Alumina stands as a cornerstone material in diverse industrial applications, ranging from advanced ceramics and refractories to electronics and automotive components. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding alumina’s multifaceted nature is essential to secure quality, cost-efficiency, and supply chain resilience.
This comprehensive guide delivers expert insights into the global alumina landscape, empowering procurement professionals to make well-informed sourcing decisions. It meticulously covers the various types of alumina, including their chemical and physical properties, alongside the raw materials and manufacturing processes that define product quality. Rigorous quality control standards and certifications are examined to help buyers evaluate supplier reliability and compliance.
Additionally, the guide offers an in-depth look at the market dynamics, highlighting key global suppliers, regional price trends, and logistical considerations critical for seamless international transactions. Practical cost analysis and negotiation strategies are included to optimize procurement budgets without compromising on material performance.
To further assist buyers, a detailed FAQ section addresses common concerns about alumina specifications, shipment, and regulatory compliance. Whether you are sourcing for industrial production in Vietnam, managing supply chains in the UK, or expanding operations in emerging markets, this guide equips you with actionable knowledge to navigate the complexities of the alumina supply chain confidently and strategically.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcined Alumina | High purity, crystalline form, produced by high-temperature treatment | Abrasives, refractories, ceramics, electronics | + High hardness and purity – Higher cost due to processing |
| Activated Alumina | Porous structure, high surface area, adsorption properties | Water purification, desiccants, catalyst support | + Excellent moisture adsorption – Limited mechanical strength |
| Hydrated Alumina | Contains water molecules, lower temperature processed | Flame retardants, fillers in plastics and rubber | + Cost-effective, versatile – Lower purity and thermal stability |
| Tabular Alumina | Dense, sintered alumina with low porosity | Refractory linings, kiln furniture, high-wear environments | + High density and durability – More expensive, heavier |
| Alpha Alumina | Thermodynamically stable phase, high hardness | Precision ceramics, cutting tools, electronic substrates | + Superior mechanical properties – Specialized processing required |
Calcined Alumina is produced by heating alumina to high temperatures, resulting in a crystalline, high-purity form. Its hardness and thermal stability make it ideal for abrasive products, advanced ceramics, and refractory materials. Buyers should consider its higher cost balanced against performance benefits, especially in industries requiring durability and resistance to wear.
Activated Alumina features a porous structure with a large surface area, making it effective for adsorption applications such as water purification and as a desiccant. It is widely used as a catalyst support in chemical industries. While cost-effective for moisture control, buyers must note its lower mechanical strength, limiting its use in structural applications.
Hydrated Alumina retains water molecules and is processed at lower temperatures, making it suitable as a flame retardant and filler in plastics and rubber. It offers a cost-efficient solution for manufacturers but has lower purity and thermal stability compared to calcined variants, which buyers should consider for high-temperature or high-purity needs.
Tabular Alumina is a dense, sintered form with low porosity, providing excellent mechanical strength and resistance to high temperatures. It is predominantly used in refractory linings and kiln furniture for heavy industrial applications. Its durability justifies a premium price, making it suitable for buyers prioritizing long service life under extreme conditions.
Alpha Alumina represents the thermodynamically stable phase of alumina, known for superior hardness and chemical stability. It is essential in precision ceramics, cutting tools, and electronic substrates. Buyers should be aware that its specialized processing increases cost but delivers unmatched performance for high-tech manufacturing sectors.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Alumina | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramics & Refractories | High-purity alumina for advanced ceramic components | Enhances wear resistance, thermal stability, and durability | Purity level, particle size distribution, consistent quality, and supplier reliability |
| Aluminum Production | Alumina as feedstock for aluminum smelting | Critical raw material enabling efficient aluminum extraction | Compliance with industry standards, consistent chemical composition, and supply chain stability |
| Electronics & Electrical | Alumina substrates and insulators | Provides excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity | High purity, low defect rates, and availability of customized formulations |
| Chemical Industry | Catalyst carrier and adsorbent material | Improves catalyst efficiency and longevity in chemical processes | Surface area, porosity, and chemical inertness tailored to process needs |
| Abrasives & Polishing | Alumina-based abrasives and polishing powders | Delivers superior hardness and cutting performance | Particle hardness, size uniformity, and contamination control |
Alumina plays a pivotal role in the ceramics and refractories industry, where high-purity alumina is used to manufacture advanced ceramic components. These components are essential for industries requiring materials that withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical wear, such as in furnace linings and cutting tools. Buyers, especially from regions with emerging manufacturing bases like Africa and South America, must prioritize suppliers who guarantee consistent purity and particle size to ensure product reliability and performance.
In the aluminum production sector, alumina is the indispensable feedstock for aluminum smelting via the Hall-Héroult process. For international buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe, sourcing alumina with a consistent chemical composition and from suppliers with robust logistics is critical to maintaining uninterrupted production flows and cost efficiency. Ensuring compliance with industry standards reduces operational risks and optimizes smelting yields.
The electronics and electrical industry extensively uses alumina as substrates and insulators due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and thermal conductivity. This application demands ultra-high purity and minimal defects to prevent device failure, which is particularly important for buyers in technology hubs such as Vietnam and the UK. Custom formulations tailored to specific electronic components can offer competitive advantages, making supplier flexibility a key consideration.
Within the chemical industry, alumina serves as a catalyst carrier and adsorbent, enhancing catalyst activity and lifespan in processes like petrochemical refining and environmental catalysis. Buyers need to assess alumina’s surface area, porosity, and chemical inertness to align with their process requirements. Regions with growing chemical manufacturing sectors, including parts of Africa and South America, should focus on suppliers that provide technical support and product customization.
Finally, in abrasives and polishing applications, alumina-based powders deliver superior hardness and cutting efficiency for metal finishing, glass polishing, and precision engineering. Uniform particle size and contamination-free supply are vital for maintaining quality standards. International buyers must evaluate supplier capabilities in quality control and consistent production to meet demanding industrial specifications, particularly in highly regulated markets across Europe and the Middle East.
Related Video: How to Produce Alumina Ceramic Parts
High-purity alumina is prized for its exceptional hardness, high melting point (~2050°C), and excellent chemical inertness. It offers superior resistance to wear, corrosion, and thermal shock, making it ideal for advanced ceramics, refractory linings, and electronic substrates.
Pros:
- Outstanding mechanical strength and abrasion resistance
- Excellent electrical insulation properties
- High chemical stability in acidic and basic environments
Cons:
- Higher production cost due to stringent purification and processing
- Manufacturing complexity requires advanced sintering techniques
- Limited flexibility in shaping compared to lower purity grades
Application Impact:
Ideal for high-temperature industrial processes, chemical reactors, and electronic components where contamination must be minimized. Its inertness suits aggressive chemical media common in oil & gas and chemical manufacturing sectors.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East often require compliance with ASTM C799 and DIN EN standards for purity and mechanical properties. African and South American buyers should verify supplier certifications due to variable regional quality controls. Vietnam and UK markets emphasize traceability and environmental compliance, favoring suppliers with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certifications.
Tabular alumina is produced by fusing alumina at very high temperatures, resulting in a dense, coarse-grained structure. It is widely used as a refractory aggregate due to its excellent thermal stability and resistance to slag corrosion.
Pros:
- Superior thermal shock resistance and structural integrity at high temperatures
- High bulk density improves refractory lining durability
- Good resistance to molten metal and slag penetration
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to calcined alumina due to energy-intensive production
- Limited use outside refractory applications due to coarse grain size
- Requires careful handling to avoid dust generation
Application Impact:
Primarily used in steelmaking, cement kilns, and glass furnaces where extreme temperatures and corrosive slags are present. Its robustness extends service life, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
International B2B Considerations:
Compliance with ASTM C704 and ISO 10012 is critical for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. African and South American buyers should consider logistical factors, including transportation costs and import duties, as tabular alumina is bulky. UK and Vietnam markets often request detailed technical data sheets and batch traceability for quality assurance.
Calcined alumina is produced by heating aluminum hydroxide to remove water content, resulting in a fine, white powder with moderate purity (typically 90-99%). It is used extensively in abrasives, ceramics, and as a filler in polymers.
Pros:
- Cost-effective and widely available
- Versatile particle size distribution for various applications
- Good hardness and chemical resistance for abrasive use
Cons:
- Lower purity than high-purity alumina limits use in high-tech applications
- Less thermal stability compared to tabular alumina
- Susceptible to moisture absorption if not properly stored
Application Impact:
Suitable for manufacturing grinding wheels, polishing compounds, and ceramic bodies. Its versatility makes it a preferred choice for industries with moderate performance demands and tighter budgets.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers from Africa and South America value calcined alumina for its affordability and availability. Compliance with ASTM B911 and JIS R1601 standards is often requested in Europe and Asia. Middle Eastern buyers focus on supplier reliability and consistent quality due to harsh operating environments.
Reactive alumina is a highly porous form of alumina with a large surface area, used mainly as a catalyst support and in adsorbents. It is characterized by its ability to chemically interact with other substances.
Pros:
- High surface area enhances catalytic activity
- Effective in adsorption and filtration processes
- Can be tailored for specific chemical reactivity
Cons:
- Lower mechanical strength compared to dense aluminas
- More sensitive to moisture and handling conditions
- Higher cost due to specialized processing
Application Impact:
Widely used in petrochemical refining, environmental catalysts, and water treatment. Its reactivity enables enhanced performance in chemical conversions and pollutant removal.
International B2B Considerations:
European and Middle Eastern buyers require compliance with ASTM D4526 and ISO 9001 for catalyst-grade alumina. African and South American industries may prioritize cost-effectiveness and availability, while Vietnam and UK markets demand detailed product data and certification for environmental impact.
| Material | Typical Use Case for alumina | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Alumina | Advanced ceramics, electronics, refractories | Exceptional purity and chemical inertness | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Tabular Alumina | Refractory linings in steel, cement, glass | Superior thermal shock and slag resistance | Bulky, costly production, limited versatility | High |
| Calcined Alumina | Abrasives, fillers, general ceramics | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower purity and thermal stability | Medium |
| Reactive Alumina | Catalyst supports, adsorbents, filtration | High surface area for chemical reactivity | Lower mechanical strength, sensitive handling | High |
This guide equips international B2B buyers with critical insights to select the optimal alumina material tailored to their industrial needs, ensuring compliance with regional standards and market expectations.
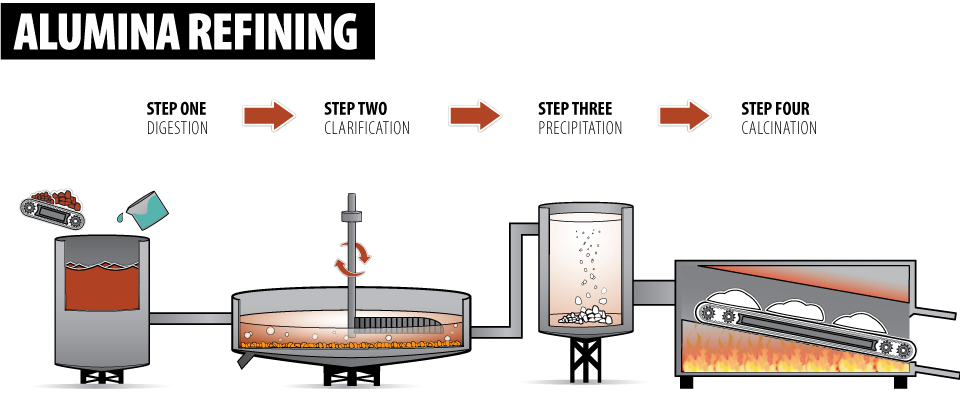
Manufacturing alumina—a critical raw material widely used in industries such as ceramics, refractories, and electronics—requires precise and controlled processes to ensure high purity and consistent quality. For international B2B buyers from regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these manufacturing stages and quality assurance protocols is essential for selecting reliable suppliers and mitigating supply risks.
The production of alumina typically follows a series of structured stages, each critical to achieving the desired chemical and physical properties.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Robust quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) frameworks are fundamental to delivering alumina that meets stringent industrial requirements. International B2B buyers should look for suppliers adhering to global and industry-specific standards.
For buyers especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where supply chain complexities and regulatory environments vary, due diligence on supplier QC is vital.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing stages, quality control protocols, and certification requirements, international B2B buyers can confidently select alumina suppliers that deliver consistent, high-quality products tailored to their industrial needs. Engaging proactively with suppliers on QC transparency and leveraging third-party verification are key strategies to mitigate risks and ensure long-term supply reliability.
Sourcing alumina for industrial use involves several critical cost components that international B2B buyers must scrutinize to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost elements include:
Several factors dynamically influence alumina pricing in the B2B market:
To optimize cost-efficiency and secure competitive pricing, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the following:
Due to volatile raw material markets, energy costs, and geopolitical factors affecting supply chains, alumina prices can fluctuate significantly. The insights provided here serve as indicative guidance; buyers should request up-to-date quotations and conduct thorough due diligence tailored to their specific sourcing context.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By carefully analyzing these cost components and pricing drivers, international B2B buyers can negotiate more effectively, optimize procurement strategies, and ensure a sustainable supply of high-quality alumina aligned with their operational and financial goals.
When sourcing alumina internationally, understanding its critical technical properties is essential for ensuring quality, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness in your supply chain. Here are the primary specifications to consider:
Material Grade (Purity Level)
Alumina is classified by its purity, typically expressed as a percentage of Al₂O₃ content. High-purity alumina (≥99.5%) is crucial for applications in ceramics, refractories, and electronics, ensuring superior performance and durability. Lower grades may be suitable for less demanding industrial uses but can impact product consistency.
Particle Size and Distribution
The granulometry affects processing behavior and final product quality. Fine powders offer better sintering and surface finish in ceramics, while coarser particles may be preferred for abrasives or refractory bricks. Clear specification of particle size range and uniformity helps avoid processing issues.
Moisture Content
Moisture can influence storage stability and handling characteristics. Low moisture alumina (<0.5%) is preferred to prevent clumping and maintain flowability during transport and processing. High moisture levels might increase shipping weight and risk product degradation.
Bulk Density
Expressed in g/cm³, bulk density impacts packing, transportation costs, and dosing in manufacturing. Consistent bulk density assures predictable volume-to-weight ratios, important for logistics and inventory management.
Chemical Composition and Impurities
Trace elements like sodium, silica, and iron affect alumina’s chemical reactivity and physical properties. For example, minimal iron content is critical in electronics-grade alumina to avoid conductivity issues. Always request detailed impurity profiles from suppliers.
Tolerance and Consistency
Tight dimensional and compositional tolerances ensure interchangeability and reduce waste. Variations can lead to manufacturing defects or incompatibility with OEM specifications.
Navigating international alumina procurement requires familiarity with standard trade and industry jargon. Understanding these terms will help you communicate effectively and negotiate better deals:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment using alumina as a raw material. Knowing whether your alumina supplier can meet OEM specifications is vital for maintaining product standards and gaining certifications.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount of alumina a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. MOQs affect inventory management and budgeting—buyers should balance order size with storage capacity and demand forecasts.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers asking for pricing, lead times, and terms. A well-prepared RFQ detailing required alumina grades, quantities, and delivery schedules enables precise and comparable supplier responses.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs between buyers and sellers. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Selecting the right Incoterm affects total landed cost and risk allocation.
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
A document provided by the supplier that details the alumina batch’s technical properties and compliance with agreed specifications. Always request a CoA to verify quality before acceptance.
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the product. For alumina, lead times can vary due to production schedules or shipping logistics. Planning ahead reduces risks of supply disruption.
By mastering these technical and trade fundamentals, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can optimize procurement strategies, ensuring alumina purchases that align with technical needs and commercial objectives.
The alumina sector remains a critical backbone for the global aluminum industry, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure growth, and expanding automotive and aerospace sectors. For international B2B buyers—particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the evolving market dynamics is key to securing competitive advantage.
Global Drivers:
- Infrastructure and Construction Growth: Emerging economies in Africa and South America are investing heavily in urban development and energy projects, boosting demand for alumina as a raw material.
- Automotive Electrification: The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) in Europe and the Middle East increases demand for lightweight aluminum components, thus stimulating alumina consumption.
- Technological Advances: Innovations in refining and smelting processes, such as automation and AI-driven quality control, are enhancing production efficiency and product consistency, enabling buyers to source higher-quality alumina with predictable specifications.
Sourcing Trends:
- Regional Diversification: Buyers are increasingly exploring sourcing opportunities beyond traditional suppliers in Australia and China, looking towards emerging producers in Africa (e.g., Guinea) and South America (e.g., Brazil) to mitigate geopolitical risks and supply chain disruptions.
- Digital Procurement Platforms: The adoption of digital marketplaces and blockchain for traceability is gaining momentum, providing transparency and reducing transaction friction in international alumina trade.
- Flexible Contracting Models: Long-term contracts with embedded price adjustment clauses tied to market indices are becoming common, helping buyers manage price volatility in alumina markets.
Market Dynamics:
- Supply Constraints: Environmental regulations and operational challenges in major producing regions occasionally lead to alumina supply tightness, driving price fluctuations that buyers must anticipate.
- Trade Policies and Tariffs: Buyers should remain vigilant about evolving trade agreements, tariffs, and export restrictions, especially between major producers and consumers, as these can impact cost structures and delivery timelines.
- Quality Differentiation: Increasingly, buyers demand tailored alumina grades to meet specific industrial applications, pushing suppliers to innovate in refining processes and product customization.
Sustainability is no longer optional in the alumina sector; it is a strategic imperative for B2B buyers who aim to meet regulatory requirements and corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals. Alumina production is energy-intensive and traditionally associated with significant environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and red mud waste generation.
Environmental Impact Mitigation:
- Buyers should prioritize suppliers adopting advanced waste management techniques, such as red mud recycling and dry stacking, which substantially reduce environmental footprint.
- Energy consumption is a major factor; sourcing alumina produced using renewable energy or from facilities with carbon capture initiatives aligns with emerging global decarbonization targets.
Ethical Supply Chains:
- Transparency in the alumina supply chain is critical. Buyers should seek suppliers who provide full traceability from bauxite mining through refining to final alumina product, ensuring compliance with labor standards and human rights.
- Certification schemes such as the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) offer credible assurance of responsible sourcing, encompassing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
Green Certifications & Materials:
- Alumina products certified under recognized sustainability standards enable buyers to differentiate their offerings in end markets increasingly focused on eco-friendly materials.
- Incorporating sustainably sourced alumina can enhance brand reputation and unlock access to markets with stringent environmental procurement policies, especially in Europe and the Middle East.
The alumina industry has evolved significantly since the late 19th century, originating from the Bayer process developed in 1888, which remains the primary method for refining bauxite into alumina. Over the decades, the sector has transitioned from small-scale, localized production to a highly globalized and technologically advanced industry.
Historically concentrated in Australia, the Caribbean, and select parts of Asia, alumina production has expanded into Africa and South America, reflecting shifting resource availability and market demands. This geographic diversification has introduced new sourcing opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers, including infrastructure development and regulatory environments.
Technological advancements have continuously improved refining efficiency and product quality, while recent decades have seen an increasing focus on environmental sustainability and supply chain ethics. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical trajectory is essential to navigating current market complexities and anticipating future developments.
How can I effectively vet alumina suppliers internationally to ensure reliability and quality?
To vet alumina suppliers, start by verifying their business licenses, export certifications, and industry memberships. Request product samples and check third-party lab test reports for quality assurance. Evaluate their production capacity and track record with references from previous international clients, particularly in your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe). Use platforms with verified supplier credentials and conduct virtual or onsite audits if possible. Clear communication and responsiveness are also key indicators of a reliable supplier.
Is it possible to customize alumina specifications to meet specific industrial requirements?
Yes, many alumina producers offer customization in terms of particle size, purity levels, and moisture content to suit different industrial applications such as refractories, ceramics, or aluminum production. When negotiating, clearly specify your technical requirements and request a detailed product datasheet. Confirm the supplier’s capability to meet these custom specs consistently and discuss how customization impacts pricing and lead times before finalizing the contract.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for international alumina orders?
MOQs vary depending on the supplier and alumina grade but generally range from 10 to 50 metric tons per shipment for bulk buyers. Lead times typically range from 3 to 8 weeks, factoring in production, quality checks, and shipping. For smaller or customized orders, lead times may extend. It’s essential to negotiate MOQs and lead times upfront and consider buffer stock due to potential shipping delays, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East where logistics can be more complex.
Which payment terms are standard in international alumina trade, and how can buyers mitigate financial risks?
Common payment terms include Letters of Credit (L/C), Telegraphic Transfers (T/T) with partial upfront payment, or open account for trusted partners. Letters of Credit offer security as payment is made only after document compliance. Buyers should negotiate clear payment milestones tied to shipment or inspection stages. Using escrow services or trade finance solutions can also reduce risk. Always verify supplier banking details to prevent fraud, especially in cross-continental transactions.
What quality assurance certifications should I look for when sourcing alumina internationally?
Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental compliance, and industry-specific certifications such as SGS or Intertek lab reports validating alumina purity and composition. For buyers in regulated industries or regions, check compliance with REACH (Europe) or equivalent chemical safety standards. Insist on batch-specific certificates of analysis (CoA) for every shipment to ensure consistent product quality.
How should I plan logistics and shipping for alumina imports to regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
Consider port infrastructure, customs regulations, and inland transport options in your destination country. Choose suppliers with experience exporting to your region to benefit from established logistics networks. Bulk alumina is typically shipped in containers or bulk carriers; ensure proper packaging to prevent moisture contamination. Work with freight forwarders familiar with alumina handling and be proactive in managing customs documentation to avoid delays or demurrage costs.
What steps can I take if there is a dispute or quality issue with an alumina shipment?
First, document the issue thoroughly with photos, third-party inspection reports, and batch testing results. Communicate promptly with the supplier to seek resolution, such as replacement shipment or refund. If unresolved, escalate via mediation or arbitration clauses specified in your contract. Maintaining clear contractual terms on quality standards, inspection rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms before purchase helps protect your interests in international trade.
Are there regional considerations for alumina sourcing that buyers should be aware of?
Yes, regional factors such as import tariffs, trade agreements, and currency fluctuations can impact cost and delivery. For example, African buyers may benefit from AGOA preferences, while European buyers must comply with stringent environmental and chemical regulations. South American buyers should consider local logistics challenges. Understanding these nuances and working with suppliers who have regional expertise will optimize your sourcing strategy and reduce risks.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of alumina remains a cornerstone for businesses aiming to secure competitive advantage in the global metals and materials market. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of supply chain dynamics, price volatility, and quality assurance is critical. Leveraging diversified supplier networks and fostering long-term partnerships can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical shifts and raw material scarcity.
Key takeaways include the importance of:
Looking ahead, alumina buyers should prioritize innovation in sourcing strategies by embracing digital procurement tools and sustainability benchmarks. Proactive engagement with emerging markets and value-added services from suppliers will enhance resilience and growth potential. International buyers are encouraged to act decisively now—to refine their sourcing frameworks and capitalize on evolving market opportunities while reinforcing supply chain robustness for the future.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina