In today’s interconnected industrial landscape, sourcing silicon carbide (SiC) rods is pivotal for manufacturers and suppliers aiming to enhance product performance and operational efficiency. These rods serve as essential components in high-temperature applications, semiconductor devices, and abrasive machining, making them indispensable across various sectors such as electronics, automotive, and chemical processing. For international B2B buyers—particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the complexities of the SiC rod market is critical to securing reliable supply chains and competitive pricing.
This comprehensive guide demystifies the global SiC rod market by providing detailed insights into the different types and grades of SiC rods, their material properties, and manufacturing processes. It also covers stringent quality control standards that ensure product consistency and durability, which are especially crucial when sourcing from diverse geographic regions. Buyers will gain clarity on evaluating suppliers, comparing cost structures, and navigating logistics challenges inherent in cross-border transactions.
Key areas covered include:
- Types and specifications of SiC rods tailored for various industrial needs
- Material composition and performance characteristics
- Manufacturing methods and quality assurance protocols
- Supplier evaluation criteria and sourcing strategies
- Pricing trends and cost optimization tactics
- Regional market dynamics affecting availability and delivery timelines
- Answers to frequently asked questions to resolve common procurement uncertainties
By leveraging the insights and practical guidance within this guide, international B2B buyers can make informed, strategic sourcing decisions that minimize risk, optimize costs, and ensure consistent product quality—empowering businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to thrive in a competitive global market.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard SiC Rod | High purity silicon carbide, uniform diameter | Industrial heating elements, kiln furniture | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited mechanical strength. |
| Sintered SiC Rod | Manufactured by sintering SiC powder under pressure | High-temperature reactors, aerospace parts | Pros: Superior strength and thermal stability. Cons: Higher cost, longer lead times. |
| Reaction-Bonded SiC Rod | Produced via silicon infiltration, porous core | Chemical processing, wear-resistant parts | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance. Cons: Porosity may limit load-bearing capacity. |
| Doped SiC Rod | Silicon carbide doped with elements like boron | Semiconductor manufacturing, electronics | Pros: Enhanced electrical properties. Cons: Specialized use, higher price. |
| Composite SiC Rod | SiC combined with other ceramics or metals | Advanced manufacturing, cutting tools | Pros: Tailored mechanical and thermal properties. Cons: Complex supply chain, variable costs. |
Standard SiC Rod
Standard silicon carbide rods are characterized by their high purity and consistent dimensions, making them a reliable choice for general industrial applications such as heating elements and kiln furniture. Their cost-effectiveness and widespread availability suit buyers seeking volume procurement without specialized performance needs. However, they exhibit limited mechanical strength, which may restrict their use in more demanding environments. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where cost efficiency is often critical, standard rods provide a practical balance of quality and price.
Sintered SiC Rod
Sintered silicon carbide rods are produced by compacting SiC powder under high pressure and temperature, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability. These rods are ideal for high-temperature reactors and aerospace components where durability under extreme conditions is paramount. While their superior properties justify higher costs, buyers should account for longer lead times and ensure supplier reliability. European and Middle Eastern companies engaged in advanced manufacturing will find sintered rods valuable for critical applications requiring longevity and performance.
Reaction-Bonded SiC Rod
Reaction-bonded rods, created through silicon infiltration into porous carbon or SiC preforms, offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for chemical processing equipment and wear-resistant parts. Their porous core, however, may limit their load-bearing capacity, which buyers must consider when specifying for structural applications. This type is particularly relevant for industries in the Middle East and Europe focused on chemical and petrochemical sectors, where material resilience against aggressive environments is essential.
Doped SiC Rod
Doped silicon carbide rods incorporate elements such as boron to modify electrical properties, catering primarily to semiconductor manufacturing and electronic component production. These rods command a premium due to their specialized nature and precise doping processes. Buyers from technologically advanced markets, including Poland and Australia, should evaluate supplier capabilities to ensure doping consistency and compliance with industry standards, as these factors directly impact device performance.
Composite SiC Rod
Composite silicon carbide rods blend SiC with other ceramics or metals to achieve tailored mechanical and thermal properties. These rods are used in advanced manufacturing processes and cutting tools where specific performance attributes like toughness or thermal conductivity are required. The complexity of their supply chain and variable costs necessitate thorough supplier vetting and contract negotiation. International buyers aiming for innovation-driven sectors will benefit from composites but must carefully balance cost against application-specific gains.
Related Video: Sicilian Defense ALL Variations Explained [Chess Opening Crash Course]
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sic rod | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Heating elements in crystal growth furnaces | High thermal stability and chemical inertness improve crystal quality and yield | Purity grade, dimensional tolerances, and supplier certifications for electronic-grade materials |
| Metallurgical Industry | Components in induction heating and metal melting | Enhances energy efficiency and extends equipment lifespan | Thermal conductivity specifications, mechanical strength, and reliable delivery schedules |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Wear-resistant parts in high-temperature environments | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs due to superior durability | Consistency in material composition, compliance with automotive standards, and batch traceability |
| Chemical Processing | Reactor liners and high-temperature seals | Corrosion resistance under harsh chemical exposure prolongs service life | Chemical compatibility data, resistance certifications, and packaging to prevent contamination |
| Renewable Energy | Components in solar power equipment and thermal storage | Improves performance and longevity in extreme environmental conditions | Custom sizing, thermal expansion properties, and logistics for remote installations |
Electronics & Semiconductors:
In semiconductor manufacturing, SiC rods are integral to heating elements used in crystal growth furnaces, such as those for silicon or gallium nitride wafers. Their exceptional thermal stability and chemical inertness ensure uniform temperature distribution and minimize contamination, which is critical for high-quality crystal formation. Buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing rods with electronic-grade purity and strict dimensional tolerances to meet the precision required by semiconductor fabs.
Metallurgical Industry:
SiC rods serve as components in induction heating systems and metal melting furnaces, where they withstand extreme temperatures and thermal cycling. Their superior thermal conductivity improves energy efficiency, while mechanical robustness reduces downtime caused by component failure. For international buyers in Europe and Australia, it is essential to verify thermal and mechanical specifications and work with suppliers who can guarantee consistent quality and timely deliveries to avoid production interruptions.
Automotive Manufacturing:
In automotive production lines, SiC rods are used for wear-resistant parts exposed to high temperatures, such as in exhaust systems or engine components. Their durability helps reduce maintenance frequency and extends equipment life, ultimately lowering operational costs. Buyers should ensure material consistency and compliance with automotive industry standards, along with batch traceability to maintain quality control throughout the supply chain.
Chemical Processing:
SiC rods are employed as reactor liners and seals in chemical processing plants, where resistance to corrosive substances and high temperatures is paramount. Their chemical inertness prevents contamination and degradation, ensuring longer service life and safer operations. International B2B buyers must request detailed chemical compatibility data and certifications, and ensure packaging protects the rods from moisture and contaminants during transit.
Renewable Energy:
In solar thermal power and energy storage systems, SiC rods are used for components that endure extreme environmental conditions and thermal stresses. Their stability enhances system efficiency and durability, which is critical for long-term energy projects. Buyers, especially from remote regions in Africa and South America, should consider custom sizing options, thermal expansion properties, and logistics solutions that support delivery to off-grid installations.
Related Video: Uses Of Polymers | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Key Properties:
Standard grade SiC rods exhibit excellent thermal conductivity and high mechanical strength, withstanding temperatures up to 1600°C. They offer good corrosion resistance against acidic and alkaline environments, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
These rods are highly durable and provide consistent performance under thermal cycling. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, which helps keep costs reasonable. However, they may have limitations in extremely aggressive chemical environments or where ultra-high purity is required.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for general-purpose applications such as kiln furniture, heating elements, and mechanical seals. Their resistance to thermal shock and moderate corrosion makes them versatile for chemical processing industries.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers in Africa and South America should verify compliance with ASTM C799 or equivalent standards to ensure quality consistency. European buyers, including Poland, often require adherence to DIN standards, while Middle Eastern clients may prioritize JIS or ISO certifications. Availability and lead times can vary regionally, so early engagement with suppliers is recommended.
Key Properties:
RB-SiC rods are characterized by their high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and good thermal stability up to 1400°C. They also exhibit superior corrosion resistance, especially against molten metals and aggressive chemical media.
Pros & Cons:
The reaction bonding process results in lower manufacturing costs compared to sintered SiC, making RB-SiC rods more cost-effective. However, they have slightly lower mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance than sintered grades, which may limit their use in highly dynamic thermal environments.
Impact on Application:
Well-suited for abrasive environments, such as pump components, valve seats, and mechanical seals in chemical and petrochemical plants. Their corrosion resistance makes them a preferred choice for handling acidic or alkaline fluids.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers from the Middle East and South America should confirm product certification against ASTM C120 or equivalent, as these standards ensure material reliability. For European markets, compliance with EN standards and RoHS directives is often necessary. Import regulations and tariffs may affect pricing and delivery schedules, so strategic sourcing is vital.
Key Properties:
Sintered SiC rods offer superior mechanical strength, exceptional thermal shock resistance, and excellent chemical inertness. They can operate continuously at temperatures exceeding 1700°C and resist oxidation better than other SiC types.
Pros & Cons:
While offering the highest performance, sintered SiC rods come at a premium price due to complex manufacturing processes. Their brittleness requires careful handling during installation and operation. The high cost may limit their use to critical applications where performance justifies the investment.
Impact on Application:
Preferred in high-stress environments such as semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace components, and high-temperature furnace parts. Their outstanding durability under extreme conditions ensures long service life and reduced downtime.
International Buyer Considerations:
European buyers, especially in advanced manufacturing hubs like Germany and Poland, often require compliance with stringent ISO and EN standards. Middle Eastern and African buyers should ensure suppliers provide full traceability and quality documentation. Given the cost, buyers must evaluate total cost of ownership, including maintenance savings.
Key Properties:
This composite SiC rod variant incorporates graphite to enhance thermal conductivity and machinability while maintaining good corrosion resistance. It performs well at temperatures up to 1500°C and offers moderate resistance to chemical attack.
Pros & Cons:
The addition of graphite improves machinability, allowing for complex shapes and tighter tolerances. However, graphite content can reduce overall corrosion resistance and mechanical strength compared to pure SiC rods. This trade-off must be carefully considered based on application needs.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in applications requiring precise machining, such as custom seals, nozzles, and wear parts in fluid handling systems. Suitable for less aggressive chemical environments where ease of fabrication is prioritized.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers in South America and Africa often favor these rods for cost-effective custom solutions. Compliance with ASTM and JIS standards is critical to ensure material consistency. European buyers may require additional certifications related to environmental impact due to graphite content.
| Material | Typical Use Case for sic rod | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (Standard Grade) | Kiln furniture, heating elements, general seals | Balanced thermal resistance and corrosion resistance | Limited performance in ultra-aggressive media | Medium |
| Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide | Pump components, valve seats, mechanical seals | Cost-effective with good wear and corrosion resistance | Lower strength and thermal shock resistance | Low |
| Sintered Silicon Carbide | Semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace, furnace parts | Superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance | High cost and brittleness | High |
| Bonded SiC with Graphite Additives | Custom machined parts, nozzles, wear components | Enhanced machinability and thermal conductivity | Reduced corrosion resistance and mechanical strength | Medium |
The production of silicon carbide (SiC) rods involves a series of highly controlled stages to ensure material integrity, dimensional accuracy, and performance under demanding industrial applications. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes helps in evaluating supplier capabilities and product suitability.
Silicon carbide rods start with high-purity raw materials, primarily silicon carbide powder synthesized via the Acheson process or chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The powder’s particle size distribution, purity level, and chemical composition are critical parameters. Suppliers typically source high-grade SiC powders with controlled impurities to achieve optimal mechanical and thermal properties.
The SiC powder is mixed with binders and additives to facilitate shaping. Common forming techniques include:
Forming methods influence the rod’s microstructure, porosity, and mechanical strength, critical factors for high-performance applications.
Post-forming, the rods undergo sintering at temperatures typically ranging from 2000°C to 2200°C in an inert or vacuum atmosphere. This process densifies the material by bonding SiC grains, enhancing hardness, thermal conductivity, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
Some manufacturers also apply secondary heat treatments or hot isostatic pressing (HIP) to improve toughness and reduce internal defects. These steps are crucial for applications requiring high thermal shock resistance and mechanical durability.
After sintering, rods are machined to final dimensions using diamond grinding wheels or laser cutting to achieve tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes. Surface treatments such as chemical etching or coating may be applied to improve oxidation resistance or electrical insulation properties.
Consistent finishing is vital for ensuring compatibility with downstream assembly processes and system integration.
Robust quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) systems are foundational to reliable SiC rod supply. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with comprehensive QC protocols aligned with global standards.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC rigor is essential to mitigate risks associated with product failures, shipment delays, and compliance issues.
Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide unbiased verification of product quality before shipment. This is particularly valuable for buyers without local presence near the manufacturing site.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
For B2B buyers sourcing SiC rods internationally, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and rigorous quality assurance frameworks is crucial. Prioritize suppliers with transparent, certified quality systems and invest in audits and third-party inspections to ensure product integrity. Tailoring quality verification to the regulatory landscapes of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe will safeguard supply continuity and product performance in demanding industrial applications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
When sourcing silicon carbide (SiC) rods, it is essential to break down the cost components to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary factors contributing to the final price include:
Several factors influence the quoted price and should be carefully evaluated:
To optimize procurement of SiC rods, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Australia and Poland), consider the following actionable insights:
Prices for SiC rods vary widely depending on specifications, order size, and market conditions. The figures provided by suppliers should be treated as indicative. Buyers are advised to conduct thorough due diligence, request multiple quotes, and verify all cost components to avoid unexpected expenses.
By understanding these cost and pricing factors, international B2B buyers can strategically source SiC rods that align with their technical requirements and budget constraints, ensuring competitive advantages in their respective markets.
When sourcing Silicon Carbide (SiC) rods, understanding key technical specifications is vital for ensuring product performance and compatibility with your application. Here are the most important properties international B2B buyers should consider:
Material Grade
SiC rods come in various grades such as Alpha (α) and Beta (β) Silicon Carbide, each with distinct crystalline structures and purity levels. Higher purity grades offer superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, which are crucial for high-temperature or abrasive environments. Selecting the correct grade impacts product lifespan and operational efficiency.
Dimensional Tolerance
This refers to the allowable variation in the rod’s diameter and length from specified dimensions. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm) are essential in precision applications like semiconductor manufacturing or high-precision machining. For buyers, understanding tolerance limits helps avoid costly rejections or rework.
Density
Density affects the mechanical strength and thermal properties of the SiC rod. Higher density generally means fewer pores and defects, leading to improved durability and resistance to thermal shock. Buyers should verify density specifications to ensure the rods meet the demands of their industrial processes.
Flexural Strength
This property measures the rod’s resistance to bending forces. High flexural strength is critical in applications where mechanical stress is frequent, such as in kiln furniture or wear-resistant parts. Knowing this parameter aids in assessing the rod’s suitability for structural or load-bearing roles.
Thermal Conductivity
SiC rods are prized for their excellent heat dissipation. Thermal conductivity ratings indicate how efficiently the rod can transfer heat, which is essential in high-temperature applications like induction heating or power electronics. Buyers must match conductivity values to operational temperature requirements.
Surface Finish
The surface quality of the rod, often specified as roughness average (Ra), affects its friction and wear characteristics. A smooth finish is important for components interacting with other precision parts, while a rougher finish might be acceptable for abrasive applications. Surface finish impacts both performance and assembly ease.
Navigating the global supply chain for SiC rods requires familiarity with industry jargon and trade terms to streamline communication and avoid misunderstandings. Here are essential terms every international buyer should know:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or components used in another company’s end products. Many SiC rod suppliers serve OEMs in automotive, aerospace, or electronics sectors. Understanding OEM requirements helps buyers ensure quality and compliance with industry standards.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell in one order. For buyers in emerging markets or smaller enterprises, negotiating MOQs can be crucial to managing inventory costs and cash flow. Awareness of MOQ policies also aids in planning procurement cycles efficiently.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal inquiry sent to suppliers asking for pricing, lead times, and terms based on specified product requirements. Crafting clear and detailed RFQs for SiC rods ensures accurate and comparable bids, enabling buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These standardized trade terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Common Incoterms for SiC rods include FOB (Free on Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Understanding Incoterms is critical to managing logistics risks and costs.
Lead Time
This is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. SiC rods, especially those with custom specifications, may have longer lead times. Buyers should factor lead times into project schedules to avoid production delays.
Batch Number / Lot Number
These identifiers track production batches for quality control and traceability. For industries requiring strict compliance, such as aerospace or medical devices, batch numbers help verify material consistency and facilitate recalls if necessary.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can better evaluate suppliers, optimize procurement strategies, and ensure that the SiC rods they acquire meet both performance and commercial expectations. This knowledge is particularly valuable for buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where supply chain complexities demand clear communication and precise specifications.
The global market for silicon carbide (SiC) rods is experiencing robust growth driven by expanding applications in high-performance electronics, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. SiC rods serve as critical components in power devices, semiconductors, and LED manufacturing due to their superior thermal conductivity, high breakdown electric field, and chemical stability. For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these market dynamics is essential for strategic sourcing and supply chain resilience.
Key Market Drivers:
- Electrification and Renewable Energy: The surge in electric vehicles (EVs) and solar power systems is propelling demand for SiC-based power electronics, which offer greater efficiency and reduced energy loss.
- Industrial Automation and 5G: Increasing automation and next-generation telecommunications infrastructure require SiC components for enhanced performance under high-frequency and high-temperature conditions.
- Supply Chain Localization: Geopolitical factors and pandemic-induced disruptions have pushed many buyers to diversify sourcing channels, emphasizing regional suppliers in Europe and the Middle East to mitigate risks.
Emerging B2B Sourcing Trends:
- Digital Procurement Platforms: Buyers are leveraging AI-driven platforms to identify reliable SiC rod suppliers, compare certifications, and optimize pricing.
- Collaborative Supply Agreements: Long-term partnerships and joint development contracts with manufacturers are becoming common to secure priority access to high-quality SiC materials.
- Customization and Technical Support: Demand is rising for tailored SiC rod specifications to meet precise industrial requirements, coupled with enhanced supplier technical assistance.
For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local production capacity is limited, establishing strong relationships with European or Asian manufacturers is crucial. Meanwhile, companies in the Middle East and Europe benefit from proximity to advanced manufacturing hubs and a growing network of certified suppliers.
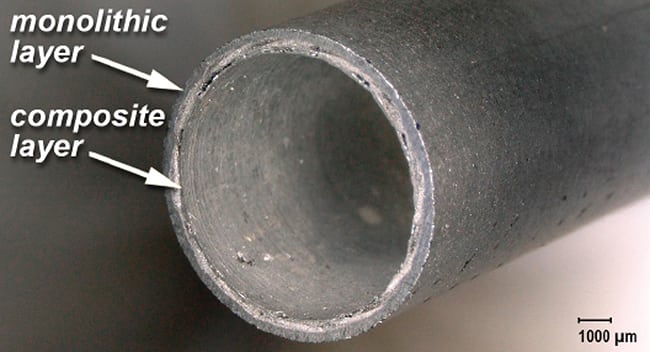
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the SiC rod sector due to the environmental impact associated with raw material extraction and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. For B2B buyers, integrating sustainability criteria into procurement decisions not only aligns with global regulatory trends but also enhances brand reputation and long-term operational viability.
Environmental Impact Considerations:
- Energy Consumption: SiC rod production involves high-temperature processes that consume significant energy, often sourced from fossil fuels. Buyers should seek suppliers utilizing renewable energy or implementing energy-efficient technologies.
- Raw Material Sourcing: Ethical sourcing of raw materials, such as silicon and carbon, ensures compliance with conflict mineral regulations and reduces ecological degradation.
Importance of Ethical Supply Chains:
- Transparency and traceability are critical to avoid supply chain risks related to labor rights violations and environmental non-compliance.
- Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) standards indicate supplier commitment to sustainable practices.
Green Certifications and Materials:
- Some suppliers are developing SiC rods with reduced carbon footprints or using recycled feedstock, appealing to eco-conscious buyers.
- Procuring SiC rods certified under recognized sustainability frameworks can facilitate compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations in Europe and beyond.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate measurable sustainability initiatives and provide comprehensive environmental impact reporting. This approach supports circular economy goals and aligns purchasing strategies with global sustainability commitments.
Silicon carbide’s journey from a laboratory curiosity to a cornerstone material in advanced electronics spans over a century. Initially discovered in the late 19th century, SiC gained industrial prominence in the mid-20th century with the advent of semiconductor technology. The development of high-purity SiC rods has been instrumental in enabling devices that operate at higher voltages and temperatures than conventional silicon.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution underscores the technological sophistication and quality control required in sourcing SiC rods. The sector’s ongoing innovation, particularly in wafer fabrication and material purity, directly impacts the performance and reliability of downstream products. This historical context highlights the importance of partnering with experienced suppliers who invest in cutting-edge manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
How can I effectively vet suppliers of SiC rods to ensure product quality and reliability?
To vet SiC rod suppliers, request detailed product specifications, including material grade and manufacturing process. Verify certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific quality standards. Ask for samples and conduct independent lab testing if possible. Review the supplier’s track record with international clients, especially in your region, and check references. Utilize platforms with verified supplier information and consider visiting factories or conducting virtual audits. Transparent communication about production capabilities and quality assurance processes is crucial to minimize risks in international transactions.
What customization options are typically available for SiC rods, and how should I approach these with suppliers?
SiC rods can often be customized in terms of diameter, length, purity, density, and surface finish to suit specific industrial applications. When discussing customization, clearly specify your technical requirements and intended use. Confirm the supplier’s ability to meet these specifications and inquire about minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom products. Request prototype samples before bulk ordering. Establish clear documentation of customization details in contracts to avoid misunderstandings, and factor in additional lead times and costs associated with bespoke manufacturing.
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms I should expect when purchasing SiC rods internationally?
MOQs for SiC rods vary widely but typically range from a few hundred to several thousand units depending on customization and supplier scale. Lead times can span 4–12 weeks, influenced by order size, production complexity, and shipping logistics. Payment terms often include a 30% advance deposit with the balance paid upon shipment or after inspection. Negotiate terms based on your buyer history and order volume; leveraging trade finance tools like letters of credit or escrow services can provide security. Always clarify incoterms to understand who bears shipping risks and costs.
Which quality assurance certifications and testing standards should I verify when sourcing SiC rods?
Prioritize suppliers that provide ISO 9001 certification, ensuring consistent quality management systems. Additional certifications like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) compliance and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) are important for environmental and safety compliance, especially for European buyers. Confirm that suppliers conduct mechanical testing (hardness, flexural strength) and chemical composition analysis. Request detailed test reports and certificates of analysis (CoA) with each shipment to ensure the rods meet your technical and regulatory requirements.
What logistical considerations should international buyers keep in mind when importing SiC rods?
SiC rods are generally non-hazardous but require careful packaging to prevent damage during transit. Opt for suppliers experienced in export packaging compliant with international shipping standards. Understand customs regulations and import duties applicable in your country to avoid unexpected costs or delays. Choose reliable freight forwarders and clarify shipping modes—air freight for urgent orders or sea freight for cost efficiency. Track shipments proactively and maintain clear communication with suppliers to manage delivery timelines effectively.
How can I mitigate risks related to disputes or product non-conformance with SiC rod suppliers?
Establish clear contractual terms covering product specifications, delivery schedules, inspection rights, and penalties for non-compliance. Use third-party inspection agencies to verify quality before shipment. Maintain thorough documentation of all communications and agreements. In case of disputes, attempt resolution through negotiation or mediation before escalating to arbitration or legal action. Choosing suppliers with a strong reputation and transparent business practices reduces the likelihood of conflicts. Consider trade insurance to protect against financial losses due to disputes.
Are there regional considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe when sourcing SiC rods?
Yes, regional factors such as import regulations, local certifications, and currency fluctuations can impact procurement. African and South American buyers may face longer shipping times and higher freight costs; consolidating orders or partnering with local distributors can optimize costs. Middle Eastern buyers should verify compliance with GCC standards, while European buyers must ensure REACH and RoHS compliance. Currency hedging and choosing suppliers with flexible payment options help mitigate financial risks. Understanding local market demands and supplier responsiveness is key for successful sourcing.
What strategies can international buyers use to build long-term partnerships with SiC rod suppliers?
Focus on transparent communication and mutual understanding of business goals. Share forecasts and feedback regularly to enable suppliers to plan production efficiently. Engage in periodic quality reviews and joint problem-solving initiatives to improve product performance. Offering volume commitments or longer contract terms can secure better pricing and priority production slots. Attend industry trade shows and supplier events to strengthen relationships. Building trust through consistent payments and respecting cultural differences enhances collaboration and supply chain resilience.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
The strategic sourcing of SiC rods demands a nuanced understanding of material specifications, supplier capabilities, and regional market dynamics. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging a well-structured sourcing strategy ensures access to high-quality silicon carbide rods that meet stringent industrial standards while optimizing cost efficiency and supply reliability.
Key takeaways include the importance of verifying supplier certifications, prioritizing partners with proven technical expertise, and considering logistics infrastructure to mitigate lead times and reduce total landed costs. Additionally, engaging in collaborative supplier relationships can unlock innovation and enhance supply chain resilience amid fluctuating global demand.
Looking ahead, the SiC rod market is poised for growth driven by expanding applications in electronics, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. Buyers who proactively invest in strategic sourcing frameworks—incorporating comprehensive supplier assessments and market intelligence—will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
For international buyers aiming to secure competitive advantages, now is the time to deepen supplier partnerships, explore diversified sourcing regions, and integrate sustainability criteria into procurement decisions. This forward-thinking approach will not only safeguard supply continuity but also drive long-term value in an increasingly dynamic global marketplace.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina