Navigating the global market for the alumina production process presents a myriad of challenges for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing high-quality materials while managing costs and supplier reliability. With alumina being a critical component in various industries, including ceramics, catalysis, and water treatment, understanding its production nuances is paramount. This guide delves into the complexities of alumina production, exploring different types such as gamma alumina and their applications across sectors.
International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can benefit significantly from this comprehensive resource. We cover essential topics such as supplier vetting strategies, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements in alumina processing. By providing actionable insights and industry best practices, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Whether you are looking to enhance your supply chain efficiency or seeking reliable partners in the alumina market, this guide serves as a crucial tool in navigating the intricate landscape of alumina production. By understanding the key factors that influence procurement, buyers can mitigate risks and seize opportunities in this vital sector.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bayer Process | Uses bauxite ore, involves high temperature and pressure | Aluminum production, ceramics, catalysts | Pros: High yield; Cons: High energy consumption |
| Hall-Héroult Process | Electrolytic reduction of alumina to aluminum | Primary aluminum production | Pros: Direct aluminum production; Cons: High emissions |
| Calcination | Heating of aluminum hydroxide to produce alumina | Ceramics, refractories | Pros: Low-cost; Cons: Limited applications |
| Hydrated Alumina Production | Production of hydrated alumina via precipitation | Water treatment, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Versatile applications; Cons: Lower purity |
| Specialty Alumina Production | Tailored alumina forms for specific applications | Electronics, automotive, aerospace | Pros: High performance; Cons: Higher costs |
The Bayer Process is the dominant method for producing alumina from bauxite ore. It involves crushing the bauxite and treating it with sodium hydroxide at high temperatures and pressures to dissolve aluminum oxides. The process yields a high percentage of alumina, making it suitable for large-scale aluminum production. B2B buyers should consider the environmental impact and energy costs associated with this process, as well as the potential for sourcing sustainable bauxite.
The Hall-Héroult Process is an electrolytic method where alumina is dissolved in molten cryolite and subjected to an electric current to produce aluminum metal. This process is critical for primary aluminum production and is characterized by its high energy requirements, leading to significant carbon emissions. Buyers must weigh the benefits of direct metal production against the environmental regulations and energy costs involved.
Calcination involves heating aluminum hydroxide to high temperatures to produce alumina. This method is often used in the production of ceramics and refractories, where a lower cost is advantageous. While calcination is relatively simple and cost-effective, it may not yield the same purity levels as other processes. Buyers should assess the specific purity requirements of their applications when considering this method.
Hydrated alumina is produced through precipitation methods and is commonly used in water treatment and pharmaceuticals. This production method allows for versatile applications but typically results in lower purity compared to other alumina types. B2B buyers should consider the specific application requirements and the trade-offs in purity and cost when selecting hydrated alumina.
Specialty alumina production focuses on creating alumina with specific properties tailored for high-performance applications in industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace. This process often involves advanced techniques and higher costs, but the resulting materials provide superior performance. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of investing in specialty alumina against the initial cost outlay, especially for high-tech applications.
Related Video: Tabular alumina production process
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alumina production process | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Adsorbent in wastewater purification | Enhances water quality and compliance with environmental regulations | Quality of alumina, particle size, and surface area specifications |
| Catalysis | Catalyst support in chemical reactions | Increases reaction efficiency and product yield | Purity of alumina, surface characteristics, and mechanical strength |
| Electronics | Insulating material in electronic components | Provides high thermal stability and electrical insulation | Compatibility with existing materials and thermal properties |
| Ceramics Manufacturing | Component in advanced ceramic materials | Improves mechanical strength and thermal resistance | Grain size, purity, and production process |
| Aerospace | Lightweight structural components | Reduces weight while maintaining strength and durability | Quality assurance, certification standards, and sourcing location |
In the water treatment industry, the alumina production process is utilized to create high-purity alumina that serves as an effective adsorbent for removing contaminants from wastewater. This application is crucial for businesses seeking to meet stringent environmental regulations and improve water quality. Buyers in this sector must consider the specific surface area and pore size distribution of alumina to ensure optimal adsorption capabilities. Additionally, sourcing alumina that meets international quality standards is essential for maintaining compliance and achieving desired treatment outcomes.
Alumina acts as a vital catalyst support in various chemical reactions, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of processes such as hydrocarbon conversion and sulfur removal in refineries. The alumina production process yields gamma-alumina, which provides high surface area and mechanical strength for stabilizing catalyst particles. For international B2B buyers, it is important to prioritize the purity of alumina, as impurities can adversely affect catalytic performance. Understanding the specific chemical reactions and conditions in which alumina will be used can guide sourcing decisions.
A stock image related to alumina production process.
In the electronics sector, alumina produced through the alumina production process is employed as an insulating material in components such as substrates and capacitors. Its high thermal stability and low electrical conductivity make it ideal for protecting sensitive electronic parts from heat and electrical interference. Buyers should consider the compatibility of alumina with existing materials and the specific thermal properties required for their applications. Ensuring that the sourced alumina meets the necessary specifications can significantly enhance product reliability and performance.
Alumina is a key ingredient in the production of advanced ceramic materials, providing improved mechanical strength and thermal resistance. The alumina production process enables the creation of fine-grained alumina that can be tailored for various ceramic applications, such as cutting tools and wear-resistant components. For international buyers, factors such as grain size, purity, and the production process must be carefully evaluated to ensure the desired properties are achieved in the final ceramic products.
In the aerospace sector, alumina is used to manufacture lightweight structural components that require high strength-to-weight ratios. The alumina production process allows for the creation of materials that can withstand extreme conditions while minimizing overall weight, which is critical for fuel efficiency and performance. Buyers in this industry should focus on quality assurance and certification standards when sourcing alumina, as these factors are essential for meeting safety regulations and performance expectations in aerospace applications.
Related Video: Alumina Ceramic Producing Process |How to Make High Density Alumina Ceramic Pieces
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the alumina production industry face the challenge of escalating production costs driven by inefficient processes. This inefficiency can stem from outdated machinery, ineffective use of raw materials, or suboptimal processing techniques. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where budgets may be tighter, these high costs can severely impact profitability and competitiveness in the global market. Additionally, fluctuations in energy prices can further exacerbate these challenges, leading to unpredictable operational expenses.
The Solution: To address high production costs, buyers should consider investing in modernizing their production equipment and optimizing their alumina refining processes. This can include integrating advanced technologies such as automated control systems and energy-efficient machinery that minimize waste and enhance throughput. Conducting a thorough energy audit can identify areas where energy consumption can be reduced, potentially leading to significant cost savings. Furthermore, collaborating with technology providers specializing in alumina production can yield tailored solutions that improve efficiency and lower overall operational costs. Regular training for staff on best practices in alumina processing can also ensure that the workforce is adept at utilizing new technologies effectively.
The Problem: Quality control is a persistent concern in alumina production, especially for international buyers looking to maintain consistency in their products. Variability in alumina quality can arise from inconsistent raw material sources, variations in the processing environment, or inadequate monitoring of production parameters. Such inconsistencies can lead to customer dissatisfaction, lost contracts, and damage to reputation, particularly in competitive markets in Europe and the Middle East where quality standards are stringent.
The Solution: Implementing a robust quality management system (QMS) is essential for overcoming quality control challenges. This system should incorporate real-time monitoring of key production parameters and regular sampling of alumina products to ensure compliance with specified quality standards. Buyers can also establish partnerships with reliable suppliers of raw materials to guarantee the consistency of inputs. Utilizing advanced analytical tools, such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), can provide deeper insights into the chemical and physical properties of alumina, allowing for adjustments to be made proactively during production. Additionally, establishing a feedback loop with end-users can help gather insights on performance, enabling continuous improvement in product quality.
The Problem: As global environmental regulations tighten, B2B buyers in the alumina production sector are increasingly challenged to comply with sustainability standards. In regions such as Africa and the Middle East, where environmental policies are becoming more stringent, failure to adhere to regulations can result in hefty fines and damage to corporate reputation. Buyers are often unsure how to balance operational efficiency with sustainable practices, leading to apprehension about investing in greener technologies.
The Solution: To navigate environmental compliance challenges, buyers should prioritize sustainable practices within their alumina production processes. This can be achieved by investing in technologies that reduce emissions, such as scrubbers and advanced filtration systems, which can capture pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere. Additionally, implementing circular economy principles, such as recycling alumina waste or using alternative materials, can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of production. Engaging with environmental consultants can provide valuable insights into regulatory requirements and help develop a comprehensive sustainability strategy that aligns with business goals. Furthermore, promoting transparency in environmental performance can enhance brand reputation and attract customers who prioritize sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
A stock image related to alumina production process.
When considering the alumina production process, selecting the right materials is crucial for optimizing performance, ensuring compliance, and minimizing costs. Below, we analyze four commonly used materials in this industry, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Bauxite is the primary raw material for alumina production, consisting mainly of aluminum oxide minerals such as gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore. It is characterized by its high alumina content (typically 30-60%), low silica content, and the ability to be processed at relatively low temperatures (around 150-200°C).
The key advantage of bauxite is its abundance and the relatively low cost of extraction. However, its composition can vary significantly, affecting the efficiency of the Bayer process used to extract alumina. Additionally, impurities like iron oxide can lead to corrosion issues in processing equipment.
Bauxite's composition directly influences the yield and quality of alumina produced. Variations in mineral content can affect the process efficiency and the quality of the end product, making it essential for buyers to source high-quality bauxite.
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local mining regulations and environmental standards. Understanding the origin of bauxite and its processing standards is crucial for maintaining product quality.
Caustic soda is a strong alkaline substance used in the Bayer process to dissolve aluminum hydroxide from bauxite. It has a high solubility in water and can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it essential for alumina extraction.
The primary advantage of caustic soda is its effectiveness in separating alumina from impurities. However, it is highly corrosive, requiring specialized handling and storage solutions, which can increase operational costs.
The concentration and purity of caustic soda can significantly impact the efficiency of the alumina production process. Impurities in caustic soda may lead to lower yields and compromised product quality.
Buyers must consider compliance with chemical handling regulations, such as those outlined by OSHA in the U.S. and REACH in Europe. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who meet international quality standards is essential.
Lime is often used in the alumina production process for neutralizing acidic waste and improving the separation of impurities. It has a high melting point and can withstand harsh chemical environments.
Lime is relatively inexpensive and widely available. However, its use can generate additional waste products that require careful disposal, complicating the overall process.
The addition of lime can enhance the overall efficiency of the Bayer process by improving the quality of the alumina produced. However, improper handling can lead to operational issues.
B2B buyers should be aware of local environmental regulations regarding lime disposal and ensure that suppliers adhere to safety and quality standards.
Aluminum hydroxide is an intermediate product in the Bayer process and serves as a precursor for producing alumina. It is characterized by its high purity and stability under various conditions.
The primary advantage of aluminum hydroxide is its ability to produce high-purity alumina with minimal impurities. However, it can be more expensive than raw bauxite, impacting overall production costs.
The purity of aluminum hydroxide directly affects the quality of the final alumina product, making it essential for applications requiring high-performance materials.
Buyers should ensure that the aluminum hydroxide sourced meets international standards such as ASTM or DIN, particularly for applications in industries like aerospace and automotive.
| Material | Typical Use Case for alumina production process | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bauxite Ore | Primary raw material for alumina extraction | Abundant and low-cost | Variable composition can affect yield | Low |
| Caustic Soda (Sodium Hydroxide) | Key chemical in Bayer process | Effective in separating alumina | Highly corrosive, requires special handling | Medium |
| Lime (Calcium Oxide) | Neutralizes acidic waste in alumina production | Inexpensive and widely available | Generates waste requiring disposal | Low |
| Aluminum Hydroxide | Precursor for high-purity alumina | Produces high-purity alumina | More expensive than bauxite | High |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, facilitating informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality in the alumina production process.
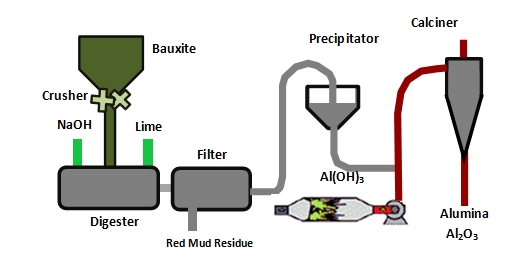
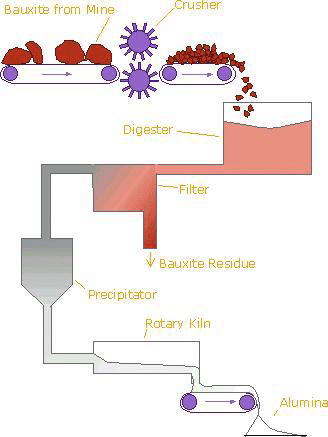
The alumina production process comprises several critical stages that ensure the efficient transformation of bauxite ore into high-quality alumina. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
The first step involves the extraction and preparation of bauxite, the primary ore of aluminum. Bauxite is typically mined using open-pit techniques, followed by crushing and grinding to reduce particle size. The resulting material is then mixed with caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) to facilitate the extraction of alumina.
During this stage, it's essential to monitor the composition of the bauxite for impurities such as iron oxides and silica, as these can affect the quality of the final product. Buyers should inquire about suppliers' testing methods for material quality before processing begins.
In this phase, the prepared bauxite is subjected to high-pressure digestion in a digester, where it reacts with the caustic soda solution. This process dissolves the aluminum oxide present in the bauxite, leaving behind impurities as a solid residue.
After digestion, the slurry undergoes a separation process, typically through sedimentation or filtration, to separate the undissolved waste from the sodium aluminate solution. Buyers should ensure that suppliers employ efficient leaching techniques to maximize alumina yield and minimize waste.
The sodium aluminate solution is then cooled and seeded with aluminum hydroxide crystals to initiate precipitation. This process is crucial, as it converts dissolved sodium aluminate back into solid aluminum hydroxide, which is then collected through filtration.
Monitoring parameters such as temperature, pH, and seed crystal size is vital during this stage. B2B buyers should request detailed operational parameters from suppliers to ensure optimal precipitation conditions are maintained.
The aluminum hydroxide obtained is subsequently dried and calcined at temperatures exceeding 1000°C to produce alumina (Al₂O₃). This process removes water and transforms the hydroxide into a stable oxide form.
Quality control at this stage is essential, as variations in temperature can lead to inconsistencies in the alumina produced. Buyers should ensure their suppliers utilize robust thermal monitoring systems to maintain consistent product quality.
The final stage of the alumina production process involves milling and packaging the alumina for shipment. This may include further processing to achieve specific particle sizes or surface characteristics based on customer requirements.
Buyers should inquire about suppliers’ milling techniques and whether they have capabilities for custom specifications to meet specific industrial applications.
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the alumina production process, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. Understanding these QA measures can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
B2B buyers should be familiar with key international quality standards that alumina producers are expected to adhere to, including:
Buyers should request certification documentation from suppliers to verify compliance with these standards.
Quality control is typically implemented at various checkpoints throughout the alumina production process, including:
B2B buyers should understand the specific QC protocols of their suppliers and request access to test reports and inspection logs.
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of alumina throughout the production process:
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methodologies employed by suppliers to ensure thorough quality assessments.
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification strategies:
Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should also be aware of regional regulations that may impact supplier quality and compliance.
When sourcing alumina internationally, B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances:
By being informed about these nuances, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they receive high-quality alumina products tailored to their needs.
In this practical sourcing guide, international B2B buyers looking to procure the alumina production process will find a comprehensive checklist. This guide is designed to streamline the sourcing journey, ensuring that buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed decisions when selecting suppliers and technologies for alumina production.
Before initiating the sourcing process, it is essential to establish clear technical specifications for the alumina production process. This includes determining the desired grade of alumina, production capacity, and specific methods (e.g., Bayer process, Hall-Héroult process). Clearly defined specifications will help ensure that suppliers understand your requirements and can deliver products that meet your operational needs.
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in alumina production. Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in the industry, particularly those with experience serving markets in your region.
Verify that potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications and comply with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001 or ISO 14001. This step is crucial for ensuring product consistency and environmental sustainability.
Evaluate the production capabilities of suppliers, including their technology and equipment used in the alumina production process. Suppliers should have modern facilities capable of producing high-quality alumina efficiently.
Before finalizing your supplier, request samples of their alumina products for quality testing. Conduct thorough analyses to ensure that the samples meet your specifications and performance criteria.
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and pricing. Consider factors such as payment terms, delivery schedules, and minimum order quantities.
Effective communication is vital for successful procurement. Establish a communication plan with your chosen supplier to facilitate ongoing discussions regarding order status, production updates, and any potential issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing the alumina production process with confidence, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers capable of meeting their specific needs.
Understanding the cost structure in alumina production is essential for international B2B buyers. The main components include:
Materials: The primary raw material, bauxite ore, is subject to market fluctuations, impacting overall costs. The quality of bauxite affects the efficiency of alumina extraction, which in turn influences material costs.
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the region and the skill level required. In Africa and South America, lower labor costs may be available, while European standards can increase overall production costs.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting the final pricing.
Tooling: The initial setup for alumina production can be capital-intensive. Investment in advanced machinery can enhance productivity but also raises upfront costs.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that alumina meets international standards requires investment in QC processes. This is particularly important for buyers in Europe, where regulatory compliance is strict.
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the distance from the production site to the buyer. Incoterms play a crucial role in defining responsibilities for shipping and insurance, directly affecting pricing.
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing. Understanding the market dynamics in different regions can help buyers negotiate better rates.
Several factors influence alumina pricing, making it essential for buyers to consider them when sourcing:
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases can lead to significant discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help negotiate better pricing.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to additional processing and quality checks. Standardized products may offer better pricing.
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials with certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may come at a premium but are crucial for applications requiring stringent quality controls.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but offer better service and quality assurance.
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (like FOB, CIF) is vital, as they define who bears the shipping costs and risks, influencing overall pricing.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance negotiation outcomes:
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand average pricing in your region. Use this information to negotiate effectively.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Factor in logistics, maintenance, and potential risks associated with lower-quality suppliers. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a reliable partnership with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and priority during stock shortages.
Leverage Local Knowledge: Engage local agents or consultants who understand regional market dynamics. Their insights can provide leverage during negotiations.
Be Clear on Specifications: Clearly communicate your requirements to avoid misunderstandings that can lead to additional costs. Ensure that suppliers understand your quality and certification needs upfront.
Prices for alumina production can vary widely based on market conditions, regional differences, and specific buyer requirements. The information provided here serves as a guideline for understanding cost structures and pricing dynamics and should not be considered as fixed or final pricing. Always consult multiple suppliers and conduct due diligence before finalizing any agreements.
As international B2B buyers explore the alumina production process, it's crucial to consider viable alternatives that may offer distinct advantages based on specific operational needs. Various methods exist to produce alumina, and each comes with its unique characteristics, benefits, and challenges. Understanding these alternatives can aid buyers in making informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
| Comparison Aspect | Alumina Production Process | Bayer Process (Alternative 1) | Hall-Héroult Process (Alternative 2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High purity alumina yield | High efficiency for bauxite | High energy consumption |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Lower operational costs | High capital costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex setup required | Relatively straightforward | Requires specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | High maintenance needs | Moderate maintenance | High maintenance demands |
| Best Use Case | High-quality alumina for ceramics and catalysts | Large-scale aluminum production | Aluminum alloy production |
The Bayer process is the most widely used method for extracting alumina from bauxite ore. It operates at relatively low temperatures and pressures, which makes it more energy-efficient compared to the Hall-Héroult process. The operational costs are generally lower, making it a preferred choice for large-scale aluminum production. However, the Bayer process requires a steady supply of high-quality bauxite, and the waste byproducts can have significant environmental impacts if not managed properly.
The Hall-Héroult process is primarily used for the electrolytic production of aluminum from alumina. While this method allows for the direct production of aluminum, it is known for its high energy consumption, which can significantly impact operational costs. Additionally, it requires specialized equipment and maintenance, making it less accessible for smaller operations. However, for businesses focused on aluminum alloys, this process is essential as it directly produces aluminum metal, thus streamlining the supply chain.
When selecting the most suitable alumina production method, B2B buyers must carefully evaluate their specific operational needs, including production scale, budget constraints, and desired product purity. Each method comes with its trade-offs; therefore, a thorough analysis of performance, cost implications, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements is essential. By aligning the chosen production process with strategic business goals, buyers can optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the overall value of their investment in alumina production.
When engaging in the alumina production process, understanding its critical technical properties is essential for B2B buyers. Here are some of the most important specifications:
Material Grade
- Material grade refers to the purity and composition of alumina. Common grades include calcined alumina, activated alumina, and γ-alumina. Higher grades typically exhibit enhanced mechanical strength and lower impurity levels, making them suitable for specific applications in industries such as ceramics and catalysts. B2B buyers should prioritize the appropriate material grade that aligns with their end-use requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Surface Area
- The surface area of alumina is crucial, especially for applications in catalysis and adsorption. A higher surface area increases the material's ability to interact with other substances, which can significantly enhance its efficacy in chemical reactions. For buyers, selecting alumina with the right surface area can directly impact the efficiency of their processes, making it a vital consideration.
Pore Volume and Pore Size Distribution
- Pore volume and size distribution characterize how well alumina can absorb or adsorb various substances. A material with adequate pore volume and a favorable size distribution is essential for applications in filtration, catalysis, and water treatment. Buyers should assess these parameters to ensure the alumina meets the specific demands of their applications.
Mechanical Strength
- Mechanical strength is a measure of how well alumina can withstand physical stress without fracturing. This property is particularly important in industries that require robust materials for high-temperature processes. Buyers need to evaluate the mechanical strength of alumina to ensure it can endure operational demands, thereby reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Chemical Stability
- Chemical stability refers to the material's resistance to degradation in various environments, particularly in acidic or alkaline conditions. This property is critical for applications in chemical processing and water treatment. Buyers must ensure that the alumina they procure is chemically stable to avoid performance issues and additional costs associated with material failure.
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and better negotiations for B2B buyers. Here are several essential trade terms related to the alumina production process:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
- OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of alumina, it often pertains to suppliers who manufacture alumina products for use in other companies' production processes. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality alumina.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
- MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the alumina industry, MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product grade. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases effectively, ensuring they meet their production needs without overcommitting.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
- An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for price estimates on specific quantities of alumina. By issuing an RFQ, buyers can compare prices, terms, and conditions from multiple suppliers, enabling informed decision-making and cost management.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
- Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. For alumina buyers, understanding Incoterms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smoother logistics and compliance.
Lead Time
- Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the alumina market, lead times can vary based on production schedules, supplier capabilities, and shipping arrangements. Buyers should factor in lead times when planning their inventory and production schedules to avoid disruptions.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and optimize their operations in the alumina production process.
The alumina production process is witnessing significant shifts due to various global drivers. One of the primary factors is the increasing demand for aluminum, which is primarily driven by sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. As industries seek lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, the demand for alumina as a precursor for aluminum production is expected to rise. Additionally, technological advancements in alumina refining processes, such as the Bayer process and alternative extraction methods, are enhancing efficiency and reducing costs, making alumina more accessible to international buyers.
Emerging B2B technology trends are reshaping the sourcing landscape for alumina. The integration of digital platforms is enabling buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to streamline procurement processes, access real-time market data, and establish direct connections with suppliers. Moreover, automation and AI-driven analytics are helping businesses optimize their supply chains, manage inventory more effectively, and forecast demand more accurately.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and trade policies. For instance, trade tariffs and restrictions can affect the availability and pricing of alumina in different markets. Buyers must stay informed about these developments to navigate potential disruptions and seize opportunities in the alumina supply chain.
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the alumina sector. The environmental impact of alumina production, particularly in terms of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, is prompting companies to seek more sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize sustainable mining and processing techniques, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with alumina production.
Ethical sourcing is becoming a fundamental aspect of supply chain management. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate suppliers based on their commitment to environmental stewardship and social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Responsible Aluminium Standard are gaining traction, providing assurance that suppliers adhere to sustainable practices.
Furthermore, the use of "green" materials and technologies in the alumina production process is on the rise. Innovations such as low-carbon alumina production methods and recycling initiatives are appealing to environmentally-conscious buyers. By prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing strategies, businesses can not only reduce their environmental impact but also enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for ethical products.
The alumina production process has evolved significantly since its inception in the 19th century. Initially, the Bayer process, developed in 1888, became the dominant method for extracting alumina from bauxite ore. Over the decades, advancements in refining technologies have improved efficiency and reduced costs, making alumina production more economically viable.
As the global demand for aluminum grew, especially post-World War II, the alumina industry expanded rapidly, leading to increased investment in mining and processing capabilities. In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and ethical sourcing, reflecting broader societal concerns about environmental impacts and corporate responsibility.
This historical context underscores the importance of adapting to changing market dynamics and sourcing trends. Buyers today must consider not only the economic factors but also the ethical and environmental implications of their sourcing decisions in the alumina production process.
How do I evaluate the quality of alumina suppliers for my business needs?
To evaluate alumina suppliers effectively, consider their certifications, production capabilities, and quality control processes. Request samples to assess the alumina's purity and physical properties. Investigate their production methods and the technology they employ, as modern techniques often yield higher-quality products. Additionally, check for customer reviews and case studies that highlight their reliability and service. Building relationships through site visits can also provide deeper insights into their operational standards.
What is the best alumina type for water treatment applications?
For water treatment, gamma alumina (γ-Al2O3) is widely recognized for its high surface area and porosity, making it an excellent adsorbent for various contaminants. Its unique structure facilitates effective removal of heavy metals and organic pollutants. When selecting alumina for this purpose, ensure it meets relevant environmental standards and has been tested for specific contaminants. Discuss your requirements with suppliers to identify the most suitable grade based on your operational conditions.
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for alumina products?
Minimum order quantities for alumina can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Typically, MOQs range from a few tons to several hundred tons, depending on the supplier's capacity and the specific alumina type. When negotiating, consider your production needs and potential future orders to establish a mutually beneficial agreement. Engaging with suppliers who are flexible with MOQs may help you test their products without committing to large quantities upfront.
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing alumina internationally?
Payment terms for international alumina transactions often include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Terms can vary based on the supplier's policies and your negotiation skills. It's advisable to establish clear payment timelines and methods upfront to avoid any misunderstandings. Research the common practices in the supplier's country, as this can influence their willingness to offer favorable terms. Always ensure that payment terms align with your cash flow requirements.
How can I ensure compliance with international trade regulations when importing alumina?
To ensure compliance with international trade regulations, familiarize yourself with the import requirements in your country and the supplier's country. Check for necessary certifications and documentation, such as origin certificates and safety data sheets. Engage with logistics partners who specialize in hazardous materials if applicable. Staying updated on changes in tariffs and trade agreements can also help mitigate risks and ensure smooth customs clearance for your alumina shipments.
What customization options are available for alumina products?
Many suppliers offer customization options for alumina, including particle size, purity levels, and specific formulations tailored to your industry needs. Engage in discussions with potential suppliers about your exact requirements, as this can enhance product performance in your applications. Customized alumina can improve efficiency and reduce costs in processes like catalysis or water treatment. Ensure that any customizations do not compromise the quality and reliability of the final product.
How do I assess the logistics and shipping options for sourcing alumina?
Assessing logistics involves understanding the supplier's shipping capabilities, lead times, and freight options. Discuss with your supplier about their preferred shipping methods, whether by sea, air, or land, and inquire about their partnerships with logistics providers. Evaluate the total shipping costs, including insurance and customs duties, to determine the best option. It's crucial to plan for potential delays and to have contingency measures in place, especially for international shipments.
What quality assurance processes should I expect from alumina suppliers?
Quality assurance processes can include regular testing of alumina batches for chemical composition, particle size distribution, and other critical parameters. Reputable suppliers should provide certificates of analysis (CoA) for each shipment, detailing the results of these tests. Ask about their adherence to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, inquire about their procedures for handling non-conforming products to ensure that you receive consistent quality in your orders.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of alumina production, strategic sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains. By leveraging local resources and establishing strong relationships with suppliers, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can enhance their competitiveness and ensure a steady flow of high-quality alumina. Understanding the complex chemistry and various applications of alumina, such as in water treatment and catalysis, allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific industrial needs.
As global demand for alumina continues to rise, staying proactive is critical. Buyers should invest in market research and establish flexible procurement strategies that can adapt to changing industry dynamics. By fostering partnerships and collaborations, companies can navigate potential disruptions and seize new opportunities in the alumina market.
In conclusion, the future of alumina production is bright for those who strategically source and innovate. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to take decisive action, ensuring they are well-positioned to thrive in this competitive landscape.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina