Black water filtration stands at the forefront of sustainable water management, addressing critical challenges faced by industries worldwide. For B2B buyers operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, securing reliable, efficient black water filtration solutions is not just a regulatory necessity but a strategic imperative. Effective filtration systems mitigate environmental impact, comply with stringent local and international standards, and optimize operational costs, thereby enhancing corporate responsibility and profitability.
This comprehensive guide delves into every essential aspect of black water filtration to empower international buyers in making well-informed sourcing decisions. It covers a broad spectrum of filtration technologies and materials, highlighting the latest innovations tailored to varied industrial applications and regional requirements. Additionally, the guide provides critical insights into manufacturing standards and quality control processes that ensure product reliability and longevity.
Understanding the supplier landscape, cost factors, and logistical considerations is vital for buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies. This resource also explores market dynamics, helping you navigate supplier negotiations and supply chain complexities effectively. To support practical decision-making, the guide includes a detailed FAQ section addressing common concerns encountered by buyers across Brazil, Spain, and other key markets.
By synthesizing technical knowledge with actionable sourcing strategies, this guide equips B2B buyers with the tools needed to confidently select black water filtration solutions that align with their operational goals and regional compliance mandates. Embrace this resource as your strategic partner in navigating the global market for black water filtration with clarity and confidence.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) | Combines biological treatment with membrane filtration | Municipal wastewater, industrial effluents | + High effluent quality, compact footprint – Higher capital cost, membrane fouling risks |
| Anaerobic Digestion Systems | Biological process breaking down organic matter without oxygen | Food processing, agriculture, chemical industries | + Energy recovery via biogas, low sludge production – Requires controlled conditions, slower process |
| Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) | Uses suspended biofilm carriers for enhanced microbial growth | Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment | + Flexible operation, robust to load variations – Moderate maintenance, requires aeration |
| Sand and Media Filtration | Physical filtration through granular media | Pre-treatment stage, small-scale industrial use | + Low cost, simple technology – Limited to particulate removal, not effective for dissolved contaminants |
| Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP) | Uses chemical oxidants and UV to degrade organic pollutants | Textile, pharmaceutical, petrochemical industries | + Effective for recalcitrant pollutants, improves biodegradability – High energy and chemical consumption |
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
MBR technology integrates biological degradation of organic waste with membrane filtration, producing high-quality effluent suitable for reuse. Its compact design is advantageous where space is limited, common in urban infrastructure projects across Europe and Middle East. Buyers should consider the higher upfront investment and ongoing membrane maintenance costs. Supplier reliability and membrane lifespan warranties are critical procurement factors to ensure operational continuity.
Anaerobic Digestion Systems
These systems treat black water by decomposing organic matter anaerobically, generating biogas as a valuable byproduct. Ideal for industries with high organic loads such as food processing and agriculture prevalent in South America and Africa. B2B buyers should evaluate system scalability, biogas integration capabilities, and local expertise in anaerobic process management to maximize ROI and sustainability benefits.
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
MBBR technology enhances microbial treatment by providing carriers for biofilm growth, improving resilience against fluctuating loads and toxic shocks. This makes it suitable for municipal and industrial wastewater plants in regions with variable influent quality, including emerging markets. Buyers must assess carrier media quality, aeration system efficiency, and modular design flexibility to optimize performance and lifecycle costs.
Sand and Media Filtration
A traditional, cost-effective method primarily used for removing suspended solids in black water pre-treatment stages. Its simplicity makes it attractive for smaller industrial operations or as a polishing step in multi-stage treatment systems in Africa and parts of South America. Buyers should consider limitations in removing dissolved contaminants and plan integration with advanced treatment to meet regulatory standards.
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP)
AOPs utilize strong oxidants combined with UV or catalysts to break down complex organic pollutants, enhancing biodegradability or achieving direct removal. This technology suits industries with stringent discharge requirements, such as pharmaceuticals and textiles, common in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers must weigh high operational costs against superior treatment efficacy and consider supplier expertise in customizing AOP systems to specific wastewater profiles.
Related Video: Purification of water | Macmillan Education India
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of black water filtration | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipal Wastewater | Treatment of sewage and urban black water to enable safe reuse | Compliance with environmental regulations, reducing discharge penalties, and enabling water reuse for irrigation or industrial processes | Robust filtration systems with high contaminant removal efficiency, scalability, and compliance with local discharge and reuse standards |
| Food & Beverage | Treatment of process black water from production and cleaning | Reducing water consumption costs, ensuring hygiene standards, and minimizing environmental impact | Systems capable of handling high organic loads, easy maintenance, and certifications for food-grade water reuse |
| Oil & Gas | Treating produced black water and wastewater from drilling sites | Protecting equipment, reducing environmental liabilities, and enabling water recycling onsite | Filtration solutions resistant to hydrocarbons and heavy metals, adaptable to harsh conditions, and compliant with international environmental standards |
| Hospitality & Tourism | Managing black water from hotels and resorts for onsite treatment | Lowering operational water costs, meeting sustainability goals, and complying with local wastewater regulations | Compact and efficient filtration units, low odor emissions, and ease of integration with existing infrastructure |
| Textile & Dyeing | Filtration of black water containing dyes and chemicals | Reducing toxic discharge, recovering water for reuse, and maintaining regulatory compliance | Systems with advanced chemical removal capabilities, durability against corrosive substances, and tailored to variable wastewater volumes |
Municipal Wastewater Treatment
Black water filtration in municipal wastewater treatment primarily addresses the challenge of safely processing sewage and urban waste streams. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in scalable filtration technologies that meet stringent environmental discharge regulations is critical. These systems help municipalities avoid costly fines and enable the reuse of treated water for irrigation or industrial applications, which is especially valuable in water-scarce regions like parts of the Middle East and Southern Europe.
Food & Beverage Industry Applications
In food and beverage manufacturing, black water filtration is essential for treating wastewater generated during production and cleaning operations. Buyers from regions like Brazil and Spain must prioritize filtration systems that manage high organic loads while ensuring hygiene and safety standards. Effective black water filtration reduces water consumption costs and environmental impact, supporting sustainability initiatives that are increasingly demanded by global consumers.
Oil & Gas Sector Usage
The oil and gas industry generates significant volumes of black water, often contaminated with hydrocarbons and heavy metals. Filtration solutions tailored for this sector protect valuable equipment from fouling and corrosion, reduce environmental liabilities, and enable onsite water recycling. B2B buyers in oil-producing regions of Africa and the Middle East should source robust filtration technologies that comply with international environmental standards and can withstand harsh operational conditions.
Hospitality & Tourism Industry
Hotels and resorts generate black water from guest facilities and kitchens, necessitating efficient onsite filtration to manage wastewater sustainably. For businesses in tourism-heavy regions such as Southern Europe and coastal South America, black water filtration systems provide operational cost savings and support compliance with local wastewater regulations. Compact, low-odor filtration units that integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure are preferred to maintain guest comfort and meet sustainability goals.
Textile & Dyeing Industry
Textile and dyeing operations produce black water rich in dyes and chemicals that pose environmental challenges. Filtration systems designed for this sector enable the removal of toxic substances, allowing water reuse and reducing discharge penalties. Buyers in textile hubs across Europe and South America should focus on durable filtration solutions capable of handling corrosive wastewater while adapting to fluctuating volumes, supporting regulatory compliance and sustainable production practices.
Related Video: Water Treatment Process: Direct and Conventional Filtration
When selecting materials for black water filtration systems, international B2B buyers must consider performance characteristics, environmental conditions, regulatory compliance, and cost-effectiveness. The following analysis covers four common materials used in black water filtration components: stainless steel, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP), and polypropylene (PP). Each material offers distinct advantages and challenges relevant to diverse markets including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, offers excellent corrosion resistance, high mechanical strength, and temperature tolerance up to 870°C. It withstands high pressures and aggressive chemical environments, making it suitable for demanding filtration applications.
Pros & Cons: Stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to biofouling and chemical attack, ensuring long service life. However, it has a higher upfront cost and requires skilled manufacturing processes such as welding and precision machining. Maintenance can be more complex compared to plastics.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for filtration systems handling harsh black water with abrasive solids or high chemical loads. It supports media like activated carbon and ceramic filters without degradation.
International Buyer Considerations: Buyers in regions such as Europe (Spain) and the Middle East should verify compliance with ASTM A240 or EN 10088 standards for stainless steel. Corrosion resistance is critical in coastal or saline environments common in Africa and South America (Brazil). Import tariffs and local fabrication capabilities influence cost and lead times.
Key Properties: HDPE is a thermoplastic with excellent chemical resistance, moderate temperature tolerance (up to 120°C), and good impact strength. It is lightweight and flexible, suitable for piping and filter housings.
Pros & Cons: HDPE is cost-effective and easy to fabricate, including welding and extrusion. It resists scaling and biological growth but has lower pressure ratings and temperature limits compared to metals. UV degradation can occur if not properly stabilized.
Impact on Application: HDPE is commonly used for black water filtration piping and containment tanks where chemical resistance and flexibility are priorities. It pairs well with media such as sand and polymeric membranes.
International Buyer Considerations: Compliance with ISO 4427 or DIN 8074/8075 standards is important for buyers in Europe and South America. HDPE’s low weight benefits logistics to remote African or Middle Eastern sites. Buyers must ensure UV stabilization additives if exposed to sunlight.
Key Properties: FRP combines a polymer matrix with glass fibers, offering high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance up to approximately 150°C. It is non-conductive and chemically inert.
Pros & Cons: FRP is highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and saltwater, making it suitable for aggressive black water environments. It is lighter than metals but more brittle and sensitive to impact damage. Manufacturing complexity and quality control are critical to avoid delamination.
Impact on Application: FRP is favored for filter vessels and piping in black water treatment plants requiring corrosion resistance and moderate mechanical strength. It supports a variety of media including ion exchange resins and biological filters.
International Buyer Considerations: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should look for compliance with ASTM D4097 or ISO 14692 standards. FRP’s lightweight nature reduces shipping costs to African and South American markets. However, local repair expertise may be limited, necessitating supplier training.
Key Properties: Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic with good chemical resistance, temperature tolerance up to 100°C, and excellent fatigue resistance. It is resistant to many acids, bases, and organic solvents.
Pros & Cons: PP is inexpensive, easy to mold, and suitable for complex shapes. It has lower mechanical strength and pressure ratings than HDPE or metals. PP can degrade under UV exposure unless stabilized.
Impact on Application: PP is widely used for filter cartridges, housings, and pre-treatment components in black water filtration. It is compatible with media such as granular activated carbon and polymer membranes.
International Buyer Considerations: Compliance with ASTM D4101 or EN ISO 1873 is relevant for buyers in Europe and South America. PP’s affordability and ease of sourcing make it attractive for cost-sensitive projects in Africa and the Middle East. Buyers should confirm UV resistance and chemical compatibility for specific black water compositions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for black water filtration | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Filter housings, piping for high-pressure/temperature systems | Superior corrosion and mechanical strength | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Piping and tanks for chemical-resistant, flexible systems | Cost-effective, lightweight, chemical resistant | Limited temperature and pressure rating | Low |
| Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) | Filter vessels and piping in corrosive environments | Excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight | Brittle, requires quality control | Medium |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Filter cartridges, housings, pre-treatment components | Low cost, easy fabrication | Lower mechanical strength, UV sensitivity | Low |
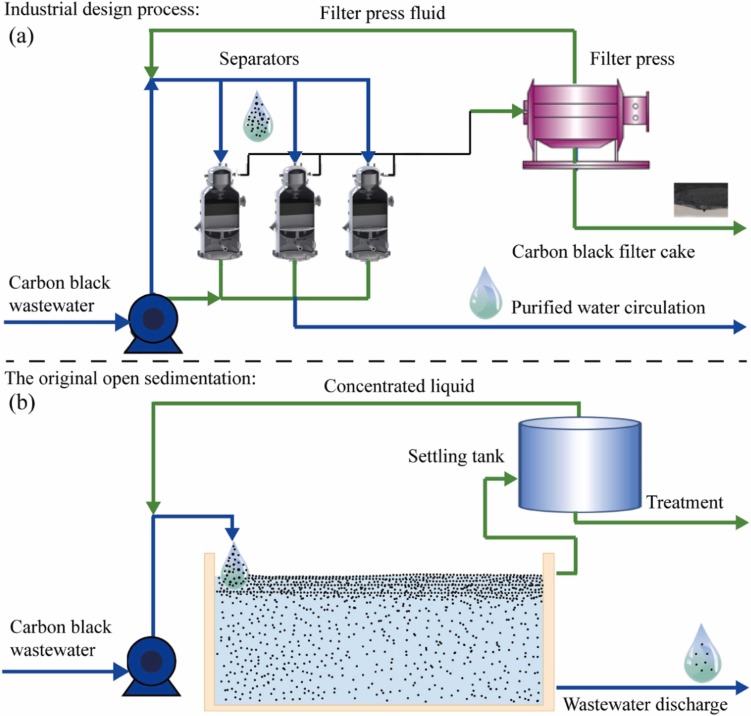
The production of black water filtration systems involves a series of meticulously controlled stages to ensure functionality, durability, and compliance with environmental standards. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evaluate potential suppliers and optimize procurement decisions.
Material selection and preparation form the foundation of effective black water filtration systems. Key materials typically include corrosion-resistant metals (e.g., stainless steel), high-grade plastics, activated carbon, advanced polymer membranes, and specialized filter media designed to handle organic waste and contaminants.
The shaping and fabrication phase transforms raw materials into components essential for black water filtration.
Assembly integrates the various components into complete filtration units.
Finishing enhances product durability and compliance.
Quality assurance (QA) is vital to ensure black water filtration systems meet international performance, safety, and environmental standards. For B2B buyers, verifying supplier QA processes reduces risks and ensures regulatory compliance across different markets.
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout manufacturing stages, typically including:
For international buyers, especially in emerging and regulated markets, supplier QC verification is crucial to mitigate risks related to product failure, regulatory non-compliance, and reputational damage.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
B2B buyers from diverse regions must navigate varying regulatory landscapes and certification requirements to ensure smooth importation and market acceptance.
Understanding these nuances helps buyers avoid costly delays, fines, or product recalls and supports sustainable supply chain partnerships.
By prioritizing these manufacturing and QA insights, international B2B buyers can secure reliable, high-performance black water filtration solutions that meet global standards and local market demands.
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of black water filtration systems is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis breaks down key cost components, pricing influencers, and actionable buyer insights to help secure competitive and sustainable sourcing outcomes.
Materials: The primary cost driver, including filtration media (e.g., activated carbon, membranes), housing materials (plastic, stainless steel), and ancillary parts. Material quality significantly impacts filtration performance and longevity, influencing overall system value.
Labor: Costs vary depending on the manufacturing location. Skilled labor for assembly and system integration can be higher in developed regions but may yield better quality control.
Manufacturing Overhead: Includes utilities, factory rent, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes and automation can reduce overhead costs.
Tooling and Equipment: Initial investments in molds, dies, and specialized machinery affect unit costs, especially for customized or complex designs.
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing, certifications (e.g., ISO, NSF), and compliance checks are essential to meet international standards and buyer expectations, adding to upfront costs but reducing long-term risks.
Logistics: Freight, customs duties, insurance, and last-mile delivery fees. Logistics costs fluctuate based on origin, destination, transport mode, and geopolitical factors.
Supplier Margin: Suppliers factor in profit margins that reflect their market positioning, exclusivity, and after-sales support services.
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger orders typically attract volume discounts, reducing the unit price. Buyers from emerging markets should negotiate MOQs aligned with their market demand to avoid excess inventory costs.
Product Specifications and Customization: Tailored filtration capacities, system sizes, and integration features increase costs. Standardized models tend to be more cost-effective but may not fulfill specific regulatory or operational needs.
Material Selection: Premium materials with enhanced durability or chemical resistance command higher prices but improve system lifespan and maintenance intervals.
Quality Certifications: Systems certified to international or regional standards (e.g., EU Drinking Water Directive compliance) often carry price premiums justified by enhanced reliability.
Supplier Reputation and Stability: Established suppliers with proven track records might charge higher prices but offer reduced supply chain risks and better service continuity.
Incoterms and Payment Terms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) impacts who bears shipping and customs costs, influencing the total landed cost. Favorable payment terms can improve cash flow and negotiating leverage.
Negotiate Beyond Price: Engage suppliers on quality guarantees, lead times, payment terms, and after-sales support. Comprehensive negotiations yield better total value rather than focusing solely on unit price.
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider operational costs such as maintenance, filter replacement frequency, energy consumption, and downtime risks. A lower upfront price may lead to higher lifecycle costs.
Leverage Local and Regional Insights: Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should account for local regulatory requirements, currency fluctuations, and regional logistics complexities when comparing quotes.
Seek Modular and Scalable Solutions: Flexible systems that allow phased upgrades or expansions can optimize initial investments and adapt to evolving water treatment demands.
Utilize Sourcing Partners and Consultants: Collaborating with global sourcing experts can uncover cost-saving opportunities in supplier selection, quality assurance, and logistics optimization.
Be Mindful of Pricing Nuances: Currency volatility, import tariffs, and customs clearance delays can unpredictably affect final costs. Incorporate contingency buffers in budgeting.
Prices for black water filtration systems vary widely based on design complexity, capacity, and supplier location. The figures discussed herein are indicative and should be validated through direct supplier engagement and detailed quotations tailored to specific buyer requirements.
By understanding these cost components and pricing factors, international buyers can make informed decisions that balance quality, cost-efficiency, and compliance, ensuring sustainable investments in black water filtration solutions suitable for their regional markets.
Understanding the essential technical specifications of black water filtration systems is crucial for international B2B buyers to ensure product suitability, compliance, and operational efficiency. Here are the key properties to focus on:
Material Grade and Composition
The filtration media and housing materials must resist corrosion and microbial degradation, typically using stainless steel (e.g., 304 or 316 grades) or high-grade polymers. For buyers in regions with harsh climates or chemical-laden wastewater, selecting the right material grade is vital to maximize lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Filtration Efficiency and Pore Size
Black water filters often specify micron ratings, indicating the smallest particle size the filter can remove. Typical pore sizes range from 1 to 50 microns, depending on application. Buyers should match pore size to the wastewater’s contaminant profile to optimize treatment and meet environmental discharge standards.
Flow Rate and Capacity
Measured in cubic meters per hour (m³/h), this indicates the volume of black water the system can process effectively. Proper sizing ensures operational efficiency and avoids system overload or underperformance. B2B buyers must align flow rate specifications with their facility’s wastewater volume to ensure cost-effective filtration.
Pressure Tolerance and Operating Range
Systems must withstand varying pressures, often between 1 to 10 bar, depending on industrial setup. Pressure tolerance affects installation options and operational safety. Buyers should verify that the filtration equipment matches their existing infrastructure and complies with local safety regulations.
Chemical Resistance
Black water can contain aggressive chemicals and biological contaminants. Filtration components must resist degradation by acids, alkalis, and solvents common in industrial wastewater. This property is essential for buyers in chemical processing or oil & gas sectors to avoid premature equipment failure.
Maintenance and Cleanability
Ease of cleaning or backflushing capability reduces downtime and operational costs. Systems designed for straightforward maintenance are preferred in markets where skilled labor or technical support is limited. Buyers should evaluate these features to ensure sustainable long-term operation.
Navigating international procurement for black water filtration requires familiarity with key trade terms that impact negotiations, logistics, and contracts:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce components or complete filtration units, which may be branded by other firms. Buyers seeking customization or private labeling often engage OEMs to tailor solutions to specific regional requirements or branding strategies.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in one order. Understanding MOQ is critical for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for buyers in emerging markets who may have limited upfront capital or storage capacity.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit detailed pricing and technical proposals from suppliers. Effective RFQs include clear technical specifications and compliance requirements, enabling suppliers to provide accurate and comparable offers.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyers and sellers. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Knowing Incoterms helps buyers control costs and risks during international shipping.
Lead Time
The total time from order placement to delivery. For black water filtration systems, lead time can vary based on customization, manufacturing complexity, and shipping distance. Buyers must factor lead time into project schedules to avoid operational delays.
Compliance Certifications
Certifications such as ISO, NSF, or local environmental standards verify that filtration products meet safety and performance benchmarks. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications to ensure regulatory compliance and reduce import hurdles.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers—from Africa to Europe and South America—can make informed decisions that optimize procurement, enhance operational reliability, and secure competitive advantages in black water filtration projects.
The black water filtration sector is experiencing accelerated growth globally, driven by increasing urbanization, stringent wastewater discharge regulations, and heightened awareness of water scarcity challenges. For international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional market dynamics is critical. Emerging economies like Brazil and countries in Africa face urgent needs to upgrade sanitation infrastructure, creating robust demand for advanced black water filtration technologies. Meanwhile, European markets, exemplified by Spain, emphasize compliance with strict environmental standards and integration of smart water management solutions.
Key trends shaping the sector include the adoption of membrane bioreactors (MBRs) and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) that enhance treatment efficiency and reduce footprint. Digitalization, including IoT-enabled filtration systems, allows real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing operational costs and downtime. Sourcing trends reveal a shift towards partnerships with suppliers offering modular, scalable solutions adaptable to diverse wastewater volumes and compositions. Additionally, buyers are prioritizing suppliers with proven expertise in customized system design to meet local regulatory and environmental conditions.
From a procurement perspective, global supply chain challenges underscore the importance of supplier diversification and risk mitigation strategies. Buyers benefit from sourcing platforms that facilitate factory audits, quality assurance, and logistics optimization. Moreover, the rise of regional manufacturing hubs, particularly in Asia and Europe, offers opportunities for cost-effective sourcing with shorter lead times. For B2B buyers in emerging markets, leveraging sourcing agents experienced in international compliance and certification expedites market entry and ensures product reliability.
Sustainability is now a cornerstone in black water filtration procurement, with environmental impact reduction a top priority. Black water, containing high organic loads and pathogens, requires treatment solutions that minimize energy consumption and chemical usage. Buyers increasingly demand filtration technologies that support circular economy principles, such as resource recovery from wastewater—nutrients, biogas, and water reuse—thereby turning waste into valuable inputs.
Ethical sourcing in this sector extends beyond environmental stewardship to include social responsibility. Ensuring suppliers adhere to fair labor practices, transparent supply chains, and local community engagement aligns with global ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), ISO 45001 (Occupational Health & Safety), and Cradle to Cradle provide buyers with assurance of supplier commitment to sustainability and ethical operations.
Material selection is pivotal: filtration media and membranes made from recyclable or biodegradable components reduce landfill burdens. Buyers should prioritize vendors offering eco-friendly chemicals and technologies that reduce sludge generation. Additionally, incorporating lifecycle assessments (LCAs) into sourcing decisions helps quantify environmental benefits and supports compliance with increasingly strict regulations across Africa, the Middle East, and Europe.
Historically, black water treatment relied on conventional biological and chemical processes with limited efficiency and significant environmental footprint. Over the past two decades, technological advancements have transformed the sector. The introduction of membrane technologies and integrated treatment systems has enabled higher-quality effluent standards and resource recovery.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution highlights the importance of investing in next-generation filtration solutions that offer operational savings and regulatory compliance. The trend towards modular, compact systems supports rapid deployment in emerging markets, while innovations in automation and digital controls enhance scalability and remote management. This evolution underscores the shift from mere waste disposal to sustainable water resource management—an imperative for global industrial and municipal buyers alike.
How can I effectively vet suppliers of black water filtration systems for international B2B procurement?
To ensure reliability, start by verifying the supplier’s certifications relevant to water filtration, such as ISO 9001 or NSF. Request product samples and technical datasheets to assess quality and compliance with your region’s standards. Conduct factory audits or virtual tours when possible, and check references from other international clients, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. Partnering with sourcing agents or firms specializing in global supply chains can further mitigate risks by providing on-the-ground supplier validation and quality assurance.
Is it possible to customize black water filtration products to meet specific industrial or regional requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options including filter media types, capacity, and system integration to suit local water characteristics and industrial needs. When sourcing, clearly communicate your technical specifications and compliance requirements upfront. Customization can also cover branding, packaging, and control systems. However, expect longer lead times and potentially higher minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom orders. Establishing a strong dialogue with suppliers helps align expectations and ensures the product meets your operational and regulatory needs.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for black water filtration systems in international trade?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier and product complexity but generally range from 10 to 100 units for standard filtration systems. Custom or large-scale industrial systems may have higher MOQs. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, factoring in manufacturing, quality checks, and shipping. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should also consider customs clearance and regional logistics delays. Negotiate flexible MOQs and staggered deliveries where possible to optimize inventory and cash flow.
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for black water filtration equipment?
Standard terms include a 30% advance payment with the balance due upon shipment or receipt of goods. Letters of credit (LC) and escrow services are also widely used to protect both parties. For first-time or high-value orders, suppliers may require full or partial prepayment. Buyers should negotiate payment terms that balance risk and cash flow, such as milestone payments tied to production stages. Utilizing trusted trade finance options can mitigate risks while facilitating smoother transactions across regions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Which quality assurance and certification standards should I prioritize when purchasing black water filtration systems internationally?
Prioritize internationally recognized certifications such as NSF/ANSI standards for water filtration, ISO 9001 for quality management, and CE marking for compliance with European regulations. Certifications related to environmental management (ISO 14001) and product safety (UL, CSA) may also be relevant depending on your market. Request suppliers’ test reports and third-party inspection results to verify compliance. These standards ensure product reliability, regulatory acceptance, and customer confidence in your target regions.
What logistics considerations are critical when importing black water filtration systems into Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Understand the import regulations, customs duties, and documentation requirements specific to each region. Choose freight options balancing cost and delivery speed, such as sea freight for bulk orders or air freight for urgent shipments. Ensure proper packaging to prevent damage during transit and compliance with local environmental regulations. Collaborate with experienced freight forwarders familiar with regional ports and inland transport. Early planning of warehousing and distribution can reduce delays and optimize supply chain efficiency.
How should I handle disputes or quality issues with international black water filtration suppliers?
Establish clear contractual terms covering product specifications, inspection rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms before placing orders. Use third-party quality inspection services to detect defects before shipment. In case of disputes, document all communications and evidence such as photos and test reports. Engage suppliers in good faith negotiations to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, leverage arbitration clauses or legal action through international trade bodies, but prioritize building long-term supplier relationships to minimize conflicts.
Can I source eco-friendly or sustainable black water filtration systems that meet international standards?
Absolutely. Many suppliers now offer sustainable filtration solutions using recyclable materials, energy-efficient designs, and low chemical usage. Look for certifications like NSF P473 for PFAS reduction or ecolabels recognized in your target markets. Sustainable products often reduce operational costs and enhance corporate social responsibility credentials. When sourcing, inquire about the supplier’s environmental policies and lifecycle assessments. This approach aligns with increasing global demand for green technologies, especially in environmentally conscious regions like Europe and parts of South America.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing in black water filtration is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize cost-efficiency, quality, and sustainability. Key takeaways include the importance of thorough supplier vetting, leveraging advanced filtration technologies, and aligning procurement strategies with regional regulatory frameworks and environmental standards. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe benefit from sourcing partners who demonstrate strong compliance, innovation, and logistical agility.
Emphasizing strategic sourcing enables businesses to:
Looking ahead, the black water filtration market is poised for growth driven by increasing environmental regulations and rising demand for water reuse solutions. International buyers should proactively engage with global sourcing experts to identify innovative suppliers, optimize total cost of ownership, and stay ahead of emerging trends.
Actionable next steps: Initiate comprehensive supplier assessments, integrate technological advancements into procurement criteria, and pursue partnerships that support circular water management goals. By doing so, businesses in Brazil, Spain, and beyond can secure resilient supply chains and contribute meaningfully to sustainable water management worldwide.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina