In an increasingly competitive landscape, sourcing boron carbide density can present a formidable challenge for international B2B buyers. This specialized material, known for its exceptional hardness and thermal stability, is pivotal in various industries, including defense, aerospace, and nuclear applications. Understanding the nuances of boron carbide density is essential for buyers aiming to optimize their procurement strategies and ensure product performance.
This comprehensive guide delves into critical aspects of boron carbide density, offering insights on its types, applications, and the importance of supplier vetting. We will also explore cost considerations, helping you identify budget-friendly options without compromising quality. With a focus on empowering B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including regions like Vietnam and the UAE—this guide serves as an invaluable resource.
By providing actionable insights and expert recommendations, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary for informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance production efficiency, ensure compliance with industry standards, or leverage the latest advancements in boron carbide technology, this guide is designed to support your strategic sourcing needs. Navigate the global market confidently and make choices that drive your business forward.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Density Boron Carbide | Density typically over 2.52 g/cm³; superior hardness | Armor plating, cutting tools, nuclear applications | Pros: High durability; Cons: Higher cost |
| Low-Density Boron Carbide | Density around 2.4 g/cm³; lighter and more versatile | Aerospace, automotive components | Pros: Lightweight; Cons: Lower hardness |
| Boron Carbide Composites | Mixture with polymers or metals; tailored properties | Aerospace components, industrial machinery parts | Pros: Customizable properties; Cons: Complex manufacturing |
| Nanocrystalline Boron Carbide | Nano-sized particles; enhanced mechanical properties | Electronics, advanced ceramics | Pros: Superior strength-to-weight ratio; Cons: Higher production costs |
| Thermally Conductive Boron Carbide | Enhanced thermal conductivity; unique structure | Heat sinks, thermal management systems | Pros: Efficient heat dissipation; Cons: Limited applications |
High-density boron carbide features a density exceeding 2.52 g/cm³, making it exceptionally hard and wear-resistant. This type is primarily used in applications requiring superior durability, such as armor plating and cutting tools. B2B buyers should consider the higher cost associated with this material due to its advanced properties. It is ideal for industries that prioritize performance and longevity over initial investment.
Low-density boron carbide has a density of approximately 2.4 g/cm³, making it significantly lighter than its high-density counterpart. This variation is particularly suitable for aerospace and automotive applications where weight reduction is crucial. Buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced weight against the trade-off in hardness. It is an excellent choice for companies looking to enhance fuel efficiency and performance without compromising on essential material properties.
Boron carbide composites combine boron carbide with polymers or metals to create materials tailored for specific applications. These composites are commonly used in aerospace components and industrial machinery parts, offering enhanced properties such as flexibility and strength. B2B buyers should consider the complexity of manufacturing these composites, as well as the potential for customized solutions that meet unique operational needs.
Nanocrystalline boron carbide is characterized by its nano-sized particles, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties, including strength and toughness. This type is particularly beneficial for electronics and advanced ceramics, where high performance is essential. Buyers should be aware of the higher production costs associated with nanocrystalline materials, but the superior strength-to-weight ratio can justify the investment for high-tech applications.
Thermally conductive boron carbide features a unique structure that enhances its thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heat sinks and thermal management systems. This variation is particularly valuable in applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. B2B buyers should consider the limited range of applications for thermally conductive boron carbide, but its efficiency in thermal management can be a critical factor in electronics and high-performance systems.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of boron carbide density | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Lightweight armor for aircraft | Enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced weight | High purity levels and compliance with aerospace standards |
| Nuclear Energy | Neutron absorbers in reactors | Improved safety and efficiency in nuclear reactions | Consistency in density and sourcing from certified suppliers |
| Defense & Security | Ballistic protection materials | Increased safety for personnel and equipment | Certifications for military-grade applications and performance testing |
| Manufacturing | Abrasives for precision machining | Higher durability and reduced production costs | Grain size distribution and sourcing from reliable manufacturers |
| Electronics | Thermal management materials | Improved device performance and longevity | Thermal conductivity specifications and supplier reliability |
In the aerospace industry, boron carbide density is critical for developing lightweight armor materials used in aircraft. The high density of boron carbide provides excellent ballistic protection while minimizing weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and overall performance. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers who can provide high-purity boron carbide that meets stringent aerospace standards.
Boron carbide's density is essential in the nuclear energy sector, where it is used as a neutron absorber in reactors. The material's ability to effectively capture neutrons enhances the safety and efficiency of nuclear reactions. Buyers in South America and Europe must focus on sourcing boron carbide that maintains consistent density levels and complies with international nuclear safety regulations to ensure operational integrity.
In defense and security applications, boron carbide density is leveraged for ballistic protection materials that safeguard personnel and equipment. The material's superior density-to-weight ratio offers enhanced protective capabilities against ballistic threats. B2B buyers in Europe and Africa should seek suppliers with certifications for military-grade boron carbide, ensuring that the products have undergone rigorous performance testing to meet defense standards.
Boron carbide density is significant in manufacturing, particularly in producing abrasives for precision machining. The high density contributes to the durability of abrasive materials, leading to reduced wear and lower production costs. Buyers in South America should consider sourcing boron carbide with specific grain size distributions from reliable manufacturers to optimize machining efficiency and product quality.
In the electronics sector, boron carbide density is utilized in thermal management materials that help dissipate heat effectively. This property is vital for improving device performance and longevity, particularly in high-performance applications. International B2B buyers must assess thermal conductivity specifications and supplier reliability when sourcing boron carbide for electronic applications to ensure optimal performance in their devices.
Related Video: How to recycle solid carbide with Sandvik Coromant
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in industries such as aerospace and defense, encounter challenges when attempting to source boron carbide with the precise density required for their specific applications. Variability in density can significantly affect performance characteristics, such as hardness and resistance to wear, which are critical for components used in armor plating or abrasives. Buyers often find that suppliers provide density specifications that do not align with their operational needs, leading to costly trial-and-error processes.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, it is essential for buyers to clearly communicate their density requirements from the outset. When engaging with suppliers, specify the exact density range needed and the context of its application—whether it is for ballistic armor or cutting tools. Additionally, consider collaborating with suppliers who offer customizable density options through tailored production processes. This proactive approach allows for better alignment of product offerings with your operational specifications, reducing the risk of receiving suboptimal materials. Furthermore, establishing a close partnership with a supplier can facilitate ongoing adjustments to density as your application needs evolve.
The Problem: International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, often face supply chain disruptions that affect the availability of boron carbide with the desired density. Political instability, logistical challenges, and fluctuating demand can lead to unexpected delays or increased costs, complicating project timelines and budgets. As a result, companies may struggle to maintain their production schedules or meet contractual obligations.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should diversify their supplier base by engaging with multiple vendors across different regions. This strategy not only enhances supply chain resilience but also provides leverage in negotiations regarding pricing and delivery times. Additionally, implementing a just-in-time inventory system can help manage stock levels effectively, reducing the impact of potential disruptions. Regularly reviewing and updating supplier performance metrics allows businesses to identify reliable partners who consistently deliver quality products on time, ensuring a smoother procurement process.
The Problem: B2B buyers in research and development settings often encounter challenges in evaluating the quality and consistency of boron carbide density during experimental phases. Inaccurate density measurements can lead to flawed research outcomes, wasted resources, and delays in product development. Buyers may struggle to determine which testing methodologies yield the most reliable results, complicating the decision-making process.
The Solution: To enhance the evaluation of boron carbide density, buyers should adopt standardized testing protocols, such as Archimedes' principle for density measurement, which provides accurate results. Collaborating with accredited laboratories that specialize in material testing can also provide unbiased results and insights into the quality of the boron carbide being sourced. It is beneficial to establish relationships with these laboratories to facilitate ongoing testing and consultation. Furthermore, buyers should consider investing in training for their teams on proper testing methods to ensure consistency and accuracy in their evaluations, ultimately leading to better-informed decisions regarding material selection.
Boron carbide is a versatile material known for its exceptional hardness and thermal stability. When considering boron carbide density in various applications, it is essential to evaluate the properties and suitability of different materials that can be used in conjunction with boron carbide. Below, we analyze four common materials that are often evaluated alongside boron carbide, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
A stock image related to boron carbide density.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is recognized for its high thermal conductivity, excellent mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock. It operates effectively at high temperatures (up to 1600°C) and is chemically inert in many environments, making it suitable for harsh conditions.
Pros & Cons: The durability of silicon carbide is a significant advantage, as it can withstand extreme conditions without degrading. However, its manufacturing complexity can lead to higher costs, particularly for precision applications. Additionally, SiC is less suitable for environments with strong alkalis.
Impact on Application: In applications requiring high thermal stability and resistance to wear, silicon carbide enhances the performance of boron carbide components, particularly in abrasive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM C 1445 for silicon carbide products. Understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact is crucial, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe.
Aluminum oxide (Al2O3), commonly known as alumina, is favored for its excellent hardness and wear resistance. It is typically used in applications requiring good electrical insulation and thermal stability.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum oxide is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a cost-effective option for many applications. However, it has lower thermal conductivity compared to silicon carbide, which can limit its use in high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: In conjunction with boron carbide, aluminum oxide can improve wear resistance in abrasive applications, but its lower thermal performance may restrict its use in high-heat environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the common standards such as JIS R 6001 for alumina, especially in Asia and South America. Ensuring that materials meet local quality and safety standards is vital for compliance.
Tungsten carbide (WC) is known for its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear, making it a popular choice in cutting tools and other high-stress applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of tungsten carbide is its durability and ability to maintain performance under extreme conditions. However, it is more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to machine due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: When combined with boron carbide, tungsten carbide enhances toughness and wear resistance, making it ideal for applications in mining and machining where durability is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the high cost associated with tungsten carbide and ensure compliance with relevant standards like ASTM B 777. Understanding the supply chain for tungsten, which may be affected by geopolitical factors, is also essential.
Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), or zirconia, is known for its toughness and thermal stability. It is often used in applications requiring high resistance to thermal shock and wear.
Pros & Cons: Zirconium dioxide offers excellent mechanical properties and can withstand high temperatures. However, it can be more brittle than other materials, which may limit its application in high-impact environments.
Impact on Application: In applications where thermal stability and wear resistance are paramount, zirconium dioxide can complement boron carbide, particularly in high-temperature settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable to zirconia, such as ISO 6872, and consider regional regulations regarding sourcing and environmental impact.
| Material | Typical Use Case for boron carbide density | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide | High-temperature applications | High thermal conductivity | Manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum Oxide | Abrasive environments | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Lower thermal conductivity | Medium |
| Tungsten Carbide | Cutting tools and mining applications | Exceptional hardness | High cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Zirconium Dioxide | High-temperature and wear-resistant uses | Excellent thermal stability | Brittle under impact | Medium |
This analysis provides international B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials that can be used alongside boron carbide, enabling informed decision-making tailored to their specific applications and regional requirements.
The manufacturing process of boron carbide, particularly in achieving specific densities, involves several critical stages that ensure the material meets the required specifications for various applications, such as abrasives, armor, and nuclear applications.
The first step is material preparation, which includes sourcing high-purity boron and carbon sources. These materials are typically processed to achieve a specific particle size distribution, which is crucial for the final density of the boron carbide. The quality of the raw materials directly affects the properties of the final product, so B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who can provide detailed material specifications and certificates of analysis.
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This can be done through various techniques such as:
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific forming techniques used by their suppliers, as the method can significantly influence the final product's performance.
In some applications, especially those requiring complex shapes or multi-component systems, assembly may be necessary. This can involve combining boron carbide with other materials or components to create a final product that meets specific performance criteria. Buyers should understand the assembly processes and the quality controls in place to ensure reliable performance in the final application.
The final stage is finishing, which may include grinding, polishing, and coating to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional tolerances. This stage is essential for applications where precision and surface quality are critical, such as in armor applications. Buyers should verify the finishing techniques employed by suppliers to ensure they meet industry standards.
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of boron carbide, ensuring that the final product meets international and industry-specific standards.
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for manufacturers of boron carbide. ISO 9001 sets out criteria for a quality management system and is based on several quality management principles, including a strong customer focus, the involvement of top management, and a process-based approach.
In addition to ISO standards, other industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area) and API certification (for oil and gas industry products) may also be relevant depending on the application of the boron carbide.
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with specifications and standards.
At the material preparation stage, Incoming Quality Control (IQC) is critical. This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the facility to ensure they meet the required specifications. B2B buyers should request IQC reports from suppliers to verify that incoming materials are of high quality.
During the manufacturing process, In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) is employed to monitor the production parameters continuously. This includes checking the pressure and temperature during forming and sintering processes. Implementing IPQC helps in identifying and rectifying issues in real-time, thus minimizing defects in the final product.
Final Quality Control (FQC) occurs after the manufacturing process is complete. This stage involves comprehensive testing of the boron carbide to ensure it meets the specified density, hardness, and other mechanical properties. Common testing methods include:
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence when selecting suppliers for boron carbide to ensure they adhere to rigorous quality control practices.
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to verify a supplier's quality control processes. These audits should focus on manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. Buyers can request to see audit reports and certifications to ensure compliance.
Buyers should also request regular QC reports from suppliers that detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports should include data on material properties, test results, and any corrective actions taken in response to non-conformities.
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. Third-party inspectors can conduct additional testing and verification, ensuring that the supplier's claims about product quality are accurate.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in boron carbide manufacturing is crucial.
Buyers must be aware of local regulations that may affect the import and use of boron carbide products. Different regions may have varying standards for product safety and performance, and suppliers should be able to demonstrate compliance with these regulations.
Language and cultural differences can pose challenges in communication regarding quality expectations and specifications. Buyers should ensure that all documentation is clear and available in the preferred language to avoid misunderstandings.
International shipping can introduce additional variables affecting product quality. Buyers should discuss logistics with suppliers to understand how products are packaged and transported to minimize damage and maintain quality during transit.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for boron carbide density is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier qualifications, compliance with international standards, and effective quality control practices, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality boron carbide that meets their specific needs.

A stock image related to boron carbide density.
To successfully source boron carbide density for your business needs, following a structured approach is essential. This checklist will guide international B2B buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—through the critical steps of the procurement process, ensuring you make informed decisions.
Establishing clear technical specifications for boron carbide density is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider the specific applications—such as abrasives, armor, or neutron capture—where you intend to use boron carbide. Pay attention to factors like purity levels, grain size, and density requirements, as these will directly impact performance in your intended application.
Begin your search by compiling a list of potential suppliers. Utilize online directories, industry trade shows, and professional networks to find manufacturers who specialize in boron carbide. Ensure that these suppliers have a proven track record in your target markets, which can significantly influence pricing and delivery timelines.
Before proceeding, it's crucial to verify that your potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications. Look for ISO 9001 or equivalent quality management certifications, as these indicate adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, consider any regional certifications relevant to your market, which may enhance your supplier's credibility.
To assess the quality of boron carbide density, request samples from shortlisted suppliers. Conduct thorough testing to ensure that the samples meet your defined specifications. This step is vital as it allows you to evaluate the material's performance and suitability for your specific applications before placing a bulk order.
Once you've identified suitable suppliers, engage in discussions regarding pricing and payment terms. Request detailed quotes that include shipping costs, delivery timelines, and payment options. This transparency will help you compare offers effectively and make a budget-friendly decision.
Before finalizing a supplier, check references and reviews from other businesses that have sourced boron carbide from them. This can provide valuable insights into the supplier's reliability, customer service, and product quality. Reach out to references to ask about their experiences, focusing on aspects like delivery timeliness and product consistency.
Once you've selected a supplier, ensure all terms are clearly defined in a contract. This should include delivery schedules, quality expectations, and recourse for non-compliance. A well-drafted contract protects both parties and fosters a strong business relationship moving forward.
By following this step-by-step checklist, international B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for boron carbide density and ensure they select the right supplier to meet their specific needs.
When sourcing boron carbide density, international B2B buyers must understand the breakdown of costs involved. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The raw materials for boron carbide, primarily boron and carbon, fluctuate in price based on global supply and demand. Buyers should be aware of current market trends and potential shortages that could impact costs.
Labor: This encompasses the workforce involved in production. Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Africa, South America, and the Middle East often having lower labor costs compared to Europe.
Manufacturing Overhead: These are indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient factories may pass savings onto buyers.
Tooling: Custom tools or molds may be required for specific product specifications, adding to the initial cost.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the density meets specified standards often requires rigorous testing and certification, which can increase costs.
Logistics: Transporting boron carbide can be significant, especially for international shipments. Costs vary based on the mode of transport and distance.
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that can range from 5% to 20%, depending on market competition and product demand.
Several factors influence the pricing of boron carbide density:
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate for volume discounts whenever possible.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to specialized production processes. Buyers should clearly define their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
Materials: The quality and source of raw materials can significantly influence price. Premium materials often result in higher costs but may offer better performance.
Quality Certifications: Certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can add to costs but are often necessary for compliance in various industries. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their budget constraints.
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality and service.
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help avoid unexpected costs.
To ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing boron carbide density, buyers should consider the following tips:
Negotiate Effectively: Building a relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing. Leverage volume and long-term commitments to negotiate favorable terms.
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, consider logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to overall savings.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors. Stay informed about global trends that could impact boron carbide pricing.
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Don’t settle for the first quote. Comparing multiple suppliers can provide insights into market rates and help identify the best value.
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, local suppliers may offer reduced shipping costs and shorter lead times.
Prices for boron carbide density can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotations to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
When evaluating materials for specific applications, especially in demanding industries such as defense, aerospace, and manufacturing, it's essential to consider alternatives to boron carbide density. This section will explore viable options that can provide similar benefits while examining their respective performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance needs, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Boron Carbide Density | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Alumina (Al2O3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High hardness, thermal stability, and neutron absorption | Excellent thermal conductivity and high wear resistance | Good hardness and electrical insulation |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to purity and processing | Moderate cost, but can vary based on purity | Low cost, widely available |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized processing techniques | Relatively easy to machine but needs high temperatures for sintering | Easy to process and shape |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable under harsh conditions | Low maintenance, but can be brittle | Low maintenance, chemically stable |
| Best Use Case | Armor, cutting tools, and high-performance applications | High-temperature applications, semiconductor devices | Insulators, abrasives, and structural ceramics |
Silicon carbide is an excellent alternative to boron carbide, particularly due to its superior thermal conductivity and wear resistance. It is widely used in high-temperature applications such as power electronics and automotive components. However, while SiC performs well, its brittleness can lead to challenges in certain applications where impact resistance is critical. Additionally, the cost can vary significantly depending on the purity and production method, making it less predictable for budgeting.
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, presents a cost-effective alternative with good hardness and electrical insulation properties. It is readily available and easy to process, making it suitable for a range of applications, including abrasives and insulators. However, alumina lacks the high thermal stability and neutron absorption capabilities of boron carbide, which limits its use in specialized fields like nuclear applications or advanced armor systems.
Selecting the right material involves understanding the specific requirements of your application. If high thermal resistance and neutron absorption are paramount, boron carbide density remains a top choice. However, if cost and ease of implementation are more critical, silicon carbide or alumina may serve as viable alternatives. Buyers should evaluate their operational needs, budget constraints, and the technical specifications of each option to make an informed decision that aligns with their strategic objectives.
Boron carbide density is a critical factor in determining the performance and applicability of this advanced ceramic material across various industries. Understanding its essential technical properties and trade terminology is vital for international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, who are looking to make informed purchasing decisions.
Material grade refers to the specific classification of boron carbide based on its purity and density. Higher grades typically exhibit superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the boron carbide meets the performance requirements for applications such as armor, abrasives, and neutron absorbers.
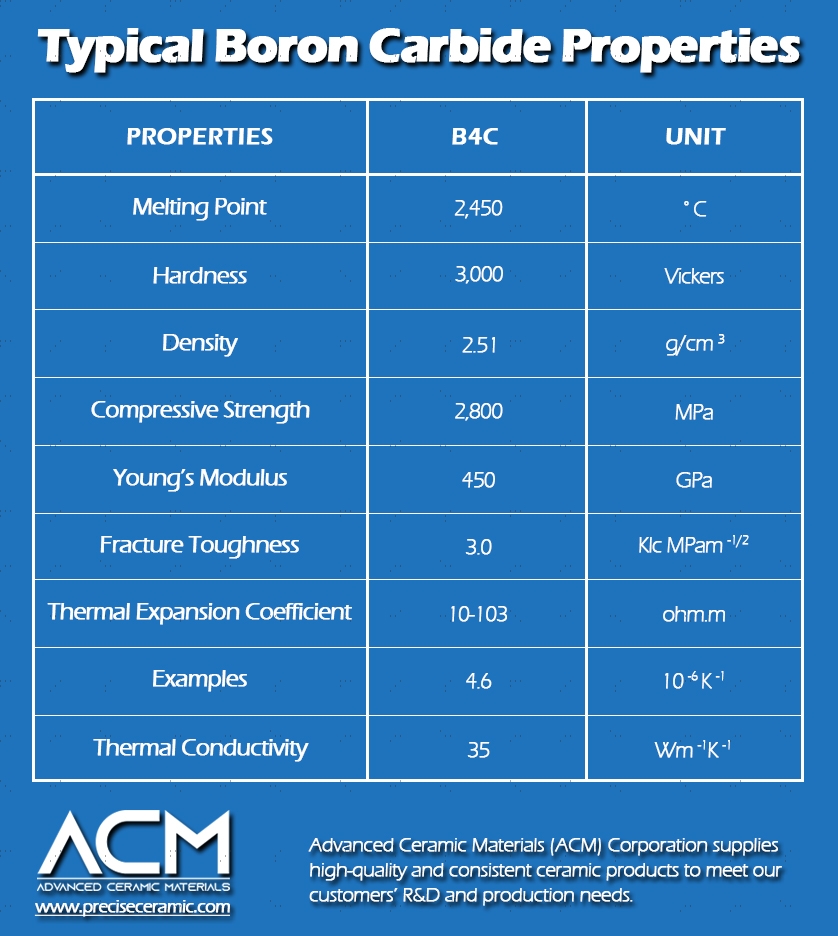
The density of boron carbide is a crucial specification that influences its mechanical properties. Typically measured in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), a higher density often correlates with increased hardness and strength. Buyers should consider density when assessing the suitability of boron carbide for specific applications, as it directly affects material performance and cost efficiency.
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For boron carbide components, precise tolerances are essential to ensure proper fitting and functionality in applications such as aerospace and defense. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers avoid costly reworks and ensures compliance with industry standards.
The particle size distribution of boron carbide affects its flowability, sintering behavior, and final density after processing. Buyers must evaluate the particle size to optimize the performance of the material in its end-use applications, particularly in manufacturing processes where uniformity is critical.
Thermal conductivity measures how well a material conducts heat. For boron carbide, which is often used in high-temperature environments, knowing its thermal conductivity helps buyers assess its suitability for applications like nuclear reactors or aerospace components. Higher thermal conductivity can enhance system performance and reliability.
Chemical stability indicates the material's resistance to chemical reactions under various conditions. For boron carbide, high chemical stability is important for applications in harsh environments, such as chemical processing or nuclear applications. Buyers should prioritize this property to ensure long-term performance and safety.
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of boron carbide, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can meet their specific requirements.
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For boron carbide, MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and product specifications. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to optimize their inventory management and budget.
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific product or service. Creating an effective RFQ for boron carbide can facilitate better negotiations and ensure competitive pricing.
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities associated with boron carbide procurement.
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. For boron carbide products, knowing the lead time is essential for project planning and ensuring timely delivery, especially in industries where delays can result in significant costs.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing boron carbide, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitiveness in the market.
The boron carbide density market is currently witnessing significant shifts driven by technological advancements and increasing demand across various sectors. Key global drivers include the rising utilization of boron carbide in the defense, nuclear, and aerospace industries due to its exceptional hardness and neutron absorption properties. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly interested in sourcing high-quality boron carbide for applications ranging from armor-piercing ammunition to radiation shielding materials.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the adoption of advanced manufacturing processes like additive manufacturing (3D printing), which allows for more precise and efficient production of boron carbide components. This trend is complemented by digital sourcing platforms that facilitate easier access to suppliers and market intelligence. Additionally, the emphasis on data-driven decision-making is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling buyers to optimize their procurement processes while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and trade policies, particularly for international buyers. Countries in Africa and the Middle East are increasingly looking to strengthen local supply chains, while European buyers are focusing on diversifying their sourcing options to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration in the boron carbide density sector. The environmental impact of boron carbide production, particularly the mining and processing phases, can be significant. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing practices that minimize environmental degradation. This shift is driven by regulatory pressures and growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Ethical supply chains are essential for companies looking to maintain their competitive edge. Buyers should seek suppliers who adhere to strict environmental standards and possess certifications such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. Furthermore, sourcing boron carbide from companies that utilize recycled materials or have "green" certifications can enhance a company's sustainability profile.
Investing in sustainable sourcing not only helps mitigate environmental impact but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. By fostering relationships with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, buyers can ensure a steady supply of high-quality boron carbide while aligning with global sustainability goals.
The history of boron carbide dates back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized. Initially, its applications were limited due to the lack of advanced production techniques. However, by the 1950s, boron carbide gained prominence in military applications, particularly for its exceptional hardness and ability to absorb neutrons. This period marked the beginning of its use in various high-performance applications, including armor and nuclear reactors.
As industries evolved, so did the applications of boron carbide, expanding into commercial and industrial sectors. The demand for high-density boron carbide has steadily increased due to its unique properties, leading to advancements in production technologies and sourcing strategies. Today, the boron carbide density market is characterized by a diverse array of applications, from automotive to aerospace, reflecting its critical role in modern manufacturing and technology.
Navigating the boron carbide density market requires a keen understanding of current trends, sustainability considerations, and historical context. By leveraging technology and ethical sourcing practices, international B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies while contributing to a more sustainable future. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be essential for success in this dynamic sector.
How do I determine the density of boron carbide for my application?
To determine the appropriate density of boron carbide for your specific application, consider the required mechanical and thermal properties. Boron carbide typically has a density of around 2.52 g/cm³. However, variations may exist based on the manufacturing process and purity levels. Conducting tests or consulting with suppliers for product specifications can help ensure the right density meets your operational requirements.
What is the best source for high-density boron carbide?
The best source for high-density boron carbide depends on your geographical location and specific needs. For international buyers, sourcing from established manufacturers with a proven track record in quality assurance is crucial. Evaluate suppliers from regions known for advanced materials, such as Europe or North America, and consider their certifications, production capabilities, and customer feedback to ensure you receive high-quality products.
How can I vet suppliers of boron carbide density?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO or ASTM compliance, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Request samples to evaluate product quality and consistency. Additionally, inquire about their production processes, sourcing of raw materials, and past client references. Finally, conducting site visits or engaging third-party inspection services can provide deeper insights into their operations.
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for boron carbide?
Minimum order quantities for boron carbide can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 100 kg to several tons, depending on the manufacturer. For smaller businesses or specific projects, some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your purchasing capacity.
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing boron carbide internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the relationship you establish. Common terms include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining balance before shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment via escrow services for added security. Always clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions.
How do I ensure quality assurance for boron carbide products?
Ensuring quality assurance involves establishing clear specifications and expectations with your supplier. Request certificates of analysis (CoA) that detail the material's density and other critical properties. Implementing regular quality checks and audits, both pre-shipment and upon receipt, can help maintain product standards. Consider engaging third-party quality control services for an unbiased assessment.
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing boron carbide?
When importing boron carbide, factor in logistics such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Work with suppliers who offer reliable shipping options and understand the import laws in your country. It’s also beneficial to use freight forwarders familiar with handling hazardous materials, as boron carbide may be classified under specific shipping regulations.
Can boron carbide density be customized for specific applications?
Yes, boron carbide density can often be customized based on specific application requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers, who may be able to adjust the manufacturing process to achieve desired densities. Customization may involve altering the material composition or processing techniques, so it’s essential to communicate your specifications clearly and work closely with the supplier throughout the development process.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
In summary, effective strategic sourcing for boron carbide density is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains. By understanding the material properties, potential applications, and market dynamics, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product performance and reduce costs. Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can further facilitate access to high-quality boron carbide products.
As the demand for boron carbide continues to rise, particularly in advanced manufacturing and defense sectors, embracing innovative sourcing strategies will become increasingly crucial. Buyers should proactively engage with suppliers to explore opportunities for collaboration, ensuring that they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Looking ahead, it is vital for B2B buyers to stay abreast of industry trends and technological advancements that may impact boron carbide density. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, companies can not only improve their bottom line but also contribute to sustainable development initiatives. Take action today—evaluate your sourcing strategies and explore new partnerships to unlock the full potential of boron carbide in your operations.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina