Carborundum, a vital industrial abrasive and semiconductor material, stands at the forefront of manufacturing, construction, and electronics sectors worldwide. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the nuances of carborundum sourcing is essential to maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring product quality.
This comprehensive guide delves into every critical facet of carborundum procurement. It covers the diverse types and grades of carborundum available, tailored for applications ranging from precision grinding to heavy-duty cutting. You will find detailed insights into raw materials and manufacturing processes, highlighting quality control measures that guarantee consistent performance and compliance with international standards.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Further, the guide offers a strategic overview of the global supplier landscape, including tips for vetting and selecting reliable manufacturers and distributors. We address cost considerations, helping you balance price with quality and supply chain efficiency. Market trends and demand drivers across key regions such as Saudi Arabia and Vietnam are analyzed to empower you with forward-looking intelligence.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Finally, an extensive FAQ section clarifies common challenges and technical questions, streamlining your decision-making process. By leveraging this guide, international B2B buyers can confidently navigate complexities, optimize sourcing strategies, and secure high-quality carborundum tailored to their unique operational needs.
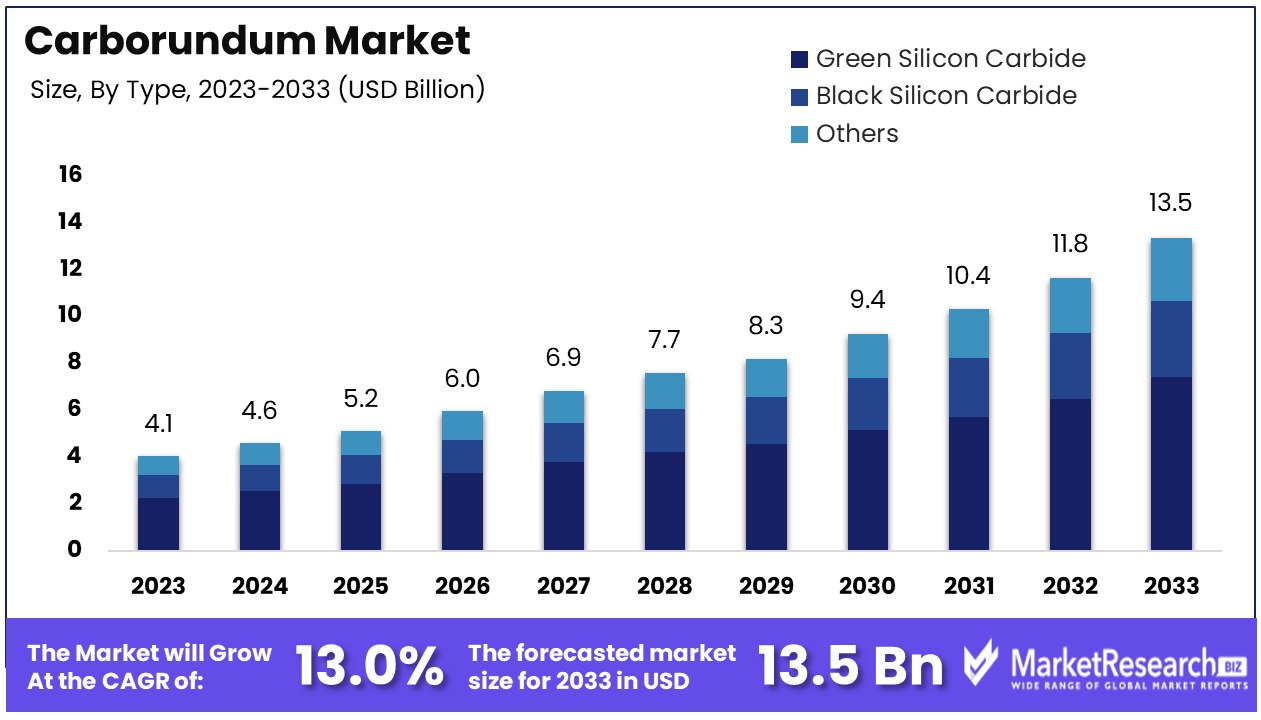
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black Silicon Carbide | High hardness, angular grain shape, excellent thermal conductivity | Abrasives, grinding wheels, sandblasting | Pros: Cost-effective, high wear resistance; Cons: Brittle, less chemical resistance |
| Green Silicon Carbide | Higher purity, sharper grains, more friable | Precision grinding, polishing, semiconductor industry | Pros: Superior finish quality, efficient cutting; Cons: Higher price, limited bulk supply |
| Fused Silicon Carbide | Manufactured by fusing silica and coke at high temperatures | Refractories, kiln furniture, high-temp applications | Pros: High thermal stability, chemical inertness; Cons: Higher energy cost in production |
| Silicon Carbide Powder | Fine particle size, available in various mesh sizes | Coatings, metallurgical additives, polishing powders | Pros: Versatile particle sizes, good dispersion; Cons: Handling dust requires safety measures |
| Ceramic Bonded Carborundum | Silicon carbide grains embedded in ceramic matrix | Heavy-duty grinding, cutting tools, industrial machining | Pros: Long tool life, high strength; Cons: Higher upfront cost, less flexible in shape |
Black Silicon Carbide is the most commonly used variation, characterized by its angular grains and high hardness. It is widely preferred in abrasive applications such as grinding wheels and sandblasting due to its cost-effectiveness and wear resistance. However, it is relatively brittle and has limited chemical resistance, which buyers should consider when sourcing for applications involving corrosive environments. For B2B buyers in regions with heavy industrial manufacturing, black silicon carbide offers a reliable balance between performance and cost.
Green Silicon Carbide boasts higher purity and sharper grains, making it ideal for precision grinding and polishing tasks, especially in the semiconductor and electronics sectors. Its friable nature allows for efficient cutting and superior surface finishes, which is critical for high-precision industries. B2B buyers should note that green silicon carbide commands a higher price and may have supply constraints, particularly when sourcing in bulk for large-scale production.
Fused Silicon Carbide is produced through a high-temperature fusion process, resulting in excellent thermal stability and chemical inertness. This type is predominantly used in refractory applications, kiln furniture, and environments exposed to extreme heat. B2B purchasers targeting industries such as metallurgy or ceramics manufacturing will benefit from fused silicon carbide's durability but must account for the higher production costs reflected in pricing.
Silicon Carbide Powder offers a range of fine particle sizes suitable for coatings, metallurgical additives, and polishing powders. Its versatility in mesh sizes allows customization for specific industrial processes. However, buyers must ensure proper handling protocols due to dust generation and associated health risks. This variation is particularly relevant for B2B clients in surface finishing and chemical industries seeking adaptable abrasive solutions.
Ceramic Bonded Carborundum integrates silicon carbide grains within a robust ceramic matrix, delivering superior strength and durability for heavy-duty grinding and cutting tools. This type is favored in industrial machining where long tool life and high strength are paramount. The initial investment cost is higher, but the longevity and performance can justify the expense for B2B buyers focused on minimizing downtime and replacement frequency in demanding operational environments.
Related Video: The Genius Behind Bach's Goldberg Variations: CANONS
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of carborundum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Metalworking | Abrasive grinding wheels and cutting tools | Enhances precision and durability in machining | Consistent grit size, purity, and hardness; supplier reliability |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Surface finishing and polishing of stone and concrete | Improves surface quality and extends lifespan of structures | Quality grade for hardness and wear resistance; compliance with safety standards |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Heat-resistant components and abrasive parts | Increases component lifespan and performance under stress | Material grade and thermal stability; certification for aerospace standards |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Substrates and insulation materials | Provides high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation | Purity level and defect control; supplier traceability |
| Energy & Power Generation | Wear-resistant seals and nozzles | Minimizes downtime and maintenance costs | Resistance to thermal and chemical degradation; supply chain stability |
Carborundum is extensively utilized in the Manufacturing and Metalworking sector, primarily for abrasive grinding wheels and cutting tools. Its exceptional hardness and thermal conductivity enable precise machining of metals and alloys, reducing tool wear and improving product quality. For international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, sourcing carborundum with consistent grit size and purity is critical to maintain machining efficiency and reduce production downtime.
In the Construction and Infrastructure industry, carborundum is used for surface finishing and polishing of stone, concrete, and tiles. This application enhances the aesthetic appeal and durability of buildings and infrastructure projects, which is especially relevant in regions experiencing rapid urban development, such as Saudi Arabia and Vietnam. Buyers must ensure the abrasive grade meets local safety and environmental regulations to avoid compliance issues.
The Automotive and Aerospace sectors benefit from carborundum’s heat-resistant properties, employing it in components that endure high temperatures and abrasive conditions. This use case extends the lifespan and reliability of critical parts, essential for markets in Europe and the Middle East where performance standards are stringent. Buyers should prioritize suppliers offering certified material grades and compliance with international aerospace standards.
In Electronics and Semiconductors, carborundum serves as an ideal substrate and insulation material due to its excellent thermal conductivity combined with electrical insulation. This makes it indispensable for manufacturing high-performance electronic devices. For B2B buyers in technologically advancing regions, ensuring high purity and minimal defect rates in carborundum is vital to guarantee device reliability and yield.
Finally, in the Energy and Power Generation sector, carborundum is applied in wear-resistant seals and nozzles, which face extreme thermal and chemical environments. This reduces maintenance frequency and operational costs, a significant advantage for energy producers in resource-rich African and South American countries. Buyers must focus on material resistance properties and stable supply chains to support continuous operations.
Related Video: Uses Of Polymers | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Key Properties: Silicon carbide, commonly known as carborundum, exhibits exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, and excellent resistance to thermal shock. It withstands temperatures up to 1600°C and offers strong chemical inertness against acids and alkalis.
Pros & Cons: SiC is highly durable and abrasion-resistant, making it ideal for grinding and cutting applications. However, its manufacturing complexity and brittleness can increase production costs and handling challenges. Its hardness can also cause wear on mating components.
Impact on Application: SiC is well-suited for high-temperature, high-pressure environments and corrosive media, such as chemical processing and semiconductor manufacturing. It performs reliably in abrasive slurry pumps and mechanical seals.
International Buyer Considerations: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure suppliers comply with ASTM C799 or ISO 9001 standards for quality assurance. In regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, where industrial standards may vary, verifying material certification and traceability is critical. SiC’s robustness aligns well with industries requiring long service life and minimal downtime.
Key Properties: Aluminum oxide offers excellent hardness (though lower than SiC), good thermal stability up to 1200°C, and high corrosion resistance, especially against acidic environments. It has moderate electrical insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: Al2O3 is cost-effective relative to SiC and easier to manufacture into complex shapes. Its toughness is superior, reducing brittleness issues. However, it has lower thermal conductivity and is less effective in highly abrasive conditions.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications requiring chemical resistance without extreme thermal demands, such as in ceramic coatings and electrical insulators. It is commonly used in wear-resistant parts and cutting tools where moderate hardness suffices.
International Buyer Considerations: Compliance with DIN EN 60672 or ASTM C799 is typical for Al2O3 products. Buyers in emerging markets should consider local availability and supplier reliability. European buyers often prioritize environmental certifications and sustainable sourcing, whereas Middle Eastern buyers may focus on material purity for petrochemical applications.
Key Properties: Boron carbide is one of the hardest materials after diamond and SiC, with excellent neutron absorption properties and resistance to wear and corrosion. It withstands temperatures up to 2450°C in inert atmospheres.
Pros & Cons: B4C offers superior hardness and chemical resistance, making it ideal for ballistic armor and abrasive applications. However, it is more expensive and difficult to machine, which can limit its use in cost-sensitive projects.
Impact on Application: Best suited for specialized applications requiring extreme hardness and chemical inertness, such as nuclear industries, ballistic protection, and abrasive nozzles. Its neutron absorption capability makes it unique for radiation shielding.
International Buyer Considerations: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should verify compliance with ASTM C799 and nuclear regulatory standards if applicable. In Africa and South America, the higher cost might restrict usage to high-value projects. Import regulations and customs duties on advanced ceramics should also be considered.
Key Properties: Synthetic diamond produced by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) exhibits the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of all carborundum-related materials. It resists chemical attack except by strong oxidizers and maintains stability at temperatures up to 900°C in inert atmospheres.
Pros & Cons: Offers unparalleled wear resistance and precision in cutting and grinding applications. However, CVD diamond is costly and requires specialized manufacturing and handling. Its thermal stability is lower than SiC and B4C, limiting some high-temperature uses.
Impact on Application: Ideal for ultra-precision machining, semiconductor wafer processing, and high-performance cutting tools. It is preferred where surface finish and tool life are critical.
International Buyer Considerations: European and Middle Eastern buyers often require certification to ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Buyers from Africa and South America should evaluate supplier logistics and after-sales support due to the material’s high value. Compliance with international trade regulations on synthetic diamonds is essential.
| Material | Typical Use Case for carbarundum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide | Abrasive tools, mechanical seals, high-temp pumps | Exceptional hardness and thermal shock resistance | Brittle, higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum Oxide | Wear-resistant parts, electrical insulators | Cost-effective, good toughness | Lower thermal conductivity and hardness | Medium |
| Boron Carbide | Ballistic armor, nuclear shielding, abrasive nozzles | Extreme hardness and chemical resistance | High cost, difficult to machine | High |
| Synthetic Diamond | Precision cutting tools, semiconductor processing | Highest hardness and thermal conductivity | Expensive, limited high-temp stability | High |
Carborundum, a synthetic abrasive primarily composed of silicon carbide (SiC), is a critical material used extensively in industrial applications such as grinding, cutting, and polishing. Understanding its manufacturing process is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable, high-performance products. The production involves several key stages, each contributing to the material’s hardness, durability, and abrasive efficiency.
The manufacturing journey begins with sourcing high-purity raw materials: silica sand and petroleum coke. These are carefully weighed and mixed in precise proportions to ensure consistent chemical composition. The quality of raw materials directly impacts the final product’s performance, making supplier selection and material testing crucial.
The mixed raw materials undergo a high-temperature reaction in an electric resistance furnace, typically reaching temperatures between 2,000°C and 2,500°C. This process, known as the Acheson process, results in the formation of silicon carbide crystals. Key techniques during this stage include:
Post-synthesis, the silicon carbide lumps are crushed into smaller particles. Milling processes, such as ball milling or jet milling, reduce the particle size to meet specific grit requirements. This stage is critical for producing abrasives with desired particle size distributions that affect cutting efficiency and surface finish.
Depending on the application, carborundum may be further processed into various forms, including:
Assembly processes emphasize uniform grain distribution and strong bonding to ensure durability under operational stress.
Final finishing involves treatments to enhance product performance and aesthetics:
For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality assurance is vital to mitigate risks and ensure product compliance with regional and global standards.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
- Verifies raw material quality through chemical composition analysis and physical inspection.
- Employs techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and sieve analysis to confirm material purity and particle size.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
- Monitors manufacturing stages including furnace temperature, grain formation, and milling.
- Uses real-time sensors and sampling to detect deviations early.
- Ensures bonding consistency and abrasive grain distribution during assembly.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
- Comprehensive testing of finished products for hardness, grit size uniformity, and bonding strength.
- Implements mechanical tests such as fracture toughness and wear resistance.
- Visual inspections to identify surface defects or contamination.
For buyers from diverse international markets, due diligence in supplier evaluation is essential. Practical steps include:
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing and quality assurance processes of carborundum, international B2B buyers can make informed procurement decisions that align with their operational requirements and compliance obligations. Robust supplier vetting and adherence to global standards will ensure consistent supply of high-quality abrasive materials tailored to diverse industrial applications.
When sourcing carborundum (silicon carbide) for industrial use, understanding the detailed cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and supplier negotiation. The main cost components include:
Pricing for carborundum is not fixed and can fluctuate based on several critical factors:
To optimize costs and secure favorable terms, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the following:
All pricing examples and cost structures provided are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific order details. Buyers are advised to conduct thorough due diligence and request formal quotations tailored to their unique requirements before finalizing procurement decisions.
Understanding the key technical properties of carborundum (silicon carbide) is essential for international buyers to ensure product suitability and optimize procurement decisions. Here are the most important specifications to consider:
Material Grade (Purity and Type):
Carborundum comes in various grades, typically distinguished by purity level and crystalline structure (alpha or beta silicon carbide). High-purity grades offer superior hardness and thermal resistance, critical for precision grinding and high-performance applications. Buyers should specify the grade to match their industrial needs, whether for abrasive use or electronic components.
Particle Size and Distribution:
The size of carborundum particles directly affects its abrasiveness and surface finish quality. Fine particles are preferred for polishing and fine grinding, while coarser grains suit heavy-duty cutting or grinding tasks. Precise particle size distribution ensures consistent performance and reduces waste in manufacturing processes.
Hardness (Mohs Scale):
Carborundum ranks between 9 and 9.5 on the Mohs hardness scale, making it one of the hardest abrasive materials. This property ensures effective cutting, grinding, and wear resistance. Buyers from sectors like automotive or construction should confirm hardness specifications to guarantee durability and efficiency.
Thermal Stability:
High thermal conductivity and stability up to around 1600°C allow carborundum to maintain structural integrity under extreme heat. This makes it ideal for high-temperature applications such as refractory linings or heat exchangers. Understanding thermal limits helps buyers avoid material degradation in demanding environments.
Tolerance and Dimensional Consistency:
For applications requiring precision, such as semiconductor manufacturing or fine abrasives, tight tolerances on particle size and shape are vital. Suppliers should provide clear tolerance ranges, ensuring that batches are consistent and meet quality control standards, reducing rework and downtime.
Chemical Resistance:
Carborundum is chemically inert to most acids and alkalis, which is important for buyers in chemical processing or harsh industrial environments. Ensuring the product's resistance to corrosion enhances longevity and safety during use.
Navigating international B2B trade requires familiarity with common industry jargon and terms. Here are essential terms buyers should know when sourcing carborundum:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may incorporate carborundum. Engaging with OEMs can ensure that materials meet specific technical standards required for original product assembly.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing MOQ helps buyers plan inventory and negotiate better pricing, especially for bulk purchases across regions like Africa or South America where logistics costs can be significant.
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
A formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers. RFQs should include detailed technical specs (grade, particle size, tolerance) to get accurate and comparable offers, facilitating informed decision-making.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
Standardized trade terms defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Common terms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight). Understanding Incoterms is crucial for cost calculation and risk management, particularly when importing carborundum into diverse markets like the Middle East or Europe.
Lead Time:
The duration from order placement to delivery. Buyers should clarify lead times to align supply with production schedules, avoiding costly delays especially in industries with just-in-time inventory systems.
Batch Number/Traceability:
Unique identifiers assigned to production batches. Traceability ensures quality control and accountability, allowing buyers to track material origin and manufacturing conditions—an important factor for compliance with international standards.
By focusing on these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can confidently evaluate carborundum suppliers and make strategic purchasing decisions that align with their operational requirements and market conditions.
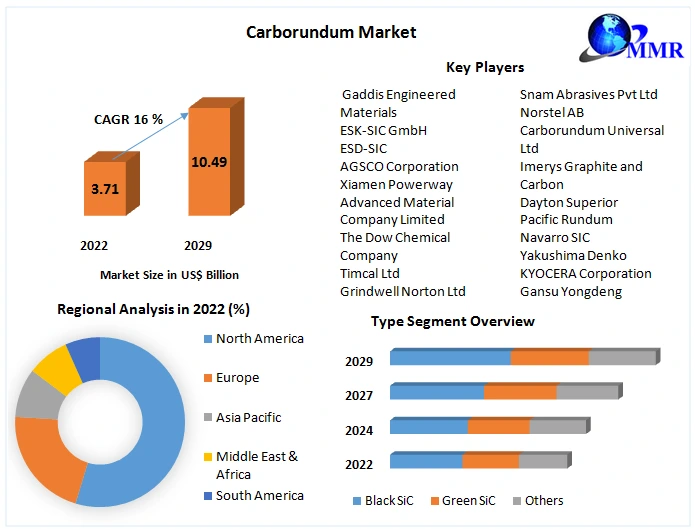
Carborundum, widely known as silicon carbide, is a critical industrial material used across sectors such as abrasives, refractories, semiconductors, and automotive components. Its global demand is primarily driven by rapid industrialization, advancements in electronics, and the expansion of renewable energy technologies. For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional market dynamics is essential for effective sourcing and supply chain optimization.
Key market drivers include:
Regional Insights:
For B2B buyers, leveraging data-driven supplier evaluation and fostering strategic partnerships with manufacturers who demonstrate technological and sustainability leadership will be vital for securing competitive advantage.
Sustainability has become a cornerstone in the carborundum sector, reflecting broader global commitments to reducing environmental impact and ensuring responsible supply chains. The extraction and processing of silicon carbide involve energy-intensive procedures and raw material consumption, which necessitate careful management to minimize carbon footprints.
Environmental considerations include:
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important:
For B2B buyers, integrating sustainability criteria into procurement policies not only aligns with regulatory requirements and corporate social responsibility goals but also enhances brand reputation and long-term supply security. Requesting environmental product declarations (EPDs) and life cycle assessments (LCAs) from suppliers can provide measurable data to support green procurement decisions.
Carborundum was first synthesized in the late 19th century by Edward G. Acheson, revolutionizing the abrasives industry with a material harder than conventional abrasives like emery. Initially adopted for grinding and cutting tools, its applications have expanded significantly due to its unique thermal conductivity and electrical properties.
Over the decades, the development of high-purity silicon carbide enabled breakthroughs in electronics, including high-voltage semiconductors and LED technology. The evolution of carborundum from a simple abrasive to a high-tech material underscores its strategic importance in modern industrial supply chains.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution highlights the material’s versatility and the importance of sourcing from suppliers who can meet increasingly sophisticated technical specifications aligned with cutting-edge industrial applications.
How can I effectively vet carborundum suppliers for international B2B trade?
To ensure reliability, start by verifying the supplier’s business license, industry certifications (ISO, REACH compliance), and export history. Request references or case studies related to previous international shipments, especially to regions like Africa, the Middle East, or Europe. Conduct factory audits or virtual tours to assess manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. Use third-party inspection services to validate product quality before shipment. Finally, evaluate their financial stability and responsiveness to communication, which are critical for smooth international transactions.
Is customization of carborundum products available, and how can it be arranged?
Many manufacturers offer customization in terms of grit size, shape, bonding agents, and packaging tailored to specific industrial applications. Begin by clearly specifying your technical requirements, intended use, and volume needs. Engage in detailed discussions with suppliers about feasibility, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and lead times for custom orders. It’s advisable to request samples to validate the customized product’s performance before committing to large orders, particularly when sourcing across continents with longer shipping timelines.
What are typical MOQ and lead times for carborundum orders in international markets?
MOQ varies widely depending on supplier scale and product type, often ranging from 500 kg to several tons per shipment. Lead times typically span 3 to 8 weeks, influenced by order complexity, customization, and shipping destination. Buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East should consider additional time for customs clearance and inland logistics. Planning orders well in advance and negotiating flexible MOQs can help manage inventory and reduce supply chain risks.
Which payment terms are commonly accepted for international carborundum purchases?
Standard payment methods include Letters of Credit (LC), Telegraphic Transfers (T/T), and, occasionally, open account terms with established partners. LCs provide security to both buyer and supplier, especially for first-time transactions. Partial payments (e.g., 30% upfront, 70% upon shipment) are common to mitigate risks. Always clarify payment schedules, currency, and bank charges upfront. For buyers in emerging markets, partnering with suppliers who accept escrow or trade finance solutions can facilitate smoother transactions.
What quality assurance certifications should I look for when buying carborundum?
Look for suppliers with ISO 9001 certification, which ensures a robust quality management system. Depending on your industry, additional certifications like REACH (for chemical safety in Europe) or specific environmental and safety compliance certificates may be necessary. Request detailed product datasheets, batch test reports, and third-party lab certifications to verify abrasive properties and purity. Consistent quality documentation is crucial for B2B buyers in regulated markets such as the EU or Saudi Arabia.
How can I optimize logistics and shipping for bulk carborundum imports?
Select suppliers with experience exporting to your region and who can provide consolidated shipping options. Sea freight is the most cost-effective for large volumes, but air freight may be necessary for urgent orders. Ensure packaging meets international standards to prevent contamination or damage during transit. Collaborate with freight forwarders familiar with your country’s customs regulations to avoid delays. Establish clear Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) and plan for warehousing or distribution upon arrival.
What steps should I take if there is a dispute over product quality or delivery?
First, document all communications, contracts, and product inspections meticulously. Engage the supplier promptly to discuss the issue and seek amicable resolution such as replacement shipments or discounts. If unresolved, leverage trade dispute resolution mechanisms like arbitration through chambers of commerce or international trade bodies (e.g., ICC). Having clear contract terms on dispute resolution and warranties is critical. Also, working with suppliers who have good reputations and references can minimize such risks.
Are there regional considerations when sourcing carborundum for markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East?
Yes, regional factors such as import regulations, tariffs, and certification requirements differ significantly. For example, Middle Eastern countries may require Halal certification for certain products, while African countries might have stricter customs inspections. Logistics infrastructure varies; some regions face longer inland transit times or limited port facilities. Understanding local market demand and partnering with suppliers who have local or regional distribution centers can streamline supply and reduce costs. Engage local trade experts to navigate regulatory environments effectively.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of carborundum requires a nuanced understanding of global supply dynamics, quality standards, and regional market conditions. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate reliability, consistency in product specifications, and compliance with environmental and safety regulations is essential to securing competitive advantage. Leveraging local partnerships and diversifying sourcing channels can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical fluctuations and logistics challenges.
Key takeaways include:
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to adopt digital procurement tools and data-driven decision-making to optimize sourcing strategies for carborundum. By proactively addressing supply chain complexities and fostering strategic alliances, businesses can unlock value, drive operational excellence, and position themselves for growth in a competitive global marketplace. Now is the time to act decisively—partner wisely and source strategically to harness the full potential of carborundum in your industrial applications.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina