Carborundum, also known as silicon carbide, stands as a cornerstone material in numerous industrial applications worldwide. Its exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and resistance to wear make it indispensable in sectors ranging from abrasives and refractories to electronics and automotive manufacturing. For international B2B buyers—particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the nuances of carborundum sourcing is critical to maintaining competitive supply chains and ensuring product quality.
This comprehensive guide delves into every essential facet of the carborundum market to empower buyers with actionable insights. You will explore the various types and grades of carborundum, tailored to different industrial needs, alongside detailed overviews of raw materials and manufacturing processes that influence product performance and consistency. Quality control measures and certification standards will be examined to help you identify reliable suppliers capable of meeting stringent requirements.
Additionally, the guide provides a thorough analysis of global and regional market dynamics, including pricing trends and logistical considerations crucial for strategic procurement. Special attention is given to sourcing challenges and opportunities unique to regions like Mexico, Argentina, the Middle East, and African markets, enabling you to navigate regulatory landscapes and optimize supplier relationships effectively.
By consolidating expert knowledge on supplier selection, cost management, and product specifications, this guide serves as an indispensable resource for B2B buyers seeking to make informed, confident decisions in the complex global carborundum marketplace.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black Silicon Carbide | Hard, sharp crystalline structure; high thermal conductivity; darker color | Abrasives, grinding wheels, sandblasting, metallurgical processes | + High hardness and thermal resistance – More brittle, careful handling needed |
| Green Silicon Carbide | Higher purity, greater toughness; typically greenish hue; superior abrasion resistance | Precision grinding, polishing, ceramics, electronics | + Better toughness and precision – Higher cost, availability may vary regionally |
| Brown Silicon Carbide | Intermediate purity; good toughness and wear resistance; cost-effective | General-purpose abrasives, cutting tools, sandpaper | + Balanced cost-performance ratio – Lower hardness compared to black and green types |
| Carborundum Powder | Fine particulate form; customizable grit sizes; used as loose abrasive | Polishing, lapping, chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) | + Versatile in particle size and application – Requires careful handling and dust control |
| Sintered Carborundum | Manufactured by sintering powder; enhanced strength and durability | Industrial cutting tools, high-performance grinding wheels | + High durability and strength – Higher upfront cost, sourcing from specialized suppliers |
Black Silicon Carbide is the most common and cost-effective variant, characterized by its hard and sharp crystalline structure. It excels in high-temperature applications and is widely used in abrasive blasting and grinding. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, it offers robust performance but requires careful handling due to its brittleness. Bulk purchasing and supplier reliability should be key considerations to ensure consistent quality.
Green Silicon Carbide stands out for its superior purity and toughness, making it ideal for precision grinding and polishing applications, especially in electronics and ceramics manufacturing. Although it commands a higher price, its enhanced abrasion resistance can lead to longer tool life and better surface finishes. Buyers from Europe and technologically advanced sectors should weigh the cost against improved efficiency and product quality.
Brown Silicon Carbide offers a middle ground with moderate purity and toughness, making it suitable for general-purpose abrasive uses such as sandpaper and cutting tools. It is often favored in markets where cost sensitivity is high, such as in emerging economies across Africa and Latin America. Buyers should evaluate their specific application needs to ensure this type meets performance requirements without overspending.
Carborundum Powder is a versatile form supplied in various grit sizes for applications ranging from polishing to chemical mechanical planarization. This form demands strict quality control and dust management during handling. For B2B buyers, especially in industrial manufacturing hubs, sourcing powder with consistent particle size distribution is critical to achieving desired finishes and process efficiencies.
Sintered Carborundum is produced by compacting and sintering carborundum powder, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength and durability. It is primarily used in high-performance industrial cutting and grinding tools. While the initial investment is higher, its longevity can reduce replacement frequency. Buyers should consider supplier expertise and technical support when procuring this variant to maximize return on investment.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Carborundun | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasives Manufacturing | Production of grinding wheels and sanding belts | High hardness and thermal conductivity improve cutting efficiency and durability | Ensure consistent particle size and purity; certifications for industrial grade |
| Metallurgy | Surface treatment and metal finishing | Enhances surface quality, reduces wear, and extends tool life | Availability of specific grit sizes; compliance with environmental regulations |
| Electronics | Semiconductor wafer polishing | Provides ultra-fine polishing to achieve smooth, defect-free surfaces | Ultra-pure grade with minimal contamination; reliable supply chain for precision applications |
| Construction | High-performance refractory materials | Withstands extreme temperatures, improving furnace and kiln durability | Consistent chemical composition; supplier capability for bulk orders |
| Automotive | Brake pads and clutches | Improves friction and thermal resistance, enhancing safety and performance | Quality control on particle uniformity; certifications for automotive standards |
Carborundum is extensively used in abrasives manufacturing, where its exceptional hardness and heat dissipation properties make it ideal for grinding wheels and sanding belts. These abrasives are crucial for industries requiring high precision and durability, such as metal fabrication and woodworking. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee consistent particle size distribution and industrial-grade purity to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the abrasive products.
In the metallurgy sector, carborundum serves as a key component for surface treatment and metal finishing processes. Its abrasive qualities help achieve smoother metal surfaces, reduce wear on tools, and extend their operational life. International buyers must consider sourcing from suppliers who offer a range of grit sizes tailored to specific metallurgical processes, while also ensuring compliance with environmental standards that vary across Europe and the Middle East.
The electronics industry leverages carborundum for semiconductor wafer polishing. This application demands ultra-fine abrasive particles to produce defect-free, highly polished surfaces critical for semiconductor performance. For B2B buyers in technologically advanced markets such as Europe and Mexico, sourcing ultra-pure carborundum with stringent contamination controls is essential. Reliable logistics and consistent quality assurance are also vital due to the sensitivity of semiconductor manufacturing.
In construction, carborundum is incorporated into high-performance refractory materials used in furnaces and kilns. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures enhances the durability and efficiency of these structures. Buyers from emerging industrial hubs in the Middle East and Africa should focus on suppliers capable of delivering consistent chemical composition and handling large-volume orders to meet infrastructure development demands.
Lastly, the automotive industry utilizes carborundum in manufacturing brake pads and clutch components. Its frictional properties and thermal resistance contribute to improved safety and vehicle performance. For international buyers, especially in markets like Argentina and Europe, it is crucial to procure carborundum that meets automotive industry certifications and quality control standards, ensuring compatibility with rigorous safety regulations.
Related Video: From Waste to Wonder: The Surprising Uses of Carbon Dioxide
When selecting materials for carborundum applications, international B2B buyers must consider a range of factors including mechanical properties, chemical resistance, manufacturing complexity, and regional standards compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in carborundum products, focusing on their suitability for various industrial applications and markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties: Silicon carbide is renowned for its exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, and excellent chemical inertness. It withstands temperatures up to 1600°C and exhibits strong resistance to oxidation and corrosion, making it ideal for abrasive and high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: SiC offers outstanding durability and wear resistance, ensuring long service life in abrasive environments. However, its brittleness can pose challenges in impact-heavy applications, and manufacturing precision parts from SiC can be costly due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: SiC is widely used in grinding wheels, cutting tools, and refractory components. It performs well in aggressive media such as acids and alkalis, making it suitable for chemical processing industries.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Buyers from regions like Mexico, Argentina, and Europe should verify compliance with ASTM C12 and DIN EN 13236 standards for abrasive grains. In Middle Eastern and African markets, availability and logistics may affect lead times; therefore, sourcing from regional distributors with certified quality is advisable.
Key Properties: Boron carbide is one of the hardest materials known, with excellent neutron absorption properties and high resistance to chemical attack. It tolerates temperatures up to approximately 2200°C but is more expensive than SiC.
Pros & Cons: Its extreme hardness and low density make it suitable for ballistic armor and wear-resistant coatings. The downside is its high cost and difficulty in machining, which limits its use to specialized applications.
Impact on Application: Boron carbide is ideal for high-performance abrasives and protective armor components. It is less common in general abrasive tools due to cost but invaluable in nuclear and defense sectors.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: European and Middle Eastern buyers often require compliance with ISO 9001 and nuclear-grade certifications when sourcing boron carbide. South American and African buyers should assess cost-benefit carefully, as import duties and transportation costs can significantly impact pricing.
Key Properties: Alumina is a ceramic material with high hardness and excellent thermal stability up to 1700°C. When combined with carborundum, it enhances toughness and chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons: Alumina composites offer improved fracture toughness compared to pure SiC, facilitating easier machining and shaping. However, they generally have slightly lower thermal conductivity and hardness than pure carborundum.
Impact on Application: These composites are favored in applications requiring a balance of hardness and toughness, such as wear-resistant linings and cutting tools in moderate-impact environments.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Compliance with ASTM C799 and DIN standards is common in Europe and South America. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should confirm supplier certifications and consider local environmental conditions that might affect material performance.
Key Properties: Incorporating synthetic diamond particles into carborundum matrices significantly improves cutting efficiency and abrasion resistance. Diamonds maintain hardness at extreme temperatures but are sensitive to oxidation above 700°C.
Pros & Cons: This hybrid material excels in ultra-precision cutting and grinding applications. The main limitation is the high cost and the need for controlled environments to prevent diamond degradation.
Impact on Application: Used in high-end machining tools, electronics manufacturing, and precision stone cutting, synthetic diamond-enhanced carborundum offers unmatched performance.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: European and Middle Eastern buyers often demand strict adherence to ISO 14001 environmental standards during production. African and South American buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including tool life and productivity gains, to justify the premium price.
| Material | Typical Use Case for carborundun | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Abrasive tools, refractory components | High hardness and thermal resistance | Brittle, costly to machine | Medium |
| Boron Carbide (B4C) | Ballistic armor, specialized abrasives | Extreme hardness and chemical resistance | High cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Alumina (Al2O3) Composite | Wear-resistant linings, cutting tools | Improved toughness and machinability | Slightly lower hardness than pure SiC | Medium |
| Synthetic Diamond-Enhanced SiC | Ultra-precision cutting and grinding tools | Superior cutting efficiency and abrasion | High cost, oxidation sensitivity | High |
This guide equips international B2B buyers with a clear understanding of material options for carborundum products, helping them make informed procurement decisions tailored to their specific industrial needs and regional market conditions.
Carborundum, or silicon carbide (SiC), is a highly durable and versatile abrasive material widely used in industrial applications such as grinding, cutting, and polishing. Understanding its manufacturing process is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to ensure product quality and consistency.
The production of carborundum begins with raw material selection, primarily silica sand and petroleum coke. These are carefully weighed and blended to maintain the correct stoichiometric ratio essential for the chemical reaction. High purity raw materials are preferred to minimize impurities that could affect the final product's performance.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The core of carborundum manufacturing is the Acheson process, a high-temperature synthesis method. The blended raw materials are placed in an electric resistance furnace and heated to temperatures between 2,000°C and 2,500°C. This intense heat facilitates a chemical reaction forming silicon carbide crystals. The process duration and temperature profile are tightly controlled to optimize crystal size and purity.
Post-synthesis, the crude carborundum is crushed and ground into various granular sizes depending on the intended application—ranging from coarse grit for heavy-duty grinding to fine powders for polishing. In some cases, additional shaping or bonding (e.g., sintering into grinding wheels or cutting tools) is performed to create finished products.
Finishing operations include sieving to classify particle sizes, washing to remove residual impurities, and drying. Surface treatments might be applied to enhance performance characteristics such as thermal stability or resistance to oxidation.
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding and verifying quality assurance (QA) protocols is essential to mitigate supply risks and ensure compliance with local and international regulations.
Effective quality control in carborundum manufacturing involves multiple checkpoints to ensure product integrity throughout the production cycle.
Given the critical role of quality in carborundum applications, buyers should adopt a proactive approach in supplier evaluation:
For buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances should be considered:
For international B2B buyers sourcing carborundum, a deep understanding of its manufacturing process—from raw material preparation to finishing—is vital to assess supplier capability. Equally important is a rigorous quality assurance approach anchored in international standards and thorough QC checkpoints. Buyers should leverage certifications, audits, third-party inspections, and sample testing to secure high-quality products tailored to their specific industrial applications. Awareness of regional regulatory nuances and logistics considerations further strengthens procurement decisions, ensuring long-term supplier partnerships and optimal product performance.
Understanding the cost and pricing dynamics of carborundum is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement and ensure competitive market positioning. The pricing structure is influenced by multiple cost components and market factors, which vary depending on sourcing region, order size, and product specifications.
Raw Materials: The primary input includes silicon carbide and related compounds. Fluctuations in raw material costs can significantly impact final pricing, especially given the global supply chain sensitivities.
Labor Costs: Labor expenses vary widely by manufacturing location. Regions with lower wage structures, such as parts of South America or Africa, may offer cost advantages but require due diligence on quality consistency.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, plant maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient production processes and automation can reduce overhead, influencing competitive pricing.
Tooling and Equipment: Specialized tooling for shaping and finishing carborundum products adds to upfront costs. Buyers should consider amortization of tooling costs over large order volumes to improve unit economics.
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes, including certifications like ISO or ASTM compliance, add cost but are crucial for ensuring product reliability, especially in demanding industrial applications.
Logistics and Freight: International shipping fees, customs duties, and insurance contribute to the landed cost. Volatile fuel prices and geopolitical factors can cause fluctuations, particularly for buyers in Africa, the Middle East, or Europe.
Supplier Margin: Manufacturers and distributors incorporate margins reflecting market demand, competition, and service levels, which affect the final price.
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger volumes typically unlock better unit pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers from emerging markets should negotiate MOQs that align with their storage and capital capabilities.
Product Specifications and Customization: Tailored grain sizes, shapes, or bonding agents increase complexity and cost. Standardized products are generally more affordable but may not meet all technical requirements.
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-grade carborundum with certifications commands premium pricing but offers greater durability and performance, crucial for specialized industrial uses.
Supplier Location and Reliability: Proximity to manufacturing hubs can reduce logistics costs and lead times. Reputable suppliers with stable production and transparent pricing foster trust and smoother transactions.
Incoterms Selection: Terms like FOB, CIF, or DDP significantly influence cost allocation between buyer and seller. Understanding these terms is vital to accurately assess total landed costs and avoid unexpected expenses.
Negotiate Beyond Price: Engage suppliers on payment terms, lead times, and after-sales support to enhance overall value.
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only purchase price but also factors like product lifespan, maintenance, and replacement frequency to optimize long-term expenditure.
Leverage Local Partnerships: Collaborating with regional agents or distributors can help navigate import regulations and reduce logistical challenges.
Monitor Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate volatility can impact final costs; locking favorable rates or using hedging strategies may protect margins.
Request Detailed Quotations: Break down pricing elements to identify cost drivers and potential areas for negotiation or substitution.
Assess Quality vs. Cost Trade-offs: For markets in Africa, South America, or the Middle East, balancing affordability with necessary quality standards ensures sustainable sourcing.
Due to variable factors such as raw material markets, geopolitical changes, and supplier-specific conditions, all price indications should be regarded as approximations. Buyers are advised to conduct thorough supplier audits and market comparisons before finalizing procurement decisions.
By carefully analyzing these cost components and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions for carborundum, achieving optimal balance between cost-efficiency and product quality across diverse global markets.
Understanding the essential technical properties of carborundum is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure the material meets specific industrial applications, from abrasives to high-temperature components.
Material Grade (Purity and Composition): Carborundum, primarily silicon carbide (SiC), comes in various purity grades affecting hardness and thermal stability. Higher purity grades deliver superior abrasion resistance and are preferred in precision machining or high-performance industrial use. Buyers should specify grade requirements to match their product’s durability expectations.
Particle Size and Grit: The size of carborundum particles or grit determines the surface finish and cutting aggressiveness. Fine grit (e.g., 220-600 mesh) is used for polishing, while coarse grit (e.g., 16-60 mesh) suits heavy material removal. Choosing the correct particle size optimizes productivity and product quality in manufacturing processes.
Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy: For carborundum components like grinding wheels or inserts, tight dimensional tolerances ensure proper fitting and consistent performance. Typical tolerances range from ±0.01 mm to ±0.1 mm depending on application. Buyers should confirm tolerance levels with suppliers to avoid assembly issues and maintain operational efficiency.
Thermal Conductivity and Stability: Carborundum exhibits excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand temperatures up to 1600°C without degradation. This makes it ideal for high-temperature industrial processes. Buyers in regions with extreme climates or thermal manufacturing processes must verify these properties for reliability.
Hardness (Mohs Scale): Silicon carbide rates around 9-9.5 on the Mohs hardness scale, making it one of the hardest materials after diamond. This hardness ensures long-lasting abrasive action but requires compatible machinery to handle the wear and tear. Understanding hardness helps in planning equipment maintenance and lifecycle costs.
Chemical Resistance: Carborundum is chemically inert to most acids and alkalis, providing durability in corrosive environments. This property is vital for buyers dealing with chemical processing industries or applications exposed to aggressive substances.
Familiarity with industry jargon facilitates clearer communication and smoother transactions between buyers and suppliers, especially across different regions.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to companies that produce carborundum products or components for other brands. B2B buyers often engage OEMs to source custom or branded abrasive tools tailored to their specifications.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity of carborundum material or products a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for managing inventory costs and negotiating order sizes, particularly for small and medium enterprises in emerging markets.
RFQ (Request for Quotation): A formal inquiry sent by buyers to suppliers to obtain pricing, lead times, and terms for specific carborundum products. An effective RFQ includes detailed technical specs and quantities, enabling suppliers to provide accurate and competitive offers.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs between buyer and seller. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Knowledge of Incoterms helps buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe plan logistics and control costs.
Lead Time: The period between placing an order and receiving the carborundum products. Lead time impacts production scheduling and inventory management. Buyers should clarify lead times upfront to align supply with demand cycles.
Certification and Compliance: Refers to adherence to industry standards (e.g., ISO, REACH) ensuring quality and safety of carborundum products. Buyers targeting regulated markets must request relevant certifications to avoid import or operational issues.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed procurement decisions, optimize supply chain efficiency, and build strong partnerships with reliable carborundum suppliers worldwide.
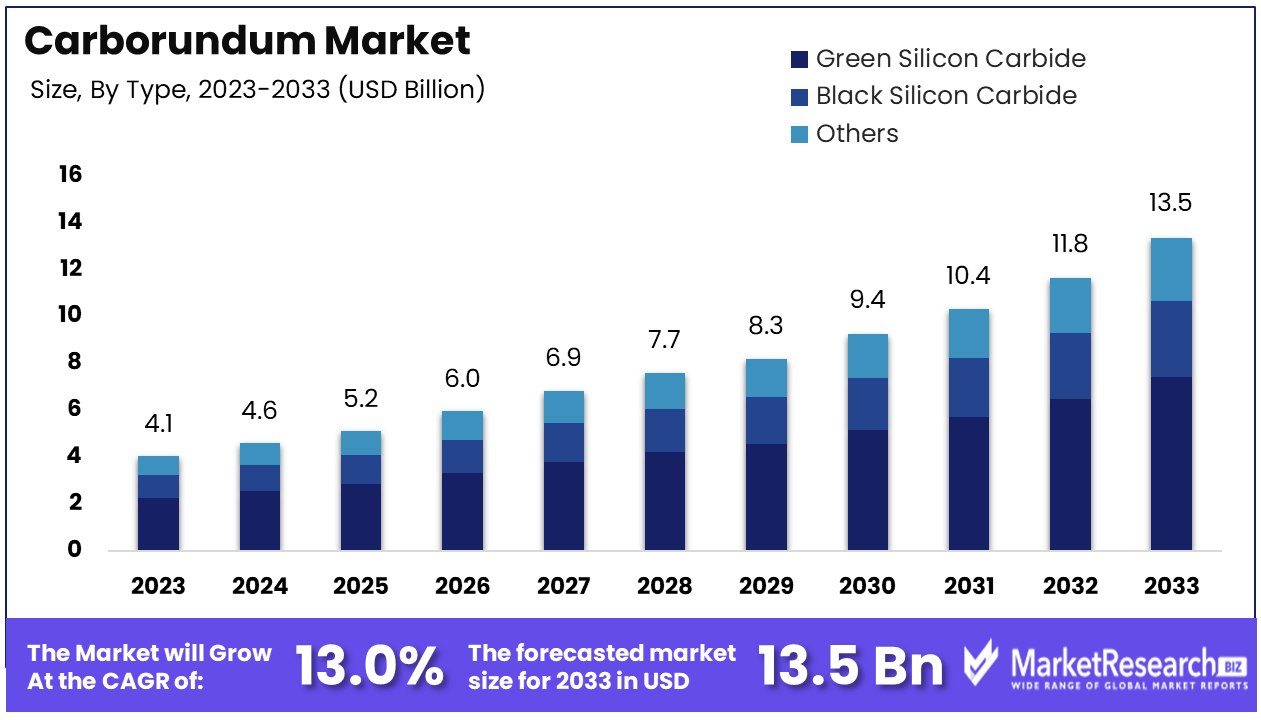
The global carborundum (silicon carbide) market is experiencing robust growth driven by its extensive industrial applications, including abrasives, refractories, ceramics, and semiconductors. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the regional dynamics is crucial. Africa’s emerging manufacturing hubs and mining sectors are increasing demand for durable abrasives and refractories, while South American markets, especially in countries like Argentina and Mexico, are expanding their automotive and electronics industries that rely on advanced silicon carbide components.
Key market drivers include technological advancements in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy sectors, where silicon carbide’s superior thermal conductivity and efficiency are critical for power electronics and inverters. This trend is pushing suppliers to innovate with higher purity grades and tailored product forms, such as wafers for semiconductor manufacturing. Buyers should watch for increasing integration of Industry 4.0 technologies in sourcing and supply chain management, improving traceability and procurement efficiency.
Sourcing trends reveal a shift towards strategic partnerships with manufacturers who can provide not only quality assurance but also supply chain resilience amid geopolitical uncertainties and raw material volatility. Regions like the Middle East are becoming important transit hubs, enhancing logistics capabilities for international trade. Buyers are also prioritizing suppliers with certifications aligned with international standards (ISO, REACH) to ensure compliance and reduce operational risks.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability is increasingly central in the carborundum supply chain, responding to both regulatory pressures and corporate social responsibility mandates. The production of silicon carbide is energy-intensive, often relying on high-temperature processes that contribute to carbon emissions. Buyers are advised to evaluate suppliers based on their adoption of cleaner production technologies, such as electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy sources, which significantly reduce environmental impact.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ethical sourcing goes beyond environmental concerns to include labor practices and community engagement, particularly in mining regions supplying raw materials like silica and carbon. B2B buyers from Africa and South America should ensure their supply partners adhere to fair labor standards and contribute positively to local economies, mitigating reputational risks.
Green certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) compliance are valuable benchmarks. Additionally, demand is rising for silicon carbide products with reduced lifecycle footprints, including recyclable or sustainably sourced variants. Engaging with suppliers who transparently report their sustainability metrics and commit to continuous improvement will position buyers favorably in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
Carborundum was first synthesized in the late 19th century as a synthetic abrasive, revolutionizing industrial manufacturing by offering a material harder than most natural minerals. Initially used primarily for grinding and cutting, its applications have expanded dramatically with advances in material science. The mid-20th century saw silicon carbide’s emergence in high-temperature and electronic applications, driven by its exceptional thermal and electrical properties.
For B2B buyers, this evolution underscores the importance of aligning procurement strategies with the material’s expanding role in cutting-edge industries such as EVs, aerospace, and renewable energy. Understanding the historical progression from basic abrasives to critical semiconductor substrates provides context for evaluating supplier capabilities and technology roadmaps that meet future market demands.
How can I effectively vet suppliers of carborundum for international B2B procurement?
To vet carborundum suppliers, start by verifying their business licenses, certifications (such as ISO or REACH compliance), and production capacity. Request samples to assess product quality firsthand. Check references and previous client testimonials, especially from your region (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe). Utilize third-party inspection agencies for factory audits and quality checks. Digital platforms with verified supplier statuses and trade history can add trust. Ensuring clear communication and understanding of your technical specifications upfront reduces risk.
Is customization of carborundum products available, and how should I approach it with international suppliers?
Many suppliers offer customization in terms of grit size, shape, bonding materials, and packaging. Clearly define your technical requirements and intended application when initiating discussions. Request technical datasheets and confirm the supplier’s ability to meet those specifications. Custom orders may require minimum order quantities (MOQs) and longer lead times—negotiate these terms early. Confirm if customization impacts certifications or quality guarantees. A prototype or sample batch approval before full production is advisable.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for carborundum shipments internationally?
MOQs vary widely depending on supplier scale and product type but generally range from 500 kg to several tons per order. Lead times can span from 2 to 6 weeks, influenced by production schedules, customization, and shipping logistics. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, factor in additional time for customs clearance and inland transport. Always clarify MOQs and lead times upfront to align with your inventory planning and demand cycles. Bulk orders often yield better pricing and priority production.
What payment terms are common in international carborundum trade, and how can buyers protect themselves?
Standard payment terms include letters of credit (L/C), telegraphic transfers (T/T), and sometimes open account for trusted partners. Letters of credit offer strong security, ensuring payment only upon document compliance. T/T in advance or partial payments are common for first-time orders. Negotiate payment milestones tied to production stages or inspection results. Use escrow services or trade finance options if available. Always verify supplier bank details and avoid full upfront payments without established trust or contractual safeguards.
Which quality assurance certifications should I look for when purchasing carborundum internationally?
Look for suppliers with ISO 9001 certification, which ensures consistent quality management systems. Depending on application, certifications like REACH (for chemical safety) or specific industry standards (e.g., ASTM for abrasives) may be relevant. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis (CoA) and material safety data sheets (MSDS) for each batch. Third-party lab test reports verifying hardness, particle size distribution, and purity can be requested. These documents help ensure compliance with your country’s import regulations and your internal quality standards.
What logistics considerations are critical for shipping carborundum to regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Carborundum is typically shipped in bulk via sea freight for cost efficiency. Choose suppliers experienced with export packaging that protects against moisture and contamination. Understand port infrastructure and customs procedures in your destination country to avoid delays. Work with freight forwarders familiar with hazardous material handling if applicable. Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) should be clearly defined to allocate responsibility and risk. Plan for inland transport capabilities and storage conditions to maintain product integrity post-arrival.
How should disputes over quality or delivery be managed in international carborundum transactions?
Start by documenting all communications, contracts, and inspection reports. Use internationally recognized arbitration clauses in contracts to specify dispute resolution methods. Engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent assessments if quality issues arise. Promptly notify the supplier with detailed evidence to facilitate resolution. Maintain open dialogue to negotiate remedies like replacement, discounts, or refunds. Legal recourse in the supplier’s jurisdiction can be complex; thus, preventive contract clarity and insurance coverage are critical.
What are the best practices for establishing long-term partnerships with carborundum suppliers globally?
Consistency in orders and clear communication build trust. Share forecasts and feedback regularly to enable suppliers to plan production efficiently. Consider joint quality improvement initiatives or technical collaborations to optimize product performance. Establish multi-year agreements with agreed terms on price, delivery, and quality to stabilize supply. Attend international trade fairs and supplier visits to strengthen relationships. Prioritize suppliers who demonstrate compliance with environmental and social governance (ESG) criteria, reflecting growing global procurement standards.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
As the demand for carborundum continues to grow across industrial applications, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize cost-efficiency, quality, and supply chain resilience. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating suppliers based on technological capabilities, certifications, and regional logistics advantages. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local and regional supplier networks can reduce lead times and import costs while enhancing responsiveness to market fluctuations.
Moreover, embracing digital tools for supplier assessment and contract management can streamline procurement processes and mitigate risks. Sustainability considerations are increasingly influencing supplier selection, making it crucial to engage with partners committed to environmentally responsible production practices.
Looking ahead, carborundum sourcing will benefit from closer collaboration between buyers and suppliers to innovate product formulations and application methods, driving competitive advantage. International buyers are encouraged to deepen market intelligence, diversify sourcing portfolios, and invest in long-term partnerships to navigate geopolitical and economic uncertainties effectively.
By adopting a proactive, informed approach to sourcing carborundum, businesses can secure reliable supply, enhance product performance, and unlock new growth opportunities in evolving global markets.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina