The global demand for carbide color—a specialized additive used extensively in industrial applications—has surged as manufacturers seek enhanced durability, aesthetic appeal, and performance in their products. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key hubs like Turkey and Brazil), understanding the nuances of carbide color is essential for sourcing the right materials efficiently and cost-effectively.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of carbide color, starting with an exploration of various types and their material compositions. It delves into manufacturing processes and quality control standards critical to ensuring product consistency and reliability. Buyers will also find detailed insights into the global supplier landscape, helping them navigate vendor selection with confidence. Cost factors and market trends are analyzed to empower strategic budgeting and procurement decisions.
Moreover, the guide addresses common challenges and frequently asked questions, providing practical solutions tailored to diverse regional needs and industrial contexts. Whether you are a manufacturer aiming to optimize product performance or a distributor seeking reliable supply chains, this resource equips you with the knowledge to make informed, strategic choices.
By leveraging these insights, B2B buyers can enhance their competitive edge, mitigate risks associated with quality and supply fluctuations, and foster long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers worldwide. This guide is your essential companion for mastering the complexities of the carbide color market and maximizing value in your international sourcing endeavors.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Carbide Color | Subtle grey to dark grey shades, often with metallic luster | Cutting tools, mining equipment, wear parts | Pros: Durable, widely available; Cons: Limited color options, less aesthetic flexibility |
| Cermet Carbide Color | Range from light grey to black with ceramic-metal composite appearance | Precision machining, aerospace, automotive parts | Pros: High wear resistance, thermal stability; Cons: Higher cost, specialized handling required |
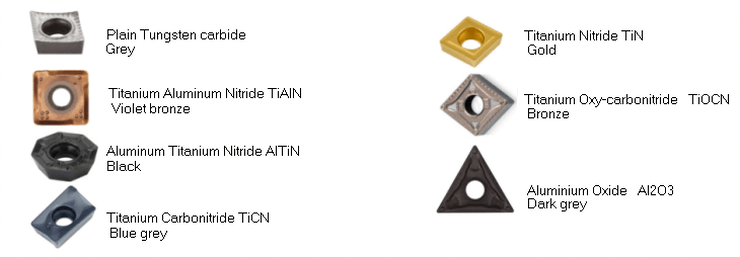
| Coated Carbide Color | Vivid colors like gold, blue, or black due to surface coatings (TiN, TiAlN, DLC) | High-speed cutting tools, milling, drilling | Pros: Enhanced performance, corrosion resistance; Cons: Coating wear over time, cost premium |
| Tungsten Carbide Variants | Variations in grey tones depending on tungsten content and grain size | Heavy-duty industrial tooling, drilling bits | Pros: Exceptional hardness, toughness; Cons: Brittle under impact, requires precise manufacturing |
| Colored Carbide Alloys | Custom alloyed carbides with colors from brown to black, sometimes with iridescence | Decorative industrial parts, specialized tooling | Pros: Unique aesthetic appeal, functional customization; Cons: Limited suppliers, variable cost |
Natural Carbide Color
Natural carbide colors typically range from subtle grey to dark grey with a metallic sheen, reflecting their pure tungsten carbide composition. This type is highly valued in industries requiring durability, such as mining and general machining. For B2B buyers, natural carbide offers reliable performance at a competitive price but lacks the aesthetic versatility of coated or alloyed variants. Bulk purchasing is common, and buyers should consider supplier consistency in color and composition for quality assurance.
Cermet Carbide Color
Cermet carbides combine ceramic and metal properties, resulting in colors from light grey to black with a distinctive composite texture. These carbides excel in precision machining and high-performance automotive or aerospace applications due to their wear resistance and thermal stability. B2B buyers should evaluate the higher upfront costs against the longer tool life and improved machining accuracy, especially for precision-critical projects.
Coated Carbide Color
Coated carbides are easily identified by their vibrant surface colors—gold, blue, or black—derived from advanced coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC). These coatings significantly enhance tool life, corrosion resistance, and cutting speed, making them ideal for high-speed milling and drilling in metalworking industries. Buyers must factor in coating durability and potential recoating needs when negotiating contracts and evaluating total cost of ownership.
Tungsten Carbide Variants
Variations in tungsten content and grain size produce a spectrum of grey tones in tungsten carbide, influencing hardness and toughness. These variants are preferred for heavy-duty tooling and drilling bits used in demanding industrial environments. For B2B procurement, understanding the balance between hardness and brittleness is crucial to ensure suitability for specific applications and to minimize tool failure risks.
Colored Carbide Alloys
Colored carbide alloys, ranging from brown to black with occasional iridescent qualities, are tailored for both functional and decorative purposes. These specialized carbides find niche applications in custom tooling and industrial parts where visual differentiation or specific material properties are required. International buyers should consider the limited availability and potentially higher costs, alongside supplier capability for custom alloy specifications.
Related Video: The Genius Behind Bach's Goldberg Variations: CANONS
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of carbide color | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining and Drilling | Wear-resistant coatings on cutting tools and drill bits | Enhances tool longevity and operational efficiency in harsh environments | Consistency in color indicating uniform carbide composition; supplier reliability and compliance with international standards |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Precision tooling and molds with carbide color coatings | Improves durability of molds, reduces downtime, and maintains product quality | Certification of carbide color for heat resistance and abrasion; logistics for timely delivery to manufacturing hubs |
| Aerospace Engineering | High-performance coatings on turbine blades and components | Increases resistance to thermal and mechanical stresses, ensuring safety and performance | Sourcing from suppliers with proven aerospace-grade carbide color materials; traceability and certification |
| Construction Equipment | Carbide color in cutting and grinding tools | Reduces wear and tear, extending tool life and lowering replacement costs | Consistent color quality for performance predictability; availability of bulk supply for large projects |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Protective coatings on semiconductor fabrication tools | Enhances precision and reduces contamination during chip production | High purity carbide color materials; supplier capability to meet stringent quality controls |
Mining and Drilling
In mining and drilling sectors, carbide color is predominantly applied as a wear-resistant coating on cutting tools and drill bits. This application addresses the critical challenge of tool degradation caused by abrasive materials and extreme operational conditions. For international buyers, especially in Africa and South America where mining is extensive, sourcing carbide color with consistent composition and color uniformity ensures predictable performance and longer tool life. Reliable suppliers who adhere to international standards and provide traceable quality certifications are essential to mitigate downtime and increase operational efficiency.
Automotive Manufacturing
Carbide color coatings are used extensively in automotive manufacturing for precision tooling and mold surfaces. These coatings improve the durability of molds, enabling them to withstand repeated high-pressure cycles without degradation. This reduces costly downtime and maintains high product quality, critical for automotive suppliers in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can certify the heat resistance and abrasion properties of their carbide color products, ensuring seamless integration into fast-paced manufacturing environments with reliable logistics support.
Aerospace Engineering
The aerospace industry demands materials with superior thermal and mechanical resistance. Carbide color coatings applied on turbine blades and critical components help enhance their lifespan and safety margins. For B2B buyers in Turkey, Europe, and the Middle East, sourcing aerospace-grade carbide color requires stringent quality assurance, traceability, and compliance with aerospace material standards. Partnering with suppliers that can provide detailed certification and testing documentation is vital to meeting regulatory and performance expectations.
Construction Equipment
Construction tools such as cutting and grinding implements benefit from carbide color coatings by experiencing significantly reduced wear. This translates into extended tool life and lower replacement costs, a major advantage for large-scale construction projects common in South America and Africa. Buyers should focus on sourcing carbide color with consistent quality and color stability to ensure predictable tool performance. Additionally, the ability to procure bulk quantities with dependable delivery schedules supports uninterrupted project timelines.
Electronics Manufacturing
In semiconductor fabrication, carbide color is used as a protective coating on precision tools to prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of micro-scale manufacturing processes. This application requires extremely high purity materials and precise color consistency to meet the rigorous quality demands of electronics manufacturing hubs in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers must select suppliers capable of delivering carbide color materials that comply with strict quality controls and provide documentation ensuring minimal impurities and optimal performance.
Related Video: How Is Carbide Made?
When selecting materials for carbide color applications, understanding the performance characteristics and regional requirements is critical for international B2B buyers. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in carbide color production, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and implications for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties: Tungsten carbide is renowned for its exceptional hardness, high melting point (~2870°C), and excellent wear resistance. It maintains structural integrity under high temperatures and pressure, making it ideal for cutting tools and wear parts.
Pros & Cons: Its durability and resistance to abrasion make it a top choice for long-lasting carbide colors. However, tungsten carbide is relatively expensive and requires sophisticated manufacturing processes such as powder metallurgy and sintering. Its brittleness can be a limitation in impact-heavy applications.
Impact on Application: Tungsten carbide-based colors are highly resistant to chemical corrosion and mechanical wear, suitable for harsh industrial environments involving abrasive media or high-temperature exposure.
Regional Considerations: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East often require compliance with ASTM and DIN standards, which tungsten carbide manufacturers commonly meet. In Africa and South America, cost sensitivity may push buyers toward blends or alternatives, but tungsten carbide remains preferred for high-performance needs in mining and heavy industry sectors. Turkish and Brazilian markets emphasize availability of certified suppliers and local technical support.
Key Properties: Titanium carbide offers high hardness, good thermal stability, and excellent corrosion resistance, with a melting point around 3160°C. It often enhances toughness when alloyed with other carbides.
Pros & Cons: TiC is less brittle than tungsten carbide and provides better corrosion resistance in acidic environments. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, and it can be produced via chemical vapor deposition or sintering. Cost is generally lower than tungsten carbide but higher than simpler carbides.
Impact on Application: TiC is favored in applications requiring resistance to chemical attack, such as in chemical processing industries or tooling exposed to acidic media. It also imparts a distinctive grayish color to carbide products.
Regional Considerations: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe value TiC for its corrosion resistance, aligning with stringent environmental regulations and industrial standards like DIN and JIS. South American buyers, particularly in Brazil, appreciate its balance of cost and performance. African markets may require supplier verification to ensure material quality due to varying local standards.
Key Properties: Chromium carbide is known for excellent corrosion resistance, especially against oxidation and acidic environments, with a melting point of approximately 1895°C. It has moderate hardness and good wear resistance.
Pros & Cons: It is less hard than tungsten and titanium carbides but offers superior chemical stability. Manufacturing is relatively straightforward, often used in coatings and claddings. Cost is moderate, making it attractive for applications prioritizing corrosion resistance over extreme hardness.
Impact on Application: Ideal for carbide colors used in environments with chemical exposure, such as marine, chemical processing, and oil & gas industries. Its color tends to be darker, which can be a design consideration.
Regional Considerations: European and Middle Eastern buyers often require compliance with ASTM and DIN standards for corrosion-resistant materials. South American industries engaged in oil and gas extraction prefer chromium carbide coatings for durability. African buyers benefit from chromium carbide’s cost-effectiveness and corrosion resistance in tropical and coastal environments.
Key Properties: Boron carbide is one of the hardest materials known (third after diamond and cubic boron nitride), with a melting point around 2763°C. It exhibits excellent chemical stability and is lightweight compared to tungsten carbide.
Pros & Cons: Its extreme hardness and low density make it suitable for abrasive and ballistic applications. However, boron carbide is brittle and can be challenging to machine. It is more costly than chromium carbide but can be competitive with tungsten carbide depending on purity and form.
Impact on Application: Used in carbide colors where abrasion resistance and lightweight properties are essential, such as in armor plating or specialized cutting tools. The color is typically black, which may influence aesthetic choices.
Regional Considerations: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East often require high-purity boron carbide with certification to meet defense or industrial standards. South American and African markets may face supply chain challenges due to limited local production, making reliable international partnerships crucial. Turkish buyers focus on availability and cost-effectiveness for industrial tooling applications.
| Material | Typical Use Case for carbide color | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten Carbide | High-performance cutting tools, wear parts | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance | High cost and brittleness | High |
| Titanium Carbide | Chemical processing tools, corrosion-prone environments | Good corrosion resistance and toughness | Moderate cost, manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Chromium Carbide | Coatings for corrosion resistance in harsh environments | Excellent chemical stability and moderate cost | Lower hardness compared to WC and TiC | Medium |
| Boron Carbide | Abrasive-resistant tools, armor plating | Extreme hardness and lightweight | Brittleness and machining difficulty | High |
This guide aids international B2B buyers in selecting the optimal carbide color material by balancing performance, cost, and regional compliance requirements. Understanding these factors ensures strategic procurement decisions aligned with operational demands and market standards.
Manufacturing and Quality Assurance of Carbide Color: Essential Insights for International B2B Buyers
The production of carbide color—a material often used in industrial tooling, coatings, and specialized applications—entails several critical stages designed to ensure durability, precision, and aesthetic consistency. International B2B buyers should understand these stages to assess supplier capabilities effectively and ensure product suitability for their specific needs.
The process begins with the careful selection and preparation of raw materials, primarily tungsten carbide powders combined with metallic binders such as cobalt. The powders are blended in precise ratios to achieve desired mechanical and color properties. Homogeneity at this stage is critical, often achieved through advanced mixing techniques like ball milling or attrition milling to ensure uniform particle size distribution and binder dispersion.
After preparation, the blended powders undergo shaping through pressing methods—typically cold isostatic pressing (CIP) or uniaxial pressing—to form green compacts. For carbide color products, specialized molds and dies are used to maintain strict dimensional tolerances. Some manufacturers employ injection molding for complex shapes, ensuring consistency in mass production.
The green compacts are sintered at high temperatures (typically 1400–1600°C) in controlled atmospheres to densify the material and develop the final mechanical properties. This stage also influences the final color tone and consistency. For multi-component assemblies, precision joining techniques such as brazing or diffusion bonding are applied post-sintering to integrate carbide color components with other substrates.
Finishing operations refine the surface quality and color consistency, including grinding, polishing, and coating. Surface treatments may include chemical etching, electroplating, or applying protective layers to enhance wear resistance and preserve color stability. Strict control during finishing ensures uniform appearance and functional performance.
Robust quality assurance (QA) is paramount in carbide color manufacturing, especially for international buyers demanding consistent performance and compliance with regulatory requirements.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Turkey and Brazil—ensuring supplier quality requires proactive verification strategies:
Understanding the intricacies of manufacturing and quality assurance for carbide color empowers international B2B buyers to make informed procurement decisions, ensuring product reliability and compliance across diverse industrial applications.
When sourcing carbide color materials, it is critical for international B2B buyers to dissect the underlying cost components to make informed procurement decisions. The cost structure typically includes:
Several factors influence the final quoted price for carbide color products:
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Turkey and Brazil), the following approaches can optimize cost-efficiency:
The cost and pricing insights provided here are indicative and may vary significantly based on supplier, market conditions, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should conduct detailed due diligence and request formal quotations tailored to their specific requirements.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding the key technical properties of carbide color is essential for B2B buyers to ensure product quality, compatibility, and performance in their applications. Here are the most important specifications to consider:
Material Grade
Carbide color products are categorized by material grade, which defines the composition and hardness of the carbide. Different grades suit varying applications, such as cutting tools or wear-resistant parts. Selecting the correct grade ensures durability and operational efficiency.
Dimensional Tolerance
This refers to the allowable deviation in size and shape from specified dimensions. Tight tolerances are crucial for precision components to fit correctly in machinery. Buyers should verify tolerance levels to minimize assembly issues and maintain product consistency.
Surface Finish
Surface finish affects the appearance and functional properties like wear resistance and friction. For carbide color products, the finish can influence both aesthetics and performance, especially in tooling and decorative uses. Confirming the finish quality helps meet end-use requirements.
Color Consistency
Since carbide color often serves as a visual or brand identifier, uniformity in color shade and intensity is vital. Inconsistent color can indicate variations in manufacturing or quality issues. Buyers should request samples or certificates verifying color standards.
Hardness (HRA or HV scale)
Hardness measures resistance to deformation and wear. Carbide color products typically have high hardness values, which correlate with longer service life in abrasive environments. Understanding hardness ratings assists in selecting materials fit for specific mechanical stresses.
Grain Size
Grain size impacts mechanical properties such as toughness and strength. Finer grains generally provide better wear resistance and strength. Buyers should inquire about grain size to ensure optimal performance for their intended application.
Navigating the carbide color market is easier when familiar with key trade terminology commonly used in international B2B transactions:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or products that are used in another company’s end product. Buyers sourcing carbide color components for OEMs should ensure compliance with specific quality and design standards required by the original manufacturer.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in one order. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan procurement volumes, manage inventory costs, and negotiate better pricing, especially important for markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East where order sizes vary widely.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal request sent by buyers to suppliers asking for price and terms on specific products. Providing detailed RFQs with technical specifications on carbide color ensures accurate quotes and reduces misunderstandings during negotiation.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs. Common terms include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Clear agreement on Incoterms is critical to avoid disputes and control shipping costs.
Lead Time
The time interval between placing an order and receiving the goods. For carbide color products, lead time affects project schedules and inventory management. Buyers should confirm lead times upfront, especially when dealing with suppliers across different continents.
Batch Number
A unique identifier assigned to a production batch. It enables traceability for quality control and warranty claims. Requesting batch numbers ensures accountability and helps in tracking product performance over time.
For B2B buyers across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, mastering these technical properties and trade terms will empower smarter purchasing decisions, reduce risk, and foster stronger supplier relationships. Always request detailed product datasheets and clear contractual terms to align expectations and secure the best value in carbide color procurement.
The carbide color sector is experiencing dynamic growth fueled by its critical applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and advanced manufacturing. Globally, the demand for high-performance carbide materials with tailored color properties is rising due to their enhanced wear resistance, thermal stability, and aesthetic versatility. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Turkey and Brazil), understanding regional supply chain nuances and emerging sourcing trends is crucial.
Key drivers include industrial modernization and increasing automation, which elevate the need for precision-engineered carbide components. Additionally, technological advancements in powder metallurgy and coating technologies are enabling novel carbide color formulations that improve product durability and performance. Buyers should note the growing trend toward customized carbide solutions, allowing end-users to specify color, texture, and functional properties tailored to specific applications.
Market dynamics reveal a shift towards regional diversification of suppliers to mitigate risks related to geopolitical tensions and raw material scarcity. For instance, South American buyers benefit from expanding local carbide production capabilities, while African markets are increasingly sourcing from Middle Eastern and European manufacturers who emphasize quality certifications and shorter lead times. Digital platforms and B2B marketplaces are gaining traction, simplifying global procurement and enabling more transparent price discovery.
Sourcing trends emphasize collaborative partnerships between buyers and suppliers to foster innovation and streamline logistics. Buyers are advised to prioritize suppliers offering robust technical support and compliance with international standards such as ISO and ASTM. Furthermore, logistics optimization—incorporating multimodal transport and inventory management—plays a vital role in ensuring timely delivery and cost efficiency.
Sustainability is rapidly becoming a non-negotiable factor in the carbide color sector, driven by stricter environmental regulations and growing corporate responsibility mandates globally. The production of carbide materials traditionally involves energy-intensive processes and the use of critical raw materials, which pose environmental and ethical challenges.
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions with emerging environmental policies like the Middle East and Africa, integrating ethical sourcing practices is essential to comply with both local regulations and global buyer expectations. This includes ensuring that raw materials are sourced from conflict-free zones and suppliers adhere to fair labor practices.
Environmental impact reduction strategies include adopting green manufacturing technologies such as recycled tungsten carbide powders and using renewable energy sources in production. Additionally, suppliers increasingly seek certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), Responsible Minerals Assurance Process (RMAP), and adherence to the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) standards to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
B2B buyers should engage with suppliers that provide full transparency over their supply chains, including traceability of raw materials and reporting on carbon footprints. Investing in carbide color products with verified eco-friendly attributes not only reduces environmental risks but also enhances corporate brand value and meets the rising demand for sustainable industrial components.
The carbide color sector has evolved significantly since the mid-20th century when tungsten carbide emerged as a revolutionary material for cutting tools and wear-resistant parts. Early applications focused primarily on functionality, with little attention to aesthetics or customization. Over time, advances in chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques allowed manufacturers to apply colored coatings to carbide substrates, enhancing both visual appeal and surface performance.
This evolution reflects a broader industry trend towards multi-functional materials that combine mechanical strength with design flexibility. For B2B buyers, understanding this history underscores the importance of leveraging modern carbide color technologies to gain competitive advantages in product differentiation and lifecycle performance. The sector’s trajectory also highlights the increasing interplay between material science innovation and sustainable industrial practices, shaping future sourcing and procurement strategies globally.
How can I effectively vet carbide color suppliers for international B2B purchases?
To vet suppliers, prioritize those with verifiable business licenses, international trade experience, and positive client testimonials, especially from your region. Request detailed product samples and technical datasheets to assess quality. Verify certifications such as ISO, REACH, or RoHS compliance. Utilize third-party inspection services and consider factory audits if feasible. Engage in direct communication to gauge responsiveness and transparency. This due diligence reduces risks and ensures a reliable supply chain tailored to your specific market needs.
Are carbide color products customizable to meet specific industrial requirements?
Yes, many carbide color manufacturers offer customization options including particle size, color shades, and binder types to suit various applications. When negotiating, clearly specify your technical requirements and intended usage. Customization may impact minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times, so plan accordingly. Discuss the possibility of pilot batches to validate performance before committing to large-scale orders. Customized solutions enhance product efficacy and can provide a competitive advantage in your local markets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for carbide color in international trade?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier and customization level, commonly ranging from 500 kg to several tons. Lead times can span 3 to 8 weeks, influenced by production capacity, customization, and shipping logistics. It’s crucial to clarify MOQ and lead times upfront during supplier negotiations to align with your procurement planning. Bulk orders might secure better pricing but require adequate storage and cash flow management. Early communication helps mitigate delays and optimize inventory management.
What payment terms are generally accepted for cross-border carbide color transactions?
Common payment methods include Letters of Credit (L/C), Telegraphic Transfers (T/T), and Escrow services. L/C offers protection by ensuring payment upon compliance with shipping documents, preferred for new supplier relationships. T/T may be used with trusted suppliers, often requiring a 30%-50% advance with balance upon shipment. Negotiate terms that balance risk and cash flow. Consider currency exchange fluctuations and transaction fees when calculating total costs. Using secure payment channels safeguards both parties in international trade.
Which quality assurance certifications should I look for when sourcing carbide color internationally?
Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, REACH for chemical safety compliance in Europe, and RoHS for restricted hazardous substances. Additionally, certifications from recognized testing labs (e.g., SGS, TÜV) validate product consistency and safety. Request Certificates of Analysis (CoA) with each batch to verify specifications. Compliance with environmental and safety standards not only ensures regulatory adherence but also enhances buyer confidence and market acceptance in diverse regions.
What logistics considerations are important when importing carbide color from global suppliers?
Carbide color is typically shipped in bulk packaging such as bags or drums, requiring careful handling to avoid contamination or damage. Assess port accessibility, customs clearance procedures, and import duties in your country to avoid delays. Engage freight forwarders experienced in chemical or mineral shipments. Factor in warehousing conditions to maintain product integrity. Planning for multimodal transport options (sea, air, road) and tracking shipments in real-time can optimize delivery schedules and cost-efficiency.
How should disputes or quality issues be managed with overseas carbide color suppliers?
Establish clear contractual terms detailing quality standards, inspection rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms such as arbitration or mediation. Upon quality issues, promptly document discrepancies with photos, samples, and inspection reports. Engage supplier communication channels to negotiate remediation such as replacements or refunds. Leveraging third-party inspection agencies can provide impartial assessments. Maintaining transparent dialogue and legal safeguards minimizes operational disruptions and preserves long-term supplier relationships.
What are best practices for building long-term partnerships with carbide color manufacturers internationally?
Focus on consistent communication, mutual trust, and understanding each other’s market dynamics. Provide feedback on product performance and collaborate on innovation or customization opportunities. Regularly review contract terms to accommodate evolving business needs. Participate in trade shows or virtual meetings to deepen connections. Reliable payment behavior and honoring agreements enhance credibility. Long-term partnerships often yield benefits such as preferential pricing, priority production slots, and joint market development support.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of carbide color materials presents a critical opportunity for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance product quality, optimize costs, and secure supply chain resilience. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of evaluating suppliers not only on price but also on consistency, technical support, and compliance with environmental and industry standards. For markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional sourcing dynamics and leveraging local partnerships can unlock competitive advantages and mitigate geopolitical risks.
Key considerations include:
Looking ahead, the carbide color sector is poised for innovation driven by evolving industrial needs and sustainability imperatives. Buyers who adopt a proactive, strategic sourcing approach will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging technologies and expanding market opportunities. To succeed, international B2B buyers should continuously monitor market trends, invest in supplier relationships, and remain agile in their procurement strategies.
Take the next step: Engage with trusted suppliers, deepen your market intelligence, and align sourcing strategies to future-proof your carbide color supply chain in an increasingly dynamic global marketplace.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina