Navigating the complexities of sourcing high-quality boron carbide, known for its exceptional hardness and durability, can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of this critical material is essential for informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves deep into the various types of boron carbide, its wide-ranging applications in industries such as aerospace, defense, and manufacturing, as well as the intricacies of supplier vetting and pricing strategies.
As a buyer, knowing how to assess the hardness of boron carbide and its implications on performance can dramatically influence your selection process. This comprehensive resource aims to empower you with actionable insights, allowing you to navigate supplier landscapes effectively, optimize procurement costs, and ensure compliance with international quality standards.
The guide will cover essential aspects such as the different grades of boron carbide, their respective applications, and how to evaluate suppliers based on quality assurance practices. Additionally, we will provide tips on negotiating favorable terms and understanding market trends that could impact pricing. By leveraging this guide, you will be better equipped to make strategic decisions that align with your business goals and operational needs.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Boron Carbide | High hardness and wear resistance | Abrasives, cutting tools | Pros: Cost-effective; widely available. Cons: Limited temperature resistance. |
| Boron Carbide Ceramics | Enhanced toughness and thermal stability | Armor plating, industrial applications | Pros: Excellent thermal properties; customizable. Cons: Higher cost; more complex manufacturing. |
| Boron Carbide Nanoparticles | Ultra-fine particles with increased reactivity | Advanced coatings, electronics, and composites | Pros: Superior performance; lightweight. Cons: Limited scalability; higher production costs. |
| Boron Carbide Composites | Combination with other materials for enhanced properties | Aerospace, automotive, and military applications | Pros: Tailored properties; improved impact resistance. Cons: Complex supply chain; potentially higher price. |
| Doped Boron Carbide | Modified with additives for specific enhancements | Semiconductor applications, neutron absorbers | Pros: Targeted property enhancements; versatile. Cons: Potentially inconsistent quality; specialized suppliers. |
Standard boron carbide is known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it a popular choice in various abrasive applications. This type is commonly used in manufacturing cutting tools and abrasive materials due to its cost-effectiveness and wide availability. However, it may not perform well under extreme temperature conditions, which is an important consideration for buyers in industries requiring heat resistance.
Boron carbide ceramics are engineered to enhance toughness and thermal stability, making them suitable for high-performance applications such as armor plating and industrial uses. Their excellent thermal properties allow them to withstand high temperatures without degrading. While they offer significant advantages, the complexity of their manufacturing process can lead to higher costs, which buyers must weigh against their specific needs.
Boron carbide nanoparticles provide unique benefits due to their ultra-fine particle size, which increases reactivity and enhances performance in advanced coatings, electronics, and composite materials. These nanoparticles are lightweight and contribute to improved functionality in various applications. However, their production can be limited in scalability, resulting in higher costs that may affect purchasing decisions for bulk buyers.
Boron carbide composites combine boron carbide with other materials to create tailored properties suitable for demanding applications in aerospace, automotive, and military sectors. These composites often exhibit improved impact resistance and can be customized to meet specific requirements. However, buyers should be aware of the complexities involved in the supply chain and the potential for higher prices associated with these specialized materials.
A stock image related to hardness of boron carbide.
Doped boron carbide is modified with various additives to achieve specific enhancements, making it versatile for applications such as semiconductors and neutron absorbers. This type provides targeted property improvements, which can be crucial for advanced technological applications. However, buyers should consider the potential for inconsistent quality and the need to source from specialized suppliers, which can complicate procurement processes.
Related Video: Boron Carbide: Hardness Unleashed
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hardness of boron carbide | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of cutting tools and abrasives | Enhanced tool longevity and performance | Evaluate supplier certifications and material quality |
| Defense and Military | Armor and ballistic protection materials | Superior protection against penetration | Assess compliance with international defense standards |
| Electronics and Semiconductors | Semiconductor manufacturing processes | Improved precision and reduced defect rates | Ensure compatibility with existing manufacturing processes |
| Mining and Mineral Processing | Wear-resistant components for machinery | Reduced downtime and maintenance costs | Focus on sourcing from established suppliers with proven track records |
| Automotive | Engine components and grinding applications | Increased efficiency and durability of parts | Look for suppliers with expertise in automotive-grade materials |
In the aerospace sector, the hardness of boron carbide is utilized in the production of cutting tools and abrasives. These tools are essential for machining high-strength materials like titanium and composites, which are commonly used in aircraft manufacturing. The exceptional hardness of boron carbide extends the life of these tools, reducing the frequency of replacements and ensuring consistent performance during operations. International buyers should seek suppliers who can guarantee the quality of their boron carbide products, along with relevant certifications that meet aerospace industry standards.
Boron carbide is a critical material in the defense industry, specifically for armor and ballistic protection applications. Its high hardness provides superior resistance against penetration from projectiles, making it ideal for personal and vehicle armor. This application is crucial for ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment in combat zones. B2B buyers must consider suppliers with experience in military-grade materials and compliance with stringent defense specifications to ensure reliability and effectiveness.
In the electronics and semiconductor sectors, boron carbide is employed in various manufacturing processes, particularly in the production of semiconductor wafers. Its hardness contributes to improved precision during cutting and grinding operations, which is vital for maintaining low defect rates in sensitive electronic components. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers who have a proven track record in semiconductor applications and can provide materials that meet the specific purity and dimensional requirements of the industry.
The mining and mineral processing industries benefit significantly from the hardness of boron carbide in creating wear-resistant components for machinery. These components, such as liners and nozzles, experience extreme wear due to abrasive materials and harsh operating conditions. By using boron carbide, companies can reduce equipment downtime and maintenance costs, leading to increased productivity. Buyers in this sector should focus on suppliers with established reputations for durability and performance in harsh environments.
In the automotive industry, boron carbide is used in various applications, including engine components and grinding processes. Its hardness enhances the efficiency and durability of parts, contributing to improved vehicle performance and longevity. For international B2B buyers, it is essential to ensure that suppliers can provide automotive-grade materials that comply with industry standards and can withstand the rigorous demands of automotive applications.
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly from industries such as aerospace and defense, often struggle with the precise hardness specifications of boron carbide materials. This is critical, as the performance of components made from boron carbide, such as armor and cutting tools, hinges on achieving specific hardness levels. Buyers may find it challenging to determine whether the boron carbide they are sourcing meets their stringent requirements, leading to potential failures in application and wasted financial resources.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should establish clear communication with suppliers regarding hardness testing methodologies. Request detailed documentation of hardness testing results, including the specific standards used (e.g., Vickers, Rockwell, or Mohs scale). Buyers can also benefit from investing in independent third-party testing to validate the hardness of boron carbide materials prior to purchase. Additionally, developing a comprehensive specification sheet that outlines the required hardness levels along with tolerances can facilitate better alignment with suppliers and ensure that the products sourced will meet performance expectations.
The Problem: Buyers often encounter inconsistencies in the hardness quality of boron carbide from different suppliers. This variation can stem from differences in production processes, raw material quality, or even geographic sourcing. Such inconsistencies not only lead to unpredictable performance in applications but also complicate inventory management and increase costs due to the need for additional testing and quality assurance measures.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize establishing long-term relationships with a select few trusted suppliers who demonstrate consistent quality control processes. Conducting supplier audits can provide insights into their production methods and quality assurance practices. Additionally, implementing a robust quality management system that includes regular incoming inspections and batch testing can help identify discrepancies early in the supply chain. Buyers may also consider collaborating with suppliers to develop joint quality improvement initiatives, ensuring that both parties are aligned on expectations and standards.
The Problem: In industries like manufacturing and mining, the effectiveness of boron carbide tools and components is directly tied to their hardness. When there are variances in hardness, users may find that tools wear out faster than expected or fail during operation, leading to costly downtimes and project delays. This unpredictability creates frustration and mistrust in the materials supplied, ultimately affecting business operations.
The Solution: To counteract these challenges, buyers should engage in thorough application testing before full-scale deployment of boron carbide products. This includes conducting pilot tests to assess the performance of tools under actual working conditions. Furthermore, buyers should ensure that they have access to comprehensive data from their suppliers regarding the hardness and wear characteristics of the materials. Implementing a feedback loop with suppliers to report performance issues can also drive improvements in product offerings. Finally, exploring advanced coatings or treatments can help enhance the durability of boron carbide tools, compensating for any minor hardness inconsistencies and extending their lifespan.
When selecting materials for applications requiring the hardness of boron carbide, it is crucial to consider various alternatives that can complement or serve specific needs in different contexts. Here, we analyze four common materials: silicon carbide, tungsten carbide, alumina, and polycrystalline diamond. Each material offers distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact product performance and suitability for international B2B buyers.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is known for its exceptional hardness, thermal stability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,600°C) and has a high thermal conductivity, making it suitable for high-performance applications, such as abrasives and cutting tools. However, its brittleness can be a disadvantage in applications requiring toughness.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: High thermal conductivity, excellent wear resistance, and good corrosion resistance.
- Cons: Brittle nature can lead to failure under shock loading; manufacturing processes can be complex and costly.
Impact on Application:
Silicon carbide is particularly effective in abrasive applications and environments involving high temperatures or corrosive media. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice for industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Tungsten carbide (WC) is renowned for its extreme hardness and toughness, often used in mining, drilling, and metalworking applications. It can withstand high pressures and is resistant to deformation. Tungsten carbide typically has a hardness level that exceeds that of boron carbide, making it an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Superior hardness and toughness, excellent wear resistance, and high impact strength.
- Cons: Higher cost and density can limit its use in lightweight applications; machining can be challenging due to its hardness.
Impact on Application:
Tungsten carbide is ideal for tools and components exposed to extreme wear and tear, such as drill bits and cutting tools. Its performance in harsh environments makes it a preferred choice in mining and construction sectors.
Alumina (Al2O3) is a ceramic material known for its hardness, thermal stability, and electrical insulation properties. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,600°C and is often used in applications requiring thermal resistance and electrical insulation. However, its brittleness is a notable downside.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: High hardness, excellent thermal stability, and good electrical insulation.
- Cons: Brittle nature limits its use in applications requiring toughness; lower toughness compared to tungsten carbide.
Impact on Application:
Alumina is commonly used in electrical insulators, wear-resistant coatings, and cutting tools. Its compatibility with high temperatures makes it suitable for applications in the electronics and aerospace industries.
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) is synthesized from diamond particles and is known for its unparalleled hardness and wear resistance. It is often used in cutting tools and abrasive applications. PCD can withstand high temperatures and has excellent thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Exceptional hardness, superior wear resistance, and high thermal conductivity.
- Cons: High manufacturing costs and brittleness can limit its application scope.
Impact on Application:
PCD is particularly effective in machining non-ferrous materials and is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries. Its performance in high-speed cutting applications makes it a valuable choice for manufacturers.
| Material | Typical Use Case for hardness of boron carbide | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide | Abrasives, cutting tools | High thermal conductivity | Brittle nature under shock loading | Medium |
| Tungsten Carbide | Mining, drilling tools | Superior hardness and toughness | Higher cost and machining challenges | High |
| Alumina | Electrical insulators, wear-resistant coatings | Excellent thermal stability | Brittle nature, lower toughness | Medium |
| Polycrystalline Diamond | Cutting tools, abrasive applications | Exceptional hardness and wear resistance | High manufacturing costs | High |
This analysis provides international B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of alternative materials for applications requiring the hardness of boron carbide, facilitating informed decision-making based on specific needs and market conditions.
Boron carbide, known for its exceptional hardness, is primarily utilized in various industries such as defense, nuclear, and abrasive applications. The manufacturing process is intricate and involves several key stages that ensure the material meets the required specifications for hardness and durability.
The manufacturing process begins with the preparation of raw materials. The primary components for boron carbide production include boron oxide (B2O3) and carbon in the form of petroleum coke or graphite. These materials are carefully weighed and mixed in precise proportions to achieve the desired chemical composition.

A stock image related to hardness of boron carbide.
Once mixed, the materials undergo a milling process to reduce particle size, enhancing homogeneity and reactivity. This is followed by a drying stage to eliminate moisture, which can negatively affect the sintering process later on.
The forming stage is crucial for shaping the boron carbide into its final form. Two primary techniques are commonly employed:
Hot Pressing: This method involves applying heat and pressure simultaneously to compact the powder into a dense form. The high temperature (typically around 2000°C) allows for the diffusion of atoms, improving the material's hardness.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): This advanced technique utilizes electrical discharges to rapidly heat and densify the boron carbide powder. SPS is known for producing materials with superior mechanical properties due to its fast processing times and reduced grain growth.
Finishing processes are essential to achieve the required dimensional tolerances and surface finishes. Common techniques include:
Grinding: This method is used to refine the dimensions and surface finish of the final product. Precision grinding ensures that the boron carbide components meet the stringent specifications demanded by various industries.
Coating: In some applications, a protective or functional coating may be applied to enhance performance or reduce wear. This is particularly important in abrasive applications where surface integrity is crucial.
Quality assurance is paramount in the production of boron carbide, especially given its applications in high-stakes environments. Adherence to international standards is critical for ensuring product reliability.
For boron carbide manufacturing, several international standards can guide B2B buyers:
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable to organizations aiming to ensure consistent quality in their products and services. Certification under ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer has established a robust quality management framework.
ISO 14001: While primarily environmental-focused, this standard also plays a role in ensuring that manufacturing processes are sustainable, which is increasingly important for B2B buyers concerned with corporate social responsibility.
Industry-Specific Standards: Depending on the application, other certifications may be relevant. For instance, CE marking is important for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), and API standards may apply for products used in the oil and gas industry.
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each stage meets the necessary quality standards. The following checkpoints are commonly implemented:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. Strict criteria are set to ensure only materials that meet specifications are used.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various parameters are monitored to ensure that the production adheres to quality standards. This includes checking temperature, pressure, and other critical variables.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the product is completed, a comprehensive evaluation is conducted to confirm that it meets all specified requirements. This may involve physical testing, such as hardness testing, microstructural analysis, and dimensional checks.
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier's quality control measures is vital to ensure product integrity. Here are several actionable steps:
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess the supplier’s quality management system and production processes. This includes reviewing documentation, inspecting facilities, and interviewing personnel.
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results. These reports should detail any deviations from standards and corrective actions taken.
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier's quality control measures. This adds an additional layer of verification, particularly for high-value contracts.
B2B buyers need to be aware of the nuances associated with quality control certifications, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. Different regions may have varying standards and certifications, which can affect product compliance.
Understanding Regional Standards: Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific standards applicable in their region. For instance, products sold in the EU must comply with CE marking requirements, while those in the Middle East may require GSO certification.
Language and Documentation Barriers: Ensure that all quality control documentation is available in a language that is understandable. This is crucial for accurate assessments and compliance verification.
Building Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality control measures. Regular discussions can lead to improved transparency and trust.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards associated with boron carbide, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and ensure the reliability of their supply chains.
When sourcing boron carbide, particularly for its hardness properties, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of specifications, suppliers, and regulations. This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed to streamline the procurement process. By following these actionable steps, you can ensure that you select the right product and supplier to meet your specific needs.
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to clearly define your technical specifications for boron carbide hardness. This includes understanding the required hardness levels, particle size distribution, and purity levels.
Engage in thorough market research to identify potential suppliers and understand the current market landscape for boron carbide. This will help you gauge pricing, quality, and availability.
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold necessary certifications that align with international standards. This is particularly important for products used in high-stakes applications.
Once you have identified potential suppliers, it’s time to negotiate terms and conditions. This step is vital to ensure favorable pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms.
Implement quality control measures to ensure that the boron carbide you receive meets your specifications. This can help mitigate risks associated with product quality.
Finally, consider the logistics and supply chain aspects of your procurement process. This includes shipping, handling, and storage of boron carbide.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for boron carbide, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to source boron carbide, particularly for applications requiring high hardness. The primary cost components include:
Several factors can influence the pricing of boron carbide, which international buyers should consider:
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can adopt several strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
It is essential to note that prices for boron carbide can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific buyer requirements. Therefore, it is advisable to request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and favorable terms.
In the competitive landscape of industrial materials, understanding the alternatives to boron carbide in terms of hardness is crucial for B2B buyers. Boron carbide is renowned for its exceptional hardness, making it a preferred choice in various applications such as armor and cutting tools. However, other materials and methods can also offer suitable hardness properties, depending on specific requirements and contexts. This analysis will compare boron carbide with two viable alternatives: silicon carbide and tungsten carbide.
| Comparison Aspect | Hardness of Boron Carbide | Silicon Carbide | Tungsten Carbide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Extremely hard (9.3 Mohs) | Hard (9.0 Mohs) | Very hard (8.5-9.0 Mohs) |
| Cost | High | Moderate | High |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate | Easy | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Best Use Case | Ballistic protection, abrasives | Abrasives, semiconductors | Cutting tools, mining |
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a widely used alternative known for its hardness and thermal conductivity. With a hardness rating of 9.0 on the Mohs scale, it is slightly less hard than boron carbide but offers excellent performance in high-temperature applications. Silicon carbide is easier to implement due to its availability and established manufacturing processes. However, while it is generally cost-effective, specific applications may demand a premium for high-purity SiC. Maintenance is minimal, making it suitable for applications in abrasives and semiconductor devices.
Tungsten carbide (WC) is another alternative that is frequently used in industrial applications. It offers a hardness range of 8.5 to 9.0 Mohs, making it very hard but slightly less so than boron carbide. Tungsten carbide is particularly valued in cutting tools and mining operations due to its durability and resistance to wear. The implementation process can be complex, often requiring specialized equipment and techniques. Although it shares a high cost with boron carbide, its longevity can justify the investment. Maintenance can be more demanding compared to silicon carbide, especially in environments with high abrasion.
When considering hardness solutions, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application needs against the performance characteristics, costs, and maintenance requirements of each material. Boron carbide remains an excellent choice for applications requiring the highest hardness and durability. However, silicon carbide may be more suitable for less demanding environments or applications with cost constraints. Tungsten carbide, while high in cost, provides exceptional wear resistance and is ideal for cutting tools. Ultimately, selecting the right hardness solution involves balancing these factors to meet operational objectives and budget constraints effectively.
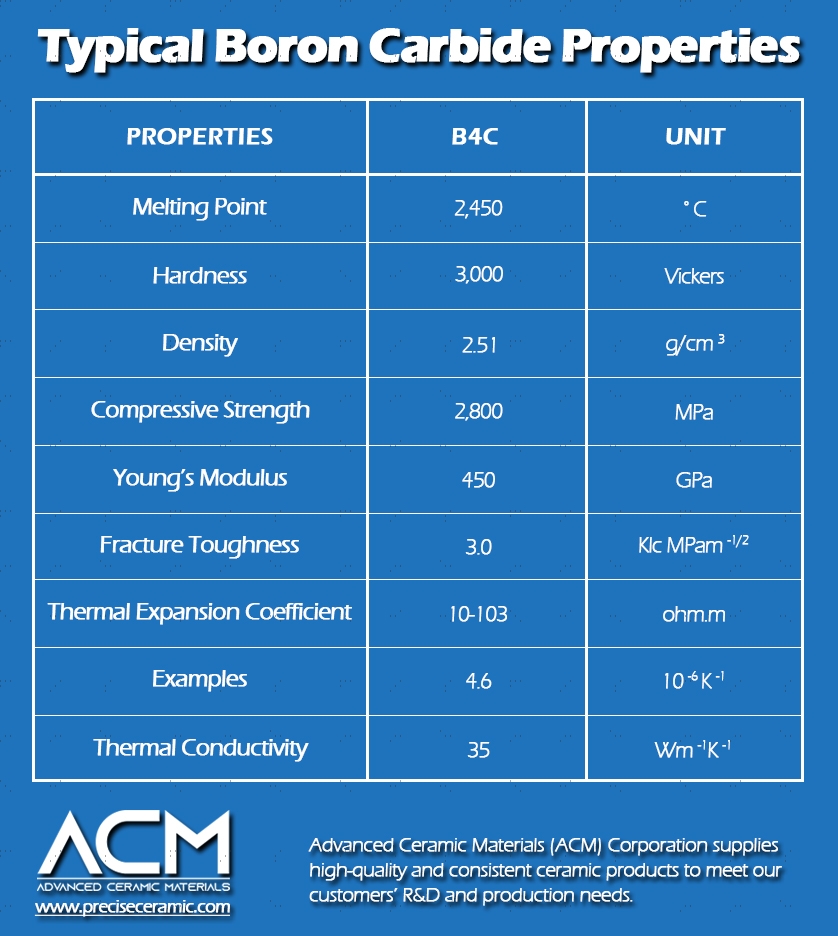
Boron carbide (B4C) is renowned for its exceptional hardness, making it a highly sought-after material in various industrial applications. Understanding its technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in sectors such as defense, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Material grade refers to the specific classification of boron carbide based on its purity and crystalline structure. Higher-grade boron carbide, typically over 90% purity, is more effective in applications requiring high hardness and durability. B2B buyers should prioritize the material grade when selecting boron carbide, as it directly impacts performance and longevity in demanding environments.
The hardness of boron carbide is commonly measured using the Vickers or Mohs scale. Boron carbide typically scores around 9.5 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials available. This property is crucial for applications such as abrasives and armor, where resistance to wear and impact is essential. Buyers should inquire about the hardness measurements provided by suppliers to ensure they meet application requirements.
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in boron carbide components. Tight tolerances are often required in precision applications, such as in the manufacturing of cutting tools or protective gear. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers assess whether the supplied materials will fit seamlessly into their production processes, minimizing waste and ensuring quality.
Density is a vital property that affects the material's weight and strength. Boron carbide has a density of approximately 2.52 g/cm³, contributing to its lightweight yet robust nature. For B2B buyers, this is particularly relevant in aerospace and automotive applications, where reducing weight without compromising strength can lead to enhanced performance and efficiency.
Boron carbide exhibits excellent thermal stability, maintaining its properties at high temperatures. This characteristic is especially important in applications involving high-heat environments, such as nuclear reactors or aerospace components. Buyers should assess thermal stability ratings to ensure that the boron carbide they purchase will perform under specific operational conditions.
Understanding industry jargon is essential for international B2B buyers to navigate procurement processes effectively.
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When purchasing boron carbide components, buyers often engage with OEMs who provide specialized products tailored to their needs. Establishing relationships with reputable OEMs can lead to better quality assurance and reliability.
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of boron carbide, understanding the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess costs or surplus inventory.
An RFQ is a formal process used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products. B2B buyers should prepare detailed RFQs when seeking boron carbide materials to ensure they receive accurate and competitive pricing. Including technical specifications in the RFQ can help suppliers provide the most relevant quotes.
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines when importing boron carbide. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight).
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times for boron carbide is crucial for planning production schedules and maintaining supply chain efficiency. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers about expected lead times to avoid project delays.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding boron carbide procurement, ensuring that they select the right materials for their specific applications.
The global market for boron carbide is witnessing significant growth, driven by rising demand across various industries including defense, nuclear, and automotive sectors. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, evaluate their sourcing strategies, it’s crucial to be aware of the key trends shaping this market. A notable driver is the increasing focus on advanced materials that offer superior hardness and lightweight properties. This trend is further amplified by technological advancements in manufacturing processes that enhance the quality and performance of boron carbide products.
Emerging sourcing trends also highlight the importance of digitalization in procurement processes. Businesses are increasingly adopting e-commerce platforms and digital supply chains to streamline operations and improve efficiency. For instance, leveraging data analytics can help international buyers identify reliable suppliers and forecast demand more accurately. Additionally, collaboration with suppliers through integrated supply chain management systems is becoming essential for ensuring timely delivery and maintaining quality standards.
Sustainability is emerging as a critical consideration for international B2B buyers in the boron carbide sector. The environmental impact of sourcing raw materials cannot be overlooked. Ethical sourcing practices are becoming a fundamental aspect of supply chain management, as businesses aim to minimize their carbon footprint and adhere to regulatory standards. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who employ environmentally friendly practices, such as reducing waste and utilizing renewable energy sources in their manufacturing processes.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other 'green' certifications for materials can serve as a benchmark for evaluating suppliers. These certifications not only enhance a company’s reputation but also align with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products. By focusing on ethical supply chains, B2B buyers can foster long-term partnerships with suppliers committed to sustainability, ultimately leading to a more resilient and responsible sourcing strategy.
The hardness of boron carbide has evolved significantly since its first commercial applications in the early 20th century. Initially utilized primarily in abrasive applications, its remarkable hardness properties made it a sought-after material in various industrial sectors. Over the decades, advancements in processing technologies have expanded its applications to include nuclear reactors, ballistic armor, and advanced composites.
Today, the versatility of boron carbide continues to drive innovation, with ongoing research focused on enhancing its properties and discovering new applications. As international B2B buyers navigate this dynamic landscape, understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into future trends and opportunities in sourcing boron carbide products.
How do I determine the hardness of boron carbide for my specific application?
To determine the hardness of boron carbide suitable for your application, consider the Mohs hardness scale, where boron carbide ranks around 9.5, making it one of the hardest materials available. Assess the operational conditions, such as the types of abrasives and environmental factors, to ensure compatibility. Conducting a hardness test, such as a Vickers or Rockwell hardness test, can provide precise measurements. Collaborate with suppliers who can offer tailored advice based on your unique requirements, ensuring optimal performance in your specific industry applications.
What are the most important properties of boron carbide for industrial use?
Boron carbide is prized for its exceptional hardness, chemical resistance, and low density, making it ideal for various industrial applications. Its high wear resistance makes it suitable for grinding and cutting tools, while its ability to withstand corrosive environments extends its usability in chemical processing. Additionally, boron carbide exhibits excellent thermal stability, making it effective in high-temperature applications. When sourcing, ensure that suppliers provide detailed material specifications to match your industrial needs.
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of boron carbide?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, production capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Request certifications like ISO 9001 to ensure they adhere to international quality standards. Evaluate their material sourcing practices to guarantee the quality and consistency of boron carbide. Additionally, consider their ability to provide technical support and customization options. Engaging with previous clients or seeking references can also provide insights into their reliability and service quality.
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for boron carbide products?
Minimum order quantities for boron carbide products can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from a few kilograms to several tons. It is essential to clarify the MOQ during initial discussions to ensure it aligns with your project needs and budget. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller enterprises, so negotiating terms can be beneficial. Understanding your projected usage can help in making an informed decision regarding the quantity you commit to.
What payment terms are typical when purchasing boron carbide internationally?
Payment terms for international boron carbide purchases typically include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days. Each supplier may have different policies, so it’s crucial to discuss and negotiate terms upfront. Consider the risks associated with each payment method, especially in international transactions, and choose a method that provides security and trust. Establishing a clear agreement on payment terms can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process.
How can I ensure quality assurance for boron carbide products?
To ensure quality assurance for boron carbide products, request a certificate of analysis (COA) from suppliers, detailing the material's hardness and other critical properties. Implement a rigorous inspection process upon receipt of goods, including random sampling and testing. Collaborate with suppliers who have established quality control measures in place and are willing to share their QA documentation. Regular audits and communication with suppliers can further enhance quality assurance and maintain consistent product standards.
What are the logistics considerations when importing boron carbide?
Logistics considerations when importing boron carbide include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial materials to facilitate smooth transport. Ensure that all documentation, including bills of lading and import permits, is accurate and complete to avoid delays. Additionally, consider the lead times for production and shipping when planning your procurement to align with your project timelines.
Can boron carbide be customized for specific applications?
Yes, boron carbide can often be customized to meet specific application requirements. Suppliers may offer variations in particle size, purity levels, and formulations tailored for particular uses, such as abrasives or protective coatings. Discuss your specific needs with suppliers to explore available customization options. Collaborating closely with manufacturers can also help in developing specialized solutions that enhance performance in your intended application.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
The strategic sourcing of boron carbide, recognized for its exceptional hardness and versatility, presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers. By understanding the unique properties and applications of boron carbide, businesses can effectively leverage this material in industries ranging from defense to manufacturing. The key takeaway is that informed sourcing decisions, backed by thorough market analysis and supplier evaluation, can lead to cost savings and enhanced product performance.
Strategic sourcing not only reduces procurement costs but also strengthens supply chain resilience. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing relationships with reliable suppliers of boron carbide can provide a competitive edge in meeting specific industry demands. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and innovation will further align with global trends and customer expectations.
As the demand for high-performance materials continues to rise, now is the time for B2B buyers to invest in relationships with suppliers and explore new markets. By staying informed about advancements in boron carbide applications and sourcing strategies, companies can position themselves for success. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your sourcing strategy today, and unlock the potential of boron carbide for your business's future growth.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina