that the materials used can withstand the rigors of electronic applications.
The construction industry benefits from the alumina poisson ratio in high-performance ceramics used in building materials. These materials provide exceptional strength and durability, which are essential for structural integrity in various applications, including roads and bridges. B2B buyers in this sector should consider local sourcing options to reduce transportation costs while also evaluating the environmental impact of their material choices, especially in regions like Europe where sustainability is a priority.
In the energy sector, particularly in nuclear reactors and energy storage systems, the alumina poisson ratio is vital for ensuring the safety and efficiency of components. Materials with an appropriate poisson ratio help manage thermal expansion and contraction, which is critical in high-stress environments. Buyers must be aware of regulatory compliance requirements and focus on suppliers that can guarantee long-term performance and reliability of materials in energy applications, especially in regions like the Middle East where energy production is a cornerstone of the economy.
In automotive engineering, the alumina poisson ratio is applied in brake systems and engine components to enhance safety and performance. The right materials can significantly reduce wear and improve the efficiency of these critical systems. International buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that consistently meet automotive standards, ensuring their vehicles maintain high safety and performance levels, particularly in competitive markets like Europe and Australia.
A stock image related to alumina poisson ratio.
Related Video: Understanding Poisson's Ratio
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of working with suppliers who provide inconsistent or inaccurate specifications for alumina's Poisson ratio. This inconsistency can lead to miscalculations in engineering designs, resulting in project delays and increased costs. For example, a construction company in South America may plan a project based on a specific Poisson ratio of alumina, only to discover that the delivered material does not meet these specifications. This can derail timelines and escalate costs, causing frustration and potential loss of client trust.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should implement a robust material verification process. This includes requesting certified test results and conducting independent testing of the alumina materials upon delivery. Establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers who have a history of compliance with industry standards can further ensure that the Poisson ratio provided is accurate. Additionally, buyers should specify their requirements clearly in contracts, including tolerances for material properties. Utilizing digital tools for tracking and verifying material specifications can enhance transparency and streamline communication between all parties involved.
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets such as Africa and the Middle East, may lack in-depth knowledge about the practical applications of alumina's Poisson ratio in their specific industries. This gap can lead to underutilization of the material or incorrect applications, negatively impacting product performance and leading to costly redesigns. For instance, a manufacturer of ceramic products may not realize that optimizing the Poisson ratio can enhance durability and performance, thus missing out on competitive advantages.
The Solution: Buyers should invest in education and training on material properties, specifically the Poisson ratio of alumina, and its implications for their applications. Engaging with industry experts through workshops, webinars, or seminars can provide valuable insights into how to leverage this property effectively. Additionally, collaborating with research institutions can facilitate access to the latest studies and innovations related to alumina materials. Documenting case studies where optimized Poisson ratios have led to improved product performance can serve as a useful reference for making informed decisions.
The Problem: Sourcing high-quality alumina that meets specific Poisson ratio requirements can be particularly challenging, especially for buyers in regions with limited supplier options. Inconsistent quality can lead to failures in applications such as electronics or aerospace, where precision is critical. A buyer in Europe may struggle to find a reliable supplier that provides alumina with the desired mechanical properties, causing uncertainty and potential project setbacks.
The Solution: To overcome sourcing challenges, buyers should broaden their supplier network by exploring international markets while ensuring compliance with local regulations. Utilizing platforms that facilitate connections with verified suppliers can streamline the sourcing process. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality control and consistent delivery can also enhance reliability. Furthermore, buyers should conduct due diligence, including reviewing supplier certifications and past performance records, to ensure that they are procuring alumina that meets their specific Poisson ratio needs. Implementing a quality assurance program that includes regular audits and feedback loops can help maintain high standards in the supply chain.
When selecting materials for applications requiring alumina with specific Poisson ratios, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including material properties, performance characteristics, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials relevant to alumina Poisson ratio applications.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide)
Alumina is a widely used ceramic material known for its exceptional hardness and thermal stability. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 2000°C) and is chemically inert, making it suitable for various harsh environments. Its Poisson ratio typically ranges between 0.2 and 0.3, which is beneficial in applications requiring dimensional stability under stress.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: High durability, excellent wear resistance, and good electrical insulation.
- Cons: Brittle nature can lead to cracking under impact; higher manufacturing costs compared to metals.
Impact on Application:
Alumina is often used in high-temperature applications such as furnace linings and wear-resistant coatings. Its compatibility with aggressive media makes it ideal for chemical processing industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may need to consider local sourcing to reduce import costs and ensure adherence to regional regulations.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide is another advanced material with a high Poisson ratio (approximately 0.14). It is known for its thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for applications in extreme environments.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Superior hardness and thermal stability, excellent corrosion resistance.
- Cons: More expensive than alumina; complex manufacturing processes can lead to higher costs.
Impact on Application:
SiC is often used in semiconductor applications and high-performance ceramic components. Its compatibility with high-stress environments is beneficial for industries like aerospace and automotive.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable to SiC components, such as JIS in Japan and ASTM in the U.S. Ensuring supplier compliance with these standards can mitigate risks associated with product performance.
Zirconia (ZrO2)
Zirconia is a versatile ceramic material with a Poisson ratio of around 0.31. It offers excellent toughness and is often used in applications requiring high strength and fracture resistance.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: High toughness and resistance to wear; can be used in applications requiring high mechanical strength.
- Cons: Higher cost compared to alumina and silicon carbide; can be challenging to process.
Impact on Application:
Zirconia is commonly used in dental applications, thermal barrier coatings, and cutting tools. Its performance in demanding conditions makes it a preferred choice in various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, adherence to specific quality standards is essential. Understanding the differences in material specifications and certifications can help streamline procurement processes.
Aluminosilicate
Aluminosilicate is a composite material that combines alumina and silica, yielding a Poisson ratio of around 0.25. It is known for its excellent thermal and chemical stability.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Good thermal shock resistance and lower cost compared to pure alumina.
- Cons: Lower strength than pure alumina; may not perform as well in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application:
Aluminosilicate is often used in refractory applications and as a filler in various composites. Its cost-effectiveness makes it attractive for large-scale production.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should evaluate the local availability of aluminosilicate and its compliance with regional standards. This can significantly affect lead times and overall procurement costs.
| Material | Typical Use Case for alumina poisson ratio | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | High-temperature furnace linings | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance | Brittle nature may lead to cracking | High |
| Silicon Carbide | Semiconductor and automotive applications | Superior hardness and thermal stability | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Zirconia | Dental applications and cutting tools | High toughness and fracture resistance | Higher cost and challenging processing | High |
| Aluminosilicate | Refractory applications | Good thermal shock resistance | Lower strength than pure alumina | Medium |
This structured approach to material selection will help international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
The manufacturing process for alumina, particularly concerning its Poisson ratio, involves several critical stages that ensure the material meets the required specifications for various applications. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to procure high-quality alumina.
The first step in the manufacturing of alumina is the preparation of raw materials. High-purity alumina is derived from bauxite ore through the Bayer process. This involves crushing and grinding the bauxite, followed by digestion with sodium hydroxide at elevated temperatures. The resulting alumina hydrate is then filtered, washed, and calcined to produce anhydrous alumina.
Actionable Insight: B2B buyers should inquire about the source of bauxite and the purity levels of the alumina produced, as impurities can significantly affect the Poisson ratio and overall material performance.
Once the alumina is prepared, the next stage is forming. This may involve processes such as pressing, extrusion, or casting, depending on the desired final shape and application.
Actionable Insight: Buyers should understand the forming techniques employed by suppliers, as they can influence the mechanical properties, including the Poisson ratio, of the final product.
In some cases, multiple components made from alumina are assembled to create a final product. This may include joining techniques like brazing or adhesive bonding, which require careful consideration to maintain the integrity of the Poisson ratio.
Actionable Insight: B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers have a robust assembly process in place, as improper joining can lead to performance issues in applications where Poisson ratio is critical.
The finishing stage encompasses surface treatments and quality enhancements. Techniques such as grinding, polishing, or coating can be applied to improve the surface finish and performance characteristics of the alumina.
Actionable Insight: Buyers should ask about the finishing processes used and any treatments that may affect the material’s mechanical properties, including the Poisson ratio.
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that alumina products meet international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards can help in evaluating potential suppliers.
Actionable Insight: Buyers should request certifications and documentation from suppliers to verify compliance with these international standards.
Actionable Insight: B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers provide clear evidence of compliance with relevant industry-specific standards.
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential to maintaining the quality of alumina throughout the manufacturing process. The main checkpoints include:
During the IQC phase, raw materials are inspected for quality before they enter the production process. This step is crucial for ensuring that the bauxite and other materials meet specified quality standards.
Actionable Insight: Buyers can request information on the IQC processes and the criteria used for raw material acceptance.
IPQC involves monitoring the manufacturing process itself. This can include real-time measurements of temperature, pressure, and material properties to ensure that they remain within specified limits.
Actionable Insight: B2B buyers should inquire about the monitoring techniques used during production and how deviations are managed.
In the FQC stage, the finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all specifications, including the Poisson ratio. Common testing methods include:
Actionable Insight: Buyers should ask for detailed reports on FQC results and any third-party testing conducted to validate the quality of the alumina.
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
Conducting audits of suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing and QC processes. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards and internal protocols.
Actionable Insight: Buyers should establish a regular audit schedule and consider third-party auditors for unbiased evaluations.
Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the QC measures in place. This includes documentation of IQC, IPQC, and FQC results, along with any corrective actions taken.
Actionable Insight: Buyers should demand comprehensive documentation as part of their procurement process to ensure traceability and accountability.
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an additional layer of assurance regarding the quality of alumina products. These agencies can offer certifications and unbiased evaluations of supplier quality.
Actionable Insight: Buyers should consider incorporating third-party inspections into their procurement strategy, especially for critical applications.
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for alumina, particularly concerning its Poisson ratio, is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, finishing processes, and stringent quality control standards, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Adhering to international standards and conducting thorough quality assessments will ensure the procurement of high-quality alumina that meets specific application requirements.
The following is a practical sourcing guide tailored for B2B buyers interested in procuring materials related to the alumina poisson ratio. This checklist will help ensure that you make informed decisions throughout the sourcing process.
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the alumina material you need. This includes the desired poisson ratio, purity levels, and any specific applications it will be used for. Having well-defined specifications helps suppliers understand your needs and ensures that you receive products that meet your quality standards.
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in alumina materials. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your target markets, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online marketplaces to compile a list of credible suppliers.
Verify that potential suppliers hold necessary certifications and comply with international standards. Look for ISO certifications, safety data sheets, and any region-specific regulations. These credentials can provide assurance of product quality and regulatory compliance, which is crucial for long-term partnerships.
Before placing a bulk order, always request samples of the alumina materials. Testing samples allows you to assess the physical and chemical properties, including the poisson ratio. Ensure that the samples meet your specifications before making a commitment.
Compare pricing from multiple suppliers to ensure you receive competitive quotes. However, don't just focus on the lowest price; consider the overall value, including quality, delivery times, and customer service. Discuss payment terms clearly, including any upfront deposits or credit arrangements, to avoid misunderstandings.
Discuss delivery timelines and logistics with your chosen supplier. Understanding the lead times for production and shipping is essential, especially if you are operating under tight deadlines. Ensure that the supplier can meet your delivery needs without compromising quality.
Set up a communication plan with your supplier to facilitate ongoing collaboration. Regular updates on production status, quality checks, and shipment tracking are vital for maintaining transparency. Effective communication can help address issues proactively and strengthen the business relationship.
By following these steps, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing alumina with greater confidence and efficiency.
Understanding the cost structure of sourcing alumina, particularly regarding its Poisson ratio, is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The cost of alumina itself is a major factor. Prices fluctuate based on global supply and demand, as well as the quality of alumina being sourced. Higher purity alumina typically costs more.
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In Africa and South America, labor may be more affordable than in Europe or Australia. However, the skill level and experience required for handling specialized materials can influence overall labor costs.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs down.
Tooling: The investment in tooling and machinery necessary for processing alumina can be substantial. This cost is often amortized over the production volume.
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC measures are essential to ensure that the alumina meets the specified Poisson ratio. This includes testing and certification costs.
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary based on location and the chosen Incoterms. Import duties and tariffs may also impact the final cost, especially for buyers from Africa and South America.
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the competitive landscape and demand.
Several key factors influence the pricing of alumina:
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also impact pricing negotiations.
Specifications and Customization: Customizing alumina to meet specific performance criteria can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
Materials Quality and Certifications: The demand for certified high-quality materials can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess the importance of certifications based on their end-use applications.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence price. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their credibility and service.
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding the implications of terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is critical for budgeting.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
Effective Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure better pricing. Highlighting the potential for long-term relationships or bulk purchases can be advantageous.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the complete lifecycle cost of the alumina, including sourcing, transportation, processing, and disposal. This approach may reveal hidden costs and help justify initial investments.
Leverage Local Suppliers: Sourcing from regional suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. This is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where local resources may be available.
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding global market trends and price fluctuations can help buyers time their purchases effectively. Subscribing to industry reports can provide valuable insights.
Prices for alumina and its associated costs can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and buyer specifications. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
When considering materials for industrial applications, understanding the alternatives to the alumina Poisson ratio is crucial for international B2B buyers. The Poisson ratio is a key mechanical property that describes how materials deform under stress. While alumina is widely recognized for its excellent mechanical properties, buyers should evaluate other materials or methods that may offer similar or enhanced benefits tailored to specific applications. This section compares alumina with other viable solutions, facilitating informed decision-making.
| Comparison Aspect | Alumina Poisson Ratio | Alternative 1: Silicon Carbide | Alternative 2: Zirconia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, good thermal stability | Superior thermal conductivity, high wear resistance | Excellent toughness and thermal shock resistance |
| Cost | Moderate | High | Moderate to High |
| Ease of Implementation | Standard processing required | Requires specialized techniques | Conventional processing applicable |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance needed | Low maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, electronics | High-temperature applications, cutting tools | Medical implants, dental applications |
Silicon carbide (SiC) offers superior thermal conductivity and high wear resistance, making it an excellent choice for high-temperature applications and cutting tools. The performance of SiC in harsh environments is outstanding, which enhances its appeal for sectors like aerospace and automotive. However, the primary drawback is its cost, which can be significantly higher than alumina. Additionally, the manufacturing process often requires specialized techniques, which may pose challenges for companies with standard processing capabilities.
Zirconia stands out for its excellent toughness and resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for applications in medical implants and dental materials. Its performance in high-stress environments is commendable, offering durability and reliability. The costs associated with zirconia can be moderate to high, depending on the required purity and processing methods. While it can be processed using conventional techniques, its unique properties may necessitate more stringent quality control measures.
In conclusion, selecting the right material involves a comprehensive analysis of specific needs and application contexts. B2B buyers should assess the performance characteristics, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements of alumina against alternatives like silicon carbide and zirconia. By understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each material, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget considerations. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific application, performance requirements, and long-term operational costs.
Understanding the technical properties of alumina, particularly its Poisson ratio, is crucial for B2B buyers in industries such as ceramics, aerospace, and electronics. The Poisson ratio, which measures the material's response to axial stress, is a pivotal factor when evaluating material performance in various applications. Here are key specifications to consider:
Material Grade
Alumina is available in different grades (e.g., 99.5%, 99.9% pure). Higher grades typically exhibit better mechanical properties, including strength and wear resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the right grade ensures optimal performance and longevity of the product in specific applications.
Poisson Ratio Value
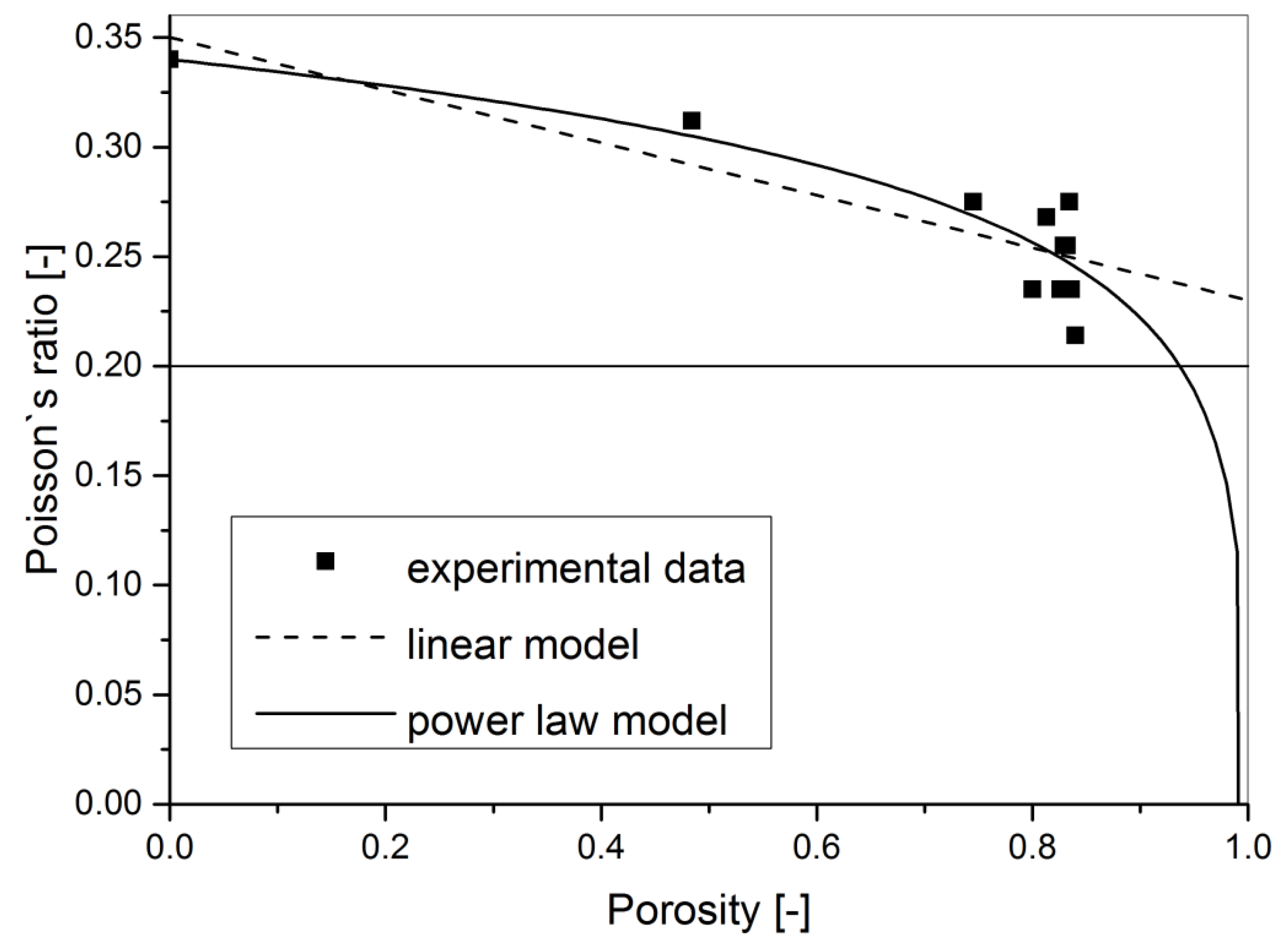
The Poisson ratio for alumina generally ranges from 0.20 to 0.30. This ratio indicates how much a material deforms in the lateral direction when subjected to axial stress. A higher Poisson ratio may suggest better ductility, which can be vital in applications requiring flexibility under load.
Tolerance Levels
Tolerances are crucial for ensuring parts fit together correctly in assemblies. For alumina products, tolerances might be specified in terms of dimensional accuracy (±0.01 mm, for example). Tight tolerances can be essential for precision applications in the aerospace and electronics sectors, where even minor deviations can lead to failure.
Thermal Conductivity
Alumina typically has a thermal conductivity range of 20-30 W/m·K. Understanding this property is essential for applications involving heat dissipation, such as in electronic components or high-temperature environments. Buyers should ensure that the chosen alumina grade matches the thermal requirements of their specific application.
Mechanical Strength
The mechanical strength of alumina is typically measured in terms of compressive and tensile strength, often exceeding 300 MPa. High mechanical strength is vital for applications in structural components or where resistance to wear and tear is necessary.
Density
The density of alumina usually ranges from 3.5 to 4.0 g/cm³. Density affects both the weight and strength of the material, influencing the design and manufacturing processes. Buyers should consider density in relation to the performance requirements of their products.
Navigating the world of alumina procurement involves understanding specific trade terms. Familiarity with these terms can enhance communication and negotiation processes:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For B2B buyers, understanding OEM relationships can help in sourcing high-quality alumina products that meet specific industry standards.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For international buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, particularly when dealing with suppliers in different regions like Africa or South America.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other details for specific products. B2B buyers should prepare clear and detailed RFQs to ensure accurate responses from suppliers, facilitating a smoother procurement process.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs and liabilities, which is especially important for international transactions.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times can aid in planning production schedules and managing customer expectations.
Certification Standards
Certification standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) are essential for ensuring product quality and compliance with industry regulations. Buyers should verify that suppliers meet relevant certification standards to mitigate risks associated with material quality.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and ultimately lead to successful partnerships in the alumina industry.
The alumina poisson ratio sector is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for lightweight, high-strength materials across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. This rising demand is primarily fueled by global trends toward energy efficiency and performance enhancement in material applications. Moreover, advancements in B2B technologies, such as digital sourcing platforms and data analytics, are reshaping how international buyers interact with suppliers.
In regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, emerging markets are beginning to harness local alumina resources, which not only reduces import costs but also fosters regional economic growth. European buyers, particularly from countries like Germany and France, are increasingly focused on sourcing alumina with optimized poisson ratios, which enhance the mechanical properties of composites. This shift reflects a broader trend toward specialized materials tailored to specific engineering requirements.
Furthermore, the ongoing challenges posed by global supply chain disruptions necessitate that B2B buyers maintain flexible sourcing strategies. Adopting a multi-supplier approach can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and fluctuating raw material prices. Understanding market dynamics, including the influence of tariffs and trade agreements, is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration for B2B buyers in the alumina poisson ratio sector. The environmental impact of mining and processing alumina is significant, prompting companies to seek suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and possess 'green' certifications, such as ISO 14001.
Ethical sourcing extends beyond environmental considerations; it encompasses the entire supply chain, including labor practices and community impact. Buyers should look for suppliers that engage in fair labor practices and contribute to local communities, ensuring that their sourcing decisions align with corporate social responsibility goals.
Moreover, the demand for 'green' materials is on the rise, as companies seek to enhance their sustainability credentials. B2B buyers should actively seek alumina products that have been processed using environmentally friendly methods, such as those that minimize carbon emissions and waste. This not only enhances a company's brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
The understanding of the alumina poisson ratio has evolved significantly since the early 20th century when it was primarily a theoretical concept in material science. Initially, the focus was on the general properties of materials; however, as industries began to recognize the advantages of aluminum and its compounds, the emphasis shifted to optimizing specific characteristics, including the poisson ratio.
In recent decades, the development of advanced manufacturing techniques and computational modeling has enabled engineers to tailor alumina properties to meet exact specifications. This evolution has been particularly relevant in high-performance applications, where the mechanical behavior of materials is critical. Today, the alumina poisson ratio is a key parameter in designing materials for aerospace, automotive, and construction applications, reflecting the sector's continuous innovation and adaptation to market demands.
Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the advancements in material science and the importance of sourcing alumina that meets modern engineering challenges.
How do I determine the appropriate Poisson ratio for my alumina application?
The Poisson ratio of alumina typically ranges from 0.22 to 0.25, depending on the specific grade and processing conditions. To determine the best ratio for your application, consider factors such as the mechanical stress it will face, the temperature range, and the type of load (tensile or compressive). Consulting with suppliers about the specific characteristics of their alumina products can provide insights into which Poisson ratio will best meet your needs.
What is the significance of the Poisson ratio in alumina procurement?
The Poisson ratio indicates how much a material deforms in directions perpendicular to the applied load. For alumina, a higher ratio suggests greater ductility, which can be beneficial in applications requiring flexibility under stress. Understanding this property helps B2B buyers assess product suitability for specific applications, ensuring that the alumina sourced will perform effectively in its intended use.
How can I assess the quality of alumina based on its Poisson ratio?
While the Poisson ratio is an important indicator of alumina's mechanical properties, it should not be the sole criterion for quality assessment. Engage with suppliers to obtain detailed technical data sheets that include Poisson ratio values along with other mechanical properties like tensile strength and hardness. Additionally, consider third-party testing results to verify the claims made by suppliers.
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alumina products with specific Poisson ratios?
MOQs can vary widely among suppliers, often influenced by the grade of alumina and market demand. Generally, larger orders may yield better pricing and terms. To ensure you meet your operational needs, communicate clearly with suppliers regarding your specific requirements, and inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are testing a new application.
What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing alumina internationally?
Payment terms can significantly affect cash flow and financial planning. Common options include letters of credit, advance payments, or net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). When negotiating, consider the risk associated with the supplier's location and reliability. Establishing a clear agreement on payment terms can help mitigate financial risks and foster a trusting supplier relationship.
How do I ensure reliable logistics for international alumina shipments?
Reliable logistics are crucial for timely delivery and product integrity. Work with suppliers who have established logistics partnerships and experience in international shipping. It’s advisable to clarify shipping methods, expected lead times, and handling procedures to minimize damage during transit. Additionally, consider using freight forwarders who specialize in handling bulk materials like alumina for a smoother shipping experience.
What quality assurance processes should I expect from alumina suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should have robust quality assurance (QA) processes in place, including regular material testing, adherence to international standards (like ISO), and traceability of material batches. Request documentation of these QA measures, including test results for properties like the Poisson ratio, to ensure the product meets your specifications. Regular audits of the supplier’s QA processes can also provide peace of mind.
How do regional regulations affect the sourcing of alumina?
Different regions may have specific regulations regarding the importation of materials like alumina, including safety standards and environmental compliance. It’s essential to understand these regulations to avoid legal complications. Consult with local trade authorities or logistics providers familiar with your destination country’s requirements. Ensuring compliance can facilitate smoother transactions and reduce the risk of costly delays or penalties.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
In summary, the strategic sourcing of alumina with a focus on its Poisson ratio is pivotal for businesses aiming for durability and performance in their applications. Understanding the Poisson ratio allows buyers to assess material behavior under stress, ensuring that they select the right specifications for their operational needs. By aligning sourcing strategies with quality assurance and supplier reliability, businesses can mitigate risks and enhance their supply chain resilience.
Investing in strategic sourcing not only optimizes costs but also fosters innovation and sustainability. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, forming partnerships with reputable suppliers can lead to improved product quality and compliance with regional standards. This alignment with local and international suppliers is essential for navigating the complexities of global trade.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality alumina is expected to rise, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications across industries. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about market trends and emerging technologies related to alumina. By engaging in proactive sourcing strategies, international B2B buyers can position themselves for success in a competitive landscape. Embrace this opportunity to refine your sourcing practices and secure a robust supply chain today.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina