The global demand for GPF (Gasoline Particulate Filter) technology is rapidly expanding as industries prioritize environmental compliance and enhanced engine performance. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging hubs like Indonesia and Mexico—understanding the complexities of sourcing high-quality GPF filters is crucial to maintaining competitive advantage and regulatory adherence.
GPF filters play a pivotal role in reducing particulate emissions from gasoline engines, helping manufacturers meet stringent global emission standards. Their importance transcends regulatory compliance, directly impacting operational efficiency, vehicle longevity, and environmental responsibility. Selecting the right GPF filter involves navigating a diverse landscape of types, materials, and manufacturing standards, all while balancing cost-effectiveness and supplier reliability.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international buyers with actionable insights across every critical aspect of GPF filter sourcing. You will gain a clear understanding of:
By consolidating expert knowledge and market intelligence, this guide enables B2B buyers to make informed, strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and regional market demands. Whether upgrading existing fleets or launching new product lines, this resource is an indispensable tool for navigating the global GPF filter market with confidence and clarity.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Filter | Uses granular activated carbon media for adsorption | Water purification in industrial and municipal settings | Pros: High contaminant removal, cost-effective; Cons: Requires regular replacement, less effective for fine particles |
| Gas Phase Filter | Incorporates activated carbon with additional media for gas adsorption | Air purification in manufacturing and chemical plants | Pros: Effective for VOCs and odors, customizable; Cons: Higher initial cost, maintenance intensive |
| Pleated GPF Filter | Features pleated media to increase surface area | HVAC systems in commercial buildings and industrial facilities | Pros: Long lifespan, high dust holding capacity; Cons: Bulkier size, higher upfront cost |
| Composite GPF Filter | Combines multiple filtration media (carbon + HEPA or others) | High-purity environments like pharmaceuticals and electronics | Pros: Superior filtration efficiency, versatile; Cons: More expensive, complex disposal |
| Regenerable GPF Filter | Designed for multiple cleaning cycles and reuse | Heavy industry and mining operations | Pros: Cost-saving over time, environmentally friendly; Cons: Requires cleaning infrastructure, technical expertise |
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Filters rely on porous carbon granules that adsorb organic contaminants and chlorine from liquids or gases. Ideal for water treatment in municipal and industrial applications, GAC filters offer a balance of cost-efficiency and performance. For B2B buyers, evaluating the filter’s lifespan and replacement frequency is essential to optimize operational costs, especially in regions with variable water quality like parts of Africa and South America.
Gas Phase Filters extend the capabilities of standard carbon filters by targeting gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and odors. These are critical in chemical manufacturing, petrochemical plants, and food processing industries. Buyers should consider the specific gas contaminants present and the filter’s capacity to handle them, as well as maintenance demands, which can impact downtime and total cost of ownership.
Pleated GPF Filters increase filtration surface area by folding the media, enhancing dust and particulate capture efficiency. Commonly used in HVAC systems across commercial and industrial facilities, they help maintain air quality and equipment longevity. For international buyers, understanding the trade-off between upfront cost and extended service life is key, especially in climates with high particulate pollution.
Composite GPF Filters combine activated carbon with other media such as HEPA to achieve multi-stage filtration. These are suited for environments requiring stringent purity levels, including pharmaceutical manufacturing and electronics assembly. Procurement decisions should weigh the premium price against the critical need for contamination control and compliance with industry standards.
Regenerable GPF Filters are engineered for repeated cleaning and reuse, making them attractive for heavy industry sectors like mining and metal processing. While they reduce long-term expenses and waste, buyers must ensure availability of cleaning facilities and trained personnel. This type is particularly relevant for markets emphasizing sustainability and operational efficiency.
Related Video: How It Works - Gasoline Particulate Filter (GPF)
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gpf filter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Emission control in gasoline-powered vehicles | Compliance with environmental regulations, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions | Certification compliance (e.g., Euro 6, EPA), durability under high temperatures, supplier reliability |
| Power Generation | Air filtration in gas turbines and industrial engines | Enhanced engine performance, reduced maintenance costs, and extended equipment lifespan | Filter efficiency ratings, compatibility with fuel types, supplier capacity for bulk orders |
| Chemical Processing | Filtration of exhaust gases in chemical reactors | Prevention of harmful emissions, protection of downstream equipment, and compliance with safety standards | Material resistance to corrosive gases, custom sizing, and local regulatory standards |
| Oil & Gas | Gas particulate filtration in refining processes | Improved process safety, reduced environmental impact, and compliance with international standards | High-temperature tolerance, explosion-proof certifications, and logistics support for remote locations |
| HVAC Systems in Commercial Buildings | Air quality control in large-scale ventilation systems | Healthier indoor environments, energy efficiency, and regulatory compliance | Filter lifespan, ease of replacement, and compatibility with existing HVAC infrastructure |
In the automotive sector, GPF (Gasoline Particulate Filter) filters are critical for reducing particulate emissions from gasoline engines. These filters help manufacturers meet stringent environmental regulations such as Euro 6 in Europe or equivalent standards in other regions like Mexico and South Africa. For B2B buyers, it is essential to source GPF filters that demonstrate proven durability under high thermal and mechanical stress, ensuring long service life and minimal impact on fuel efficiency. Suppliers should provide certifications and robust quality assurance to facilitate regulatory compliance.
Gas turbines and industrial engines used in power generation rely on GPF filters to maintain clean combustion and reduce particulate emissions. This application is particularly relevant in emerging markets in Africa and the Middle East where power plants are expanding rapidly. High filtration efficiency extends engine life and reduces costly downtime. Buyers should prioritize filters that are compatible with local fuel types and that come from suppliers capable of meeting large volume demands with consistent quality.
In chemical plants, GPF filters play a vital role in capturing particulate matter from exhaust gases to prevent environmental contamination and protect downstream equipment. This application demands filters made from materials resistant to corrosive and high-temperature gases, which is a crucial consideration for buyers in regions with strict industrial safety regulations, such as the EU or Middle East countries. Custom sizing and adherence to local emission standards are key sourcing factors.
The oil and gas industry uses GPF filters to control particulate emissions during refining and processing activities. These filters contribute to safer operations by minimizing explosion risks and reducing environmental impact. For B2B buyers in remote or harsh environments like offshore platforms or desert refineries in the Middle East and Africa, selecting filters with high-temperature tolerance and explosion-proof certifications is essential. Reliable logistics and supplier support are also critical to ensure timely delivery and maintenance.
Large commercial HVAC systems utilize GPF filters to improve indoor air quality by trapping fine particulates. This application is increasingly important in urban centers across South America and Europe where air pollution affects occupant health and productivity. For buyers, filters with long lifespans, easy replacement mechanisms, and compatibility with existing systems reduce operational costs and downtime. Compliance with regional air quality standards and certifications should guide procurement decisions.
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, offers excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature tolerance (up to 870°C for 316), and robust mechanical strength. It withstands high pressures typically encountered in industrial filtration systems and resists chemical degradation from acidic or alkaline media.
Pros & Cons: Stainless steel is highly durable and requires minimal maintenance, making it ideal for long-term applications. Its resistance to rust and corrosion reduces downtime and replacement costs. However, it is relatively expensive and manufacturing processes such as welding or precision machining can be complex, potentially increasing lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel filters are suitable for aggressive media, including solvents, oils, and acidic fluids. Their hygienic properties make them preferred in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. They perform well in environments with fluctuating temperatures and pressures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should verify compliance with ASTM A240 (for stainless steel plates) or DIN EN 10088 standards to ensure material quality. In regions like Mexico and Indonesia, local import regulations may require certifications confirming corrosion resistance. Stainless steel’s higher cost may be a factor in price-sensitive markets, but its longevity often justifies the investment.
Key Properties: Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer with good chemical resistance, especially to acids and alkalis, and operates effectively in temperatures up to around 100°C. It is lightweight and has moderate mechanical strength, suitable for low to medium pressure filtration systems.
Pros & Cons: PP filters are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for rapid production and customization. They are resistant to many chemicals but have limited temperature and pressure tolerance compared to metals. Their lower durability may lead to more frequent replacements in demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Ideal for water treatment, food processing, and light chemical filtration where corrosive resistance is needed but extreme temperatures or pressures are not present. PP filters are often used in disposable or semi-permanent filtration setups.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D4101 or ISO 1873 standards ensures polypropylene quality. Buyers in tropical regions like Indonesia and parts of Africa should consider UV stabilization additives to prevent material degradation from sunlight exposure. PP’s affordability makes it attractive in emerging markets, but buyers must assess lifecycle costs versus durability.
Key Properties: Carbon steel offers high strength and good machinability but has limited corrosion resistance unless coated or treated. It can handle moderate to high pressures and temperatures up to approximately 400°C but is prone to rust in humid or chemically aggressive environments.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is generally less expensive than stainless steel and easier to fabricate, making it suitable for large-scale industrial applications where cost control is critical. However, it requires protective coatings or regular maintenance to prevent corrosion, which can add to operational costs.
Impact on Application: Best suited for filtration of non-corrosive fluids such as oils, fuels, and gases in controlled environments. Not recommended for acidic or saline media unless adequately protected.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions with high humidity or corrosive atmospheres like coastal areas in South America or the Middle East, carbon steel filters may require additional surface treatments compliant with standards such as ASTM A36 or EN 10025. Buyers should factor in maintenance infrastructure and local availability of protective coatings.
Key Properties: PTFE is renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness, wide temperature range (-200°C to 260°C), and excellent resistance to almost all chemicals. It has a low coefficient of friction and is non-stick, making it ideal for highly corrosive or sticky media.
Pros & Cons: PTFE filters provide unmatched chemical compatibility and longevity in harsh environments. However, they have lower mechanical strength and are more expensive than common polymers. Manufacturing complexity and limited pressure ratings can restrict their use to specialized applications.
Impact on Application: PTFE is preferred in aggressive chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and industries handling highly corrosive fluids or gases. Its non-reactive nature ensures minimal contamination risk.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D4894 or JIS K6760 standards ensures PTFE quality. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East often require certifications for pharmaceutical-grade materials. The higher cost and specialized nature mean PTFE filters are typically procured for critical applications rather than general use.
| Material | Typical Use Case for gpf filter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Chemical, food, pharmaceutical filtration | Excellent corrosion resistance & durability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Polypropylene | Water treatment, light chemical filtration | Cost-effective and good chemical resistance | Limited temperature and pressure tolerance | Low |
| Carbon Steel | Oil, fuel, gas filtration in non-corrosive environments | High strength and low initial cost | Prone to corrosion without protection | Medium |
| PTFE | Aggressive chemical processing, pharma | Superior chemical inertness and temperature range | Lower mechanical strength and higher cost | High |
Manufacturing Gasoline Particulate Filters (GPF filters) involves several critical stages designed to ensure the final product meets stringent performance and durability requirements. For B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these stages and key techniques is essential to evaluate supplier capabilities and product quality.
The process begins with selecting high-quality raw materials, typically ceramic substrates (cordierite or silicon carbide) combined with catalyst coatings. Material preparation includes:
- Powder blending: Precise mixing of ceramic powders to achieve optimal porosity and thermal resistance.
- Catalyst slurry formulation: Preparing catalyst coatings that reduce particulate emissions effectively.
- Quality checks: Ensuring raw materials meet chemical and physical property standards before proceeding.
The ceramic substrate forms the core of the GPF filter, usually manufactured through:
- Extrusion: Ceramic paste is extruded through a die to create a honeycomb structure with thousands of small channels.
- Drying: Controlled drying removes moisture to prevent defects.
- Cutting: The extruded block is cut to specified dimensions for assembly.
This stage is crucial for achieving the right cell density and wall thickness, directly impacting filtration efficiency and backpressure.
Assembly involves:
- Catalyst coating: Applying washcoats containing precious metals (e.g., platinum, palladium) onto the substrate to enable catalytic reactions.
- Mounting: Encasing the substrate in a metal housing designed to withstand thermal expansion and mechanical stresses.
- Sealing: High-temperature sealants ensure no gas bypass occurs around the substrate.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Advanced techniques such as dip-coating or spray-coating ensure uniform catalyst distribution, critical for consistent filter performance.
Final manufacturing steps include:
- Sintering: High-temperature firing to bond catalyst layers and cure ceramic substrates.
- Inspection: Visual and dimensional checks to confirm adherence to design specifications.
- Packaging: Protective packaging to prevent damage during transport, often customized for international shipping requirements.
Quality assurance (QA) in GPF filter manufacturing is multi-layered, incorporating international standards and industry-specific certifications to guarantee product reliability and regulatory compliance.
Effective QC programs typically incorporate three main checkpoints during production:
B2B buyers should be aware of the following testing protocols used to verify GPF filter quality and functionality:
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QA processes is critical due to diverse regulatory landscapes and logistical challenges.
Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide impartial verification of product quality and compliance, reducing risks associated with new or distant suppliers.
Actionable Takeaways for B2B Buyers:
Understanding the intricate manufacturing steps and robust quality assurance mechanisms behind GPF filters empowers international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions, mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with local and global standards.
When evaluating the cost and pricing structure of gpf filters for international B2B procurement, understanding the detailed components and market influencers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This analysis aims to equip buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with actionable insights to optimize sourcing strategies and manage total cost of ownership effectively.
Materials
The primary cost driver is the raw materials used, including specialized metals, ceramics, or composite materials that affect the filter’s durability and efficiency. Variations in material quality and sourcing location can significantly impact prices.
Labor
Skilled labor costs vary by manufacturing region. Countries with advanced production capabilities may have higher labor costs but offer better quality and precision, while others may provide cost advantages with potential trade-offs in quality consistency.
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes factory utilities, maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient factories with modern automation tend to have lower overhead per unit, influencing competitive pricing.
Tooling and Setup Costs
Initial tooling for gpf filters, especially customized designs, can be substantial. These costs are often amortized over the production volume, affecting unit costs for smaller orders.
Quality Control (QC)
Rigorous QC processes ensure compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, CE certifications). While increasing production costs, QC is crucial for reliability and reducing downstream failures.
Logistics and Shipping
Transportation from manufacturing hubs to buyer locations includes freight, customs duties, taxes, and insurance. For buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, logistics can add a significant premium due to longer transit times and complex customs procedures.
Supplier Margin
Supplier profit margins vary by market competition, order size, and supplier positioning. Negotiation can influence margins, especially for repeat or bulk buyers.
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Larger volumes typically reduce unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that balance inventory costs and price benefits.
Product Specifications and Customization
Customized filters with specific dimensions or enhanced performance features command higher prices. Standardized products tend to offer better pricing but may not meet all operational requirements.
Material Quality and Certification
Filters certified for stringent emissions standards or made from premium materials cost more but ensure compliance and longevity, reducing replacement frequency.
Supplier Reputation and Location
Established suppliers with proven track records may charge premiums but reduce risk. Proximity to manufacturing hubs can lower shipping costs and lead times.
Incoterms and Payment Terms
Different Incoterms (FOB, CIF, DAP) shift cost and risk responsibilities between buyer and seller, impacting landed costs. Favorable payment terms can improve cash flow and reduce financial risk.
Leverage Volume Discounts
Consolidate orders or collaborate with regional partners to meet MOQ thresholds and negotiate better pricing.
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Evaluate not just purchase price but also installation, maintenance, warranty, and disposal costs. Higher upfront costs may yield savings over the product lifecycle.
Prioritize Quality and Certification
Especially for buyers in regulated markets, insist on certified products to avoid compliance penalties and costly replacements.
Optimize Logistics Strategy
Work with freight forwarders familiar with your region’s customs and import regulations. Consider consolidated shipments to reduce freight costs.
Negotiate Flexible Payment and Incoterms
Aim for terms that minimize upfront payments and transfer risk appropriately. For example, CIF terms can simplify logistics for buyers less familiar with international shipping.
Engage in Supplier Audits and Samples
Validate supplier quality and manufacturing capabilities before large orders to mitigate risks.
Disclaimer: Pricing for gpf filters varies widely based on specifications, order volume, supplier, and market conditions. The insights provided are indicative and should be supplemented with direct supplier quotations and market research tailored to your specific sourcing context.
Understanding the critical technical properties and trade terminology related to GPF (Gasoline Particulate Filter) filters is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. This knowledge helps ensure product compatibility, compliance with environmental standards, and smooth transaction processes.
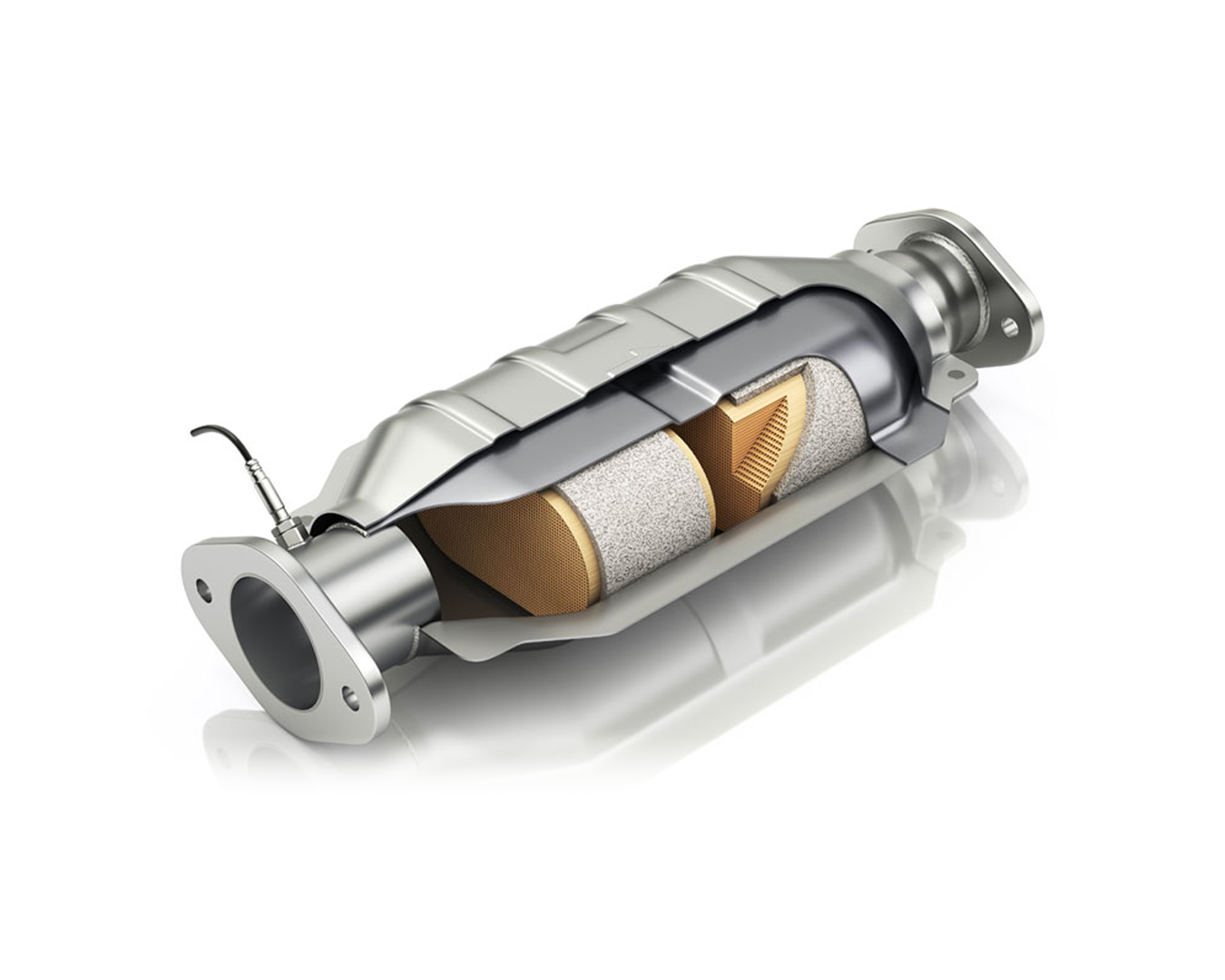

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Material Grade
GPF filters are typically made from ceramic materials such as cordierite or silicon carbide. The choice of material impacts durability, thermal resistance, and filtration efficiency. For buyers, selecting the correct material grade ensures the filter performs reliably under specific engine conditions and meets emission standards relevant to their market.
Filtration Efficiency
This measures the filter’s ability to capture particulate matter (PM) emitted by gasoline engines. Efficiency is often expressed as a percentage, indicating how much particulate matter is trapped. High filtration efficiency is crucial for compliance with increasingly strict environmental regulations, particularly in Europe and parts of the Middle East.
Porosity and Cell Density
Porosity refers to the size and volume of pores in the filter substrate, while cell density indicates the number of channels per square inch (CPSI). These factors influence backpressure and flow rate. Buyers need to balance filtration performance with engine efficiency; a filter with optimal porosity and cell density minimizes power loss and fuel consumption.
Thermal Durability
GPF filters must withstand high operating temperatures without cracking or degrading. Thermal durability is measured by the maximum continuous temperature the filter can endure. This property is critical for markets with demanding driving conditions or high ambient temperatures, such as parts of Africa and South America.
Dimension Tolerances
Precise dimensions and tolerances are vital for proper fitment within the exhaust system. Variations can lead to installation issues or reduced effectiveness. Buyers should verify tolerances against OEM specifications to avoid costly returns or compatibility problems.
Backpressure Characteristics
Backpressure refers to the resistance the filter imposes on exhaust gas flow. Excessive backpressure can reduce engine performance and increase fuel consumption. Understanding this parameter helps buyers assess how the GPF will affect vehicle efficiency and longevity.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to the company that originally manufactures the vehicle or component. Purchasing OEM-compliant or OEM-approved GPF filters ensures quality and compatibility. For B2B buyers, sourcing from OEM or trusted OEM suppliers reduces risk and supports warranty compliance.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for buyers in emerging markets or smaller businesses where upfront investment must be carefully managed.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit price and delivery terms from multiple suppliers. Issuing a clear RFQ with detailed specifications helps buyers compare offers and negotiate better terms, which is particularly important in international trade.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define responsibilities between buyers and sellers during shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP). Familiarity with Incoterms protects buyers from hidden costs and clarifies who handles transportation, insurance, and customs clearance.
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Lead times can vary significantly depending on supplier location, production capacity, and shipping method. Accurate lead time estimation is critical for supply chain planning, especially for markets with fluctuating demand.
Certification and Compliance
Certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management) or compliance with Euro 6 emission standards are often required in the GPF filter industry. Buyers should verify these documents to ensure product reliability and regulatory adherence, reducing the risk of market entry barriers.
By focusing on these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can better evaluate GPF filter suppliers, optimize procurement strategies, and ensure long-term operational success in diverse markets.
The global GPF (Gasoline Particulate Filter) market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasingly stringent emissions regulations worldwide, particularly in Europe, the Middle East, and emerging economies across Africa and South America. Regions such as Indonesia and Mexico are also witnessing rising demand due to urbanization and stricter environmental policies aimed at reducing vehicular particulate emissions. For international B2B buyers, understanding these regulatory frameworks is critical, as compliance often dictates procurement priorities and supplier selection.
Key trends shaping the sourcing landscape include the integration of advanced materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and cordierite that enhance filter efficiency and durability. Suppliers are increasingly adopting digital tools such as AI-driven quality control and IoT-enabled supply chain tracking to improve transparency and reduce lead times. Buyers from Africa and South America should focus on partners who can provide not only compliant products but also logistical flexibility given infrastructure variability.
Additionally, modular and customizable GPF solutions are gaining traction, allowing OEMs and fleet operators to tailor filters to specific engine types and emission standards. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on localized manufacturing and assembly in regions like the Middle East and Europe, which helps reduce costs and environmental impact. For B2B buyers, leveraging regional supplier networks that offer adaptive product designs and robust after-sales support can significantly improve operational resilience.
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the GPF supply chain, with buyers increasingly prioritizing environmental impact alongside cost and quality. GPF manufacturing involves energy-intensive processes and raw materials that can contribute to environmental degradation if not responsibly sourced. Therefore, international buyers should seek suppliers committed to green certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to REACH regulations for chemical safety.
Ethical sourcing practices also extend to labor conditions and transparent supply chain governance. Many buyers in Europe and the Middle East require their suppliers to demonstrate compliance with international labor standards and traceability of raw materials to mitigate reputational risks and ensure long-term supply security.
In terms of materials, there is a growing shift towards using recycled ceramics and bio-based binders in GPF production, which help reduce carbon footprints. Partnerships with suppliers investing in circular economy initiatives can provide buyers with competitive advantages in markets increasingly driven by sustainability mandates. Furthermore, embracing lifecycle analysis tools enables buyers to quantify environmental benefits and communicate sustainability credentials effectively to end customers.
GPF technology has evolved significantly since its inception, initially emerging as a response to tightening particulate matter (PM) emission standards for gasoline engines. Early GPFs focused primarily on mechanical filtration, but advances in materials science led to the adoption of porous ceramic substrates that combine filtration with catalytic functions, improving both efficiency and durability.
The evolution has been closely linked to regulatory milestones, such as the Euro 6d and China 6 emission standards, which pushed OEMs and suppliers to innovate rapidly. This historical progression underscores the importance for B2B buyers to stay informed about regulatory trends and technological advancements to ensure procurement decisions align with future compliance and performance requirements.
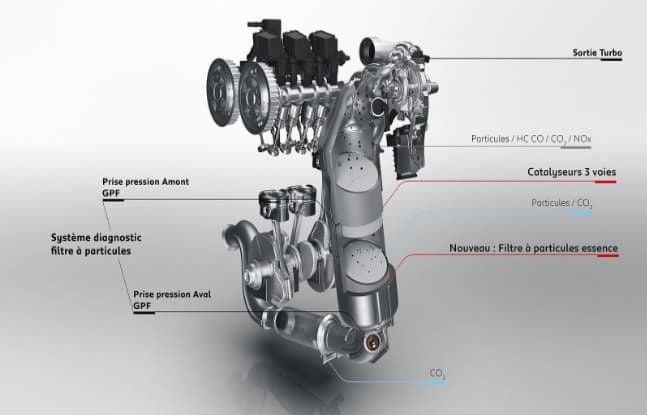
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Is customization of gpf filters available, and what should I consider when requesting tailored products?
Many manufacturers offer customization to meet specific filtration requirements, such as size, material, or filtration efficiency. When requesting customization, clearly define your technical specifications and intended application. Discuss minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized units, as they are often higher than standard products. Ensure that the supplier can provide prototypes or samples before bulk production. Also, verify the impact of customization on lead times and pricing. For international buyers, confirm that any custom products meet your country’s regulatory standards.
What are typical MOQ and lead times for ordering gpf filters in bulk for international shipments?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier and customization level, typically ranging from 500 to 5,000 units. Lead times usually span 4 to 8 weeks, factoring in production and shipping durations. Buyers from regions like the Middle East or Europe should account for additional customs clearance time. Negotiating MOQs is sometimes possible, especially for repeat orders or long-term partnerships. Planning orders well in advance and consolidating shipments can reduce costs and delays associated with international logistics.
What payment terms are common for international B2B transactions when purchasing gpf filters?
Standard payment methods include Telegraphic Transfer (T/T), Letter of Credit (L/C), and increasingly, secure online platforms. Typical terms are 30% upfront deposit and 70% upon shipment or before delivery. For new buyers or large orders, suppliers may request full or partial payment in advance to mitigate risk. It’s advisable to use escrow services or trade assurance programs to protect funds. Clarify currency preferences and exchange rate responsibilities upfront to avoid disputes.
Which quality assurance certifications should I look for to ensure the gpf filters meet international standards?
Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management, CE marking for European markets, and RoHS compliance for environmental safety. Depending on application, certifications like UL or NSF might be relevant. Verification through third-party testing labs adds credibility. These certifications demonstrate adherence to manufacturing best practices and product safety, which is critical for regulatory approvals in your country. Request copies of certificates and test reports during supplier evaluation.
What logistics considerations are crucial when importing gpf filters to regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
Consider port accessibility, customs clearance procedures, and local import regulations. Shipping methods vary from sea freight (cost-effective for large orders) to air freight (faster but expensive). Collaborate with freight forwarders experienced in your region to navigate tariffs, duties, and documentation requirements. Factor in potential delays due to political or infrastructure challenges common in some regions. Consolidating shipments or using bonded warehouses can optimize costs and delivery times.
How should disputes related to product quality or delivery be handled in international gpf filter transactions?
Establish clear contract terms including specifications, delivery schedules, and penalty clauses. Use Incoterms to define responsibilities and risk transfer points. In case of disputes, initiate dialogue with the supplier to seek amicable resolution, possibly involving mediation. Document all communications and discrepancies with evidence such as photos or inspection reports. If unresolved, consider arbitration through international trade bodies like the ICC. Having a well-drafted contract and third-party inspection can minimize risks.
Can suppliers provide after-sales support or maintenance services for gpf filters, and how important is this for international buyers?
After-sales support is crucial, especially for technical products like gpf filters. Many reputable suppliers offer warranty periods, technical guidance, and replacement parts. For buyers in remote or developing markets, confirm the availability of local service partners or remote support options. Effective after-sales service reduces downtime and enhances product lifespan, protecting your investment. Negotiate support terms before purchase and include them in the contract to ensure accountability.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
The strategic sourcing of GPF filters presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers to enhance operational efficiency while meeting increasingly stringent environmental standards. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of partnering with reliable manufacturers who offer certified, high-performance filters that align with regional regulatory requirements and sustainability goals. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers with proven expertise in customization and robust after-sales support to ensure long-term value.
Strategic sourcing enables buyers to leverage competitive pricing, optimize supply chain resilience, and access cutting-edge filtration technologies. This approach not only mitigates risks related to quality and compliance but also facilitates scalability as emission regulations evolve globally.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced GPF filters is expected to grow, driven by heightened environmental awareness and tightening emissions policies. International buyers are encouraged to adopt a proactive sourcing strategy—engaging early with innovative suppliers, investing in thorough due diligence, and fostering collaborative partnerships. By doing so, businesses can secure a sustainable competitive advantage and contribute meaningfully to global emission reduction efforts. Embrace strategic sourcing today to future-proof your supply chain and drive long-term success in the evolving landscape of GPF filtration technology.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina