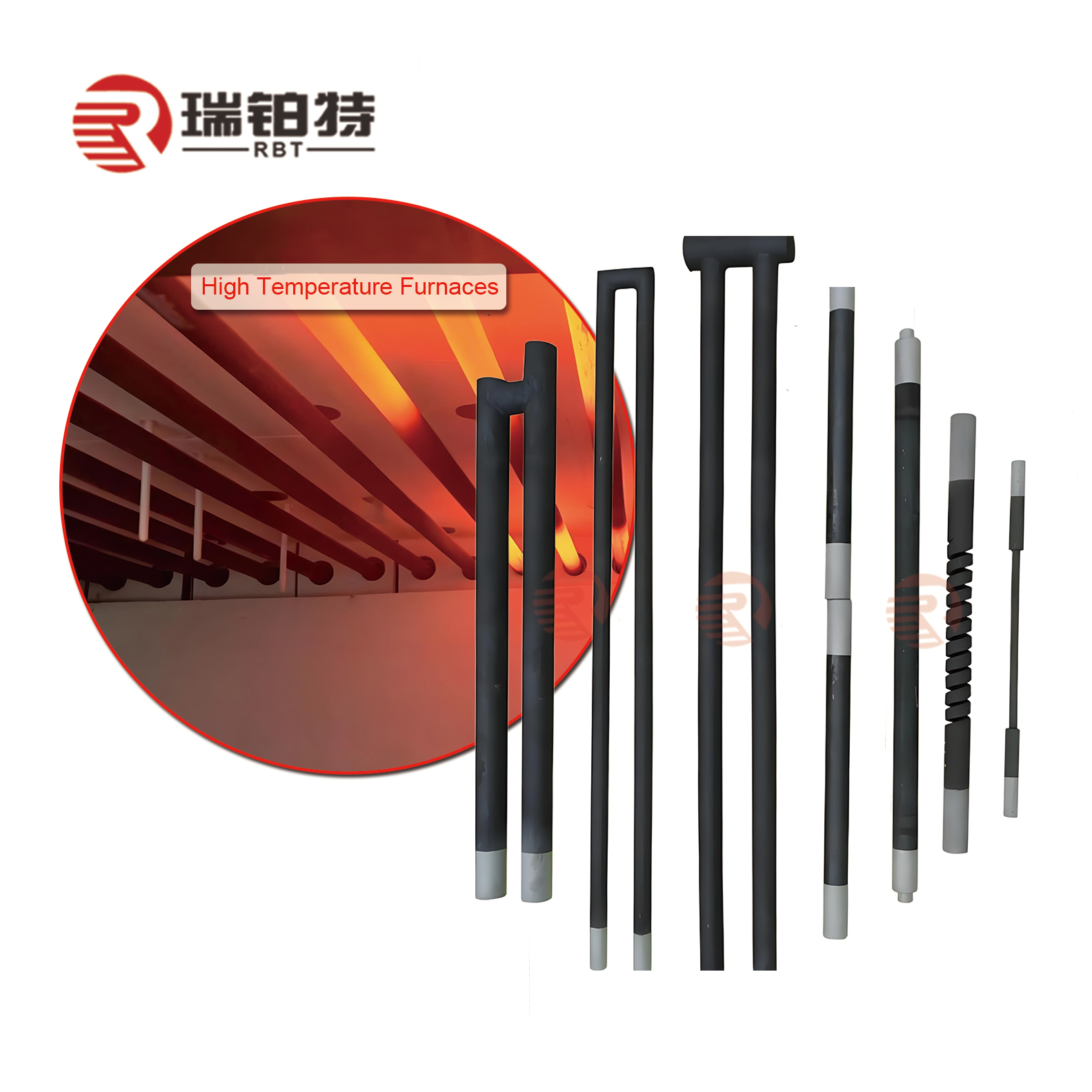
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, silicon carbide (SiC) rods have emerged as indispensable components across a wide range of high-performance applications—from electronics and aerospace to energy and manufacturing. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the complexities of the SiC rods market is crucial to securing reliable, cost-effective, and quality-driven supply chains.
SiC rods offer exceptional properties such as high thermal conductivity, superior hardness, and outstanding chemical resistance, making them vital for sectors demanding durability and precision. However, the global market for SiC rods is diverse and often fragmented, with variations in types, manufacturing processes, quality standards, and supplier capabilities. This diversity can pose challenges for buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies while mitigating risks related to quality and delivery timelines.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international buyers with actionable insights into the SiC rods market. It covers:
By leveraging this knowledge, buyers from Colombia, Argentina, Nigeria, UAE, Germany, and beyond can make strategic sourcing decisions that enhance operational efficiency, reduce total cost of ownership, and build resilient supply chains in an increasingly competitive global market.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard SiC Rods | High-purity silicon carbide, uniform diameter | Industrial heating elements, kilns, furnaces | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available Cons: Limited customization, moderate thermal shock resistance |
| Doped SiC Rods | Silicon carbide with additives (e.g., boron, nitrogen) for enhanced conductivity | Electric heating, semiconductor manufacturing | Pros: Improved electrical properties Cons: Higher cost, specialized handling required |
| Sintered SiC Rods | Manufactured via sintering process for high density and strength | High-temperature structural components | Pros: Superior mechanical strength, excellent thermal stability Cons: More expensive, heavier weight |
| Reaction-Bonded SiC Rods | Produced by reacting silicon with carbon, resulting in high purity and toughness | Chemical processing, corrosive environments | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight Cons: Lower mechanical strength compared to sintered rods |
| Composite SiC Rods | Silicon carbide combined with other ceramics or metals | Aerospace, advanced electronics, wear parts | Pros: Tailored properties, enhanced durability Cons: Complex manufacturing, premium pricing |
Standard SiC Rods
Standard silicon carbide rods are characterized by their high purity and consistent diameter, making them a reliable choice for general industrial heating applications such as kilns and furnaces. They offer a balance of performance and cost, suitable for buyers seeking dependable thermal resistance without specialized requirements. When sourcing, buyers should consider supplier quality control and availability to ensure consistent batch performance, especially for large-scale operations in regions like Africa and South America where supply chain reliability can vary.
Doped SiC Rods
These rods incorporate specific additives like boron or nitrogen to enhance electrical conductivity, making them ideal for electric heating elements and semiconductor manufacturing processes. For B2B buyers, the increased cost is justified by improved efficiency and product lifespan. However, handling and storage require more care due to their specialized nature. Buyers in technologically advanced sectors, including electronics manufacturing hubs in Europe and the Middle East, will find doped rods particularly valuable for precision applications.
Sintered SiC Rods
Produced through a high-temperature sintering process, these rods exhibit superior density and mechanical strength, suited for high-temperature structural components. Their robustness makes them attractive to industries requiring durability under extreme conditions, such as heavy manufacturing or energy sectors. The higher price point reflects enhanced performance, so buyers should evaluate lifecycle costs versus upfront investment, especially when targeting markets with demanding industrial standards like those in Europe.
Reaction-Bonded SiC Rods
Formed by reacting molten silicon with carbon, these rods offer excellent corrosion resistance and lighter weight compared to sintered variants. They are well-suited for chemical processing equipment and environments exposed to aggressive media. B2B buyers focusing on chemical plants or harsh environmental conditions, prevalent in Middle Eastern and African markets, should prioritize these rods for their longevity and reduced maintenance costs. However, the trade-off includes somewhat lower mechanical strength, which must be factored into design considerations.
Composite SiC Rods
Composite rods blend silicon carbide with other ceramics or metals to achieve tailored properties such as enhanced wear resistance or thermal stability. These are often employed in aerospace, advanced electronics, and high-wear parts manufacturing. Due to their complex production and premium pricing, composite rods are typically procured by buyers requiring customized solutions and willing to invest in cutting-edge materials technology. International buyers from sectors emphasizing innovation, including South America and Europe, should assess supplier capabilities and certification standards carefully to ensure product performance aligns with stringent application demands.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sic rods | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Wafer processing and equipment components | High thermal conductivity and electrical insulation improve device performance and longevity | Purity grade and dimensional tolerances critical; ensure supplier can meet stringent specs |
| Metallurgy & Foundry | Heating elements in high-temperature furnaces | Enhanced durability and resistance to thermal shock reduce downtime and maintenance costs | Consistent quality and batch uniformity essential; verify heat resistance certifications |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Components in high-performance braking systems | Superior wear resistance and thermal stability increase safety and component lifespan | Compliance with industry-specific standards and traceability important for certification |
| Chemical Processing | Corrosion-resistant parts in reactors and pipelines | Improved chemical resistance extends equipment life and reduces replacement frequency | Material composition and compatibility with local chemical environments must be verified |
| Renewable Energy | Components in solar power equipment and thermal systems | High efficiency and thermal stability contribute to energy conversion efficiency and durability | Supplier capability to provide customized shapes and sizes to fit specific system designs |
In the electronics sector, silicon carbide (SiC) rods are widely used in wafer processing equipment and as components in semiconductor manufacturing tools. Their exceptional thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties help maintain stable operating conditions, essential for producing high-quality semiconductors. For international buyers, especially from regions like Europe and South America, sourcing high-purity SiC rods with tight dimensional tolerances is critical to meet the stringent requirements of semiconductor fabrication. Establishing relationships with suppliers who can provide certification and consistent quality ensures process reliability and reduces the risk of costly production interruptions.
SiC rods serve as heating elements in high-temperature industrial furnaces used in metallurgy and foundry operations. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist thermal shock significantly extends furnace life and reduces maintenance frequency. For B2B buyers in Africa and the Middle East, where operational conditions can be harsh, selecting SiC rods with proven heat resistance and uniform quality is vital. Evaluating supplier credentials and testing certifications for thermal durability can help mitigate operational risks and optimize furnace performance.
In automotive and aerospace industries, SiC rods are utilized in manufacturing components such as high-performance brake systems and wear-resistant parts. Their superior wear resistance and thermal stability contribute to enhanced safety and longer service intervals. Buyers from regions like Colombia and Argentina must ensure that SiC rods comply with relevant industry standards and certifications, as traceability and material consistency are paramount for safety-critical applications. Partnering with suppliers who understand these compliance requirements can streamline procurement and quality assurance processes.
Chemical reactors and pipelines often incorporate SiC rods for their excellent corrosion resistance against aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. This application reduces equipment degradation and replacement costs, boosting operational uptime. International buyers should carefully assess the chemical compatibility of SiC rods with their specific process fluids and operating environments. In markets such as the Middle East, where chemical processing is a major industry, verifying material composition and obtaining detailed technical data sheets from suppliers is essential for ensuring long-term performance.
The renewable energy sector leverages SiC rods in solar power generation equipment and thermal energy systems. Their high thermal stability and efficiency improve energy conversion rates and system durability under fluctuating environmental conditions. For buyers in Europe and South America aiming to optimize renewable installations, sourcing SiC rods tailored to precise shapes and sizes can enhance system integration and performance. Working with manufacturers capable of customization and rapid delivery supports project timelines and innovation goals.
Related Video: Wide Bandgap SiC and GaN Devices - Characteristics & Applications
Key Properties:
Pure silicon carbide rods exhibit exceptional hardness and thermal conductivity, withstanding temperatures up to 1600°C. They offer excellent corrosion resistance against acids and alkalis, and maintain structural integrity under high pressure. Their low thermal expansion reduces thermal shock risk, making them ideal for demanding environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage is durability and resistance to wear, which translates into long service life and reduced maintenance costs. However, pure SiC rods are relatively expensive and require sophisticated manufacturing processes, including sintering at high temperatures. This complexity can lead to longer lead times and higher upfront costs.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for high-temperature furnaces, chemical reactors, and abrasive environments. Their chemical inertness makes them suitable for handling aggressive media such as strong acids or molten metals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Africa and South America should verify compliance with ASTM C799 (Standard Specification for Dense Silicon Carbide) or equivalent DIN standards to ensure material quality. In the Middle East and Europe, JIS and EN standards are commonly referenced, so suppliers must provide certification accordingly. Due to import costs, buyers should consider local or regional suppliers with proven quality to optimize logistics and tariffs.
Key Properties:
RB-SiC rods combine silicon carbide with residual free silicon, offering moderate thermal conductivity and excellent corrosion resistance. They perform well up to 1400°C and have good mechanical strength but slightly lower hardness compared to pure SiC.
Pros & Cons:
This material is more cost-effective than pure SiC due to a simpler manufacturing process involving silicon infiltration. However, the presence of free silicon reduces chemical resistance in highly acidic environments and limits performance under extreme thermal cycling.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in applications where moderate chemical resistance is sufficient, such as kiln furniture, pump components, and heat exchangers. RB-SiC is suitable for media like molten glass and mild alkalis.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like Colombia and Argentina, where cost sensitivity is high, RB-SiC offers a good balance between performance and price. Buyers should ensure the material meets ASTM C1204 or equivalent standards and confirm the silicon content to avoid premature corrosion. European buyers often require compliance with EN 60672-4 for ceramic materials used in thermal applications.
Key Properties:
Sintered SiC rods are fully dense with no free silicon, offering superior hardness, thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness. They withstand temperatures up to 1700°C and are highly resistant to oxidation and abrasion.
Pros & Cons:
SSiC rods provide the best overall performance but come at a premium price due to complex sintering processes and raw material costs. Manufacturing lead times can be longer, and machining is challenging, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for ultra-demanding environments such as semiconductor processing, aerospace components, and advanced chemical reactors. Their resistance to aggressive media, including strong oxidizers and molten metals, makes them indispensable in high-end industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, where stringent quality and certification are critical, SSiC rods should comply with ASTM C1464 or ISO 8009 standards. African and South American buyers should evaluate total cost of ownership, factoring in durability and reduced downtime, to justify the higher initial investment.
Key Properties:
SiC-C composite rods combine silicon carbide with carbon phases to enhance toughness and thermal shock resistance. They perform well up to 1500°C and exhibit improved fracture toughness compared to pure SiC.
Pros & Cons:
The addition of carbon improves mechanical resilience but reduces chemical resistance, especially in oxidizing environments. These rods are moderately priced and easier to machine than pure or sintered SiC.
Impact on Application:
Well-suited for applications requiring impact resistance and moderate chemical exposure, such as mechanical seals and wear parts in slurry pumps. Not recommended for highly acidic or oxidizing media.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with variable environmental conditions, such as parts of Africa and South America, may benefit from the enhanced toughness of SiC-C composites. However, compliance with ASTM C795 or equivalent standards should be verified to ensure consistent quality. European buyers often demand traceability and certification to EN or ISO standards.
| Material | Typical Use Case for sic rods | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High-temperature furnaces, chemical reactors | Exceptional hardness and chemical resistance | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide (RB-SiC) | Kiln furniture, pump parts, heat exchangers | Cost-effective with good corrosion resistance | Limited chemical resistance due to free silicon | Medium |
| Sintered Silicon Carbide (SSiC) | Semiconductor processing, aerospace, advanced reactors | Superior thermal shock resistance and durability | Premium price and difficult machining | High |
| Silicon Carbide with Carbon Additives (SiC-C Composite) | Mechanical seals, wear parts in slurry pumps | Improved toughness and thermal shock resistance | Reduced chemical resistance in oxidizing media | Medium |
Silicon carbide (SiC) rods are critical components in numerous industrial applications, including electronics, metallurgy, and chemical processing, due to their exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance. Understanding the manufacturing process enables B2B buyers to assess supplier capabilities and product consistency effectively.
The manufacturing journey begins with high-purity raw materials: silicon and carbon sources such as petroleum coke or graphite. These materials undergo precise weighing and mixing to ensure the correct stoichiometric balance for SiC synthesis. The purity and particle size of these inputs significantly influence the final rod quality.
The mixture is then subjected to shaping processes to form the rod’s initial geometry:
The choice of forming technique impacts dimensional tolerances and mechanical strength, critical factors for end-use performance.
Post-forming, the rods undergo sintering, a high-temperature heat treatment that bonds SiC particles into a dense, solid structure:
For multi-component assemblies, rods may be integrated with metallic or ceramic parts during this stage using brazing or mechanical fastening.
After sintering, rods often require finishing operations to meet precise dimensional and surface quality requirements:
Quality assurance is paramount to ensure SiC rods meet stringent performance and safety standards. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with typical QC frameworks and verification methods to mitigate supply risks.
Buyers should verify that suppliers maintain certifications relevant to their industry and export markets, ensuring regulatory compliance and product acceptance.
Quality control is integrated at multiple stages to detect and correct defects early:
For international buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality systems is crucial due to varying regulatory environments and logistical complexities.
Requesting comprehensive QC documentation helps confirm adherence to standards:
Employing independent laboratories or inspection bodies can validate supplier claims, especially for critical applications:
Navigating quality assurance in global SiC rod procurement requires attention to regional and sector-specific nuances:
By mastering the manufacturing and quality assurance landscape of SiC rods, international B2B buyers can secure reliable partnerships and high-performance products tailored to their market needs.
When sourcing silicon carbide (SiC) rods, international buyers must grasp the multifaceted cost components that influence final pricing. The primary cost elements include:
Several factors beyond basic cost components shape the quoted price of SiC rods:
To optimize sourcing costs while maintaining quality, international B2B buyers should consider the following:
Prices for SiC rods vary widely based on size, grade, and order volume. Typical unit prices can range from $50 to $200 per kilogram, with custom or high-purity rods commanding higher premiums. These figures are indicative and should be confirmed with multiple suppliers to reflect current market conditions, regional factors, and specific buyer requirements.
By understanding these cost drivers and pricing influences, international buyers from Colombia, Argentina, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed procurement decisions, ensuring competitive pricing without compromising on quality or supply reliability.
When sourcing silicon carbide (SiC) rods, understanding critical technical properties is essential to ensure product suitability, performance, and cost-effectiveness in your applications. Here are the primary specifications international buyers should evaluate:
Material Grade
SiC rods come in various grades defined by purity, grain size, and manufacturing process (e.g., sintered vs. reaction bonded). Higher purity grades offer improved thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, which is vital for high-temperature or abrasive environments. Selecting the right grade ensures durability and optimal performance in sectors such as metallurgy, electronics, or ceramics.
Dimensional Tolerance
This refers to the permissible variation in rod diameter and length, typically measured in millimeters or microns. Tight tolerances are crucial for precision applications where fit and alignment impact assembly or function. Buyers should specify tolerance requirements upfront to avoid costly rework or incompatibility.
Density
Density affects the mechanical strength and thermal properties of SiC rods. Higher density rods usually provide better wear resistance and thermal shock endurance. For industries like semiconductor manufacturing or aerospace, density specifications directly correlate with product longevity and process stability.
Flexural Strength
This measures the rod’s ability to resist bending forces without breaking. Higher flexural strength is important when rods are subjected to mechanical stress or dynamic loads. It ensures reliability under operational stresses, reducing downtime and replacement frequency.
Thermal Conductivity
SiC rods are prized for their excellent heat conduction. The thermal conductivity rating indicates how efficiently heat is transferred through the rod, which affects cooling performance and energy efficiency in thermal management systems. Buyers targeting high-temperature applications should prioritize this property.
Surface Finish
The surface quality, including smoothness and absence of defects, impacts the rod’s performance in friction-sensitive or sealing applications. A fine surface finish minimizes wear and improves compatibility with mating parts.
Understanding industry jargon is key for smooth communication and negotiation with suppliers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are essential trade terms every B2B buyer should know:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or components used in another company’s final product. If you are an OEM, you may require customized SiC rods to meet specific design criteria. Clarifying OEM status can influence pricing, minimum order quantities, and technical support.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell per order. MOQ impacts inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their demand forecasts to avoid overstocking or supply shortages.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document sent to suppliers to obtain pricing, lead times, and terms for specified SiC rods. A clear, detailed RFQ helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and reduces misunderstandings, speeding up the procurement process.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Common terms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Understanding Incoterms ensures clarity on delivery obligations and cost allocation.
Lead Time
The total time from order placement to delivery. Lead times can vary significantly based on supplier location and production capacity. Buyers should factor lead times into project schedules, especially when sourcing from distant regions like South America or the Middle East.
Batch Number
A unique identifier assigned to a production lot of SiC rods. This number is crucial for traceability, quality control, and warranty claims. Buyers should request batch numbers to track product history and ensure consistency across orders.
By mastering these technical specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize supply chain efficiency, and build stronger supplier relationships in the competitive SiC rod market.
Silicon carbide (SiC) rods are a critical component in various industrial applications, including electronics, automotive, and manufacturing sectors, due to their exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical corrosion. Globally, demand for SiC rods is driven by rapid advancements in semiconductor technology, electric vehicle (EV) production, and renewable energy sectors. For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these market dynamics is essential to secure competitive sourcing and ensure supply chain resilience.
Key market drivers include:
Emerging sourcing trends:
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Colombia, Argentina, and other emerging economies, aligning sourcing strategies with these trends ensures access to high-quality SiC rods while optimizing cost and delivery timelines.
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the procurement of silicon carbide rods, reflecting broader industry shifts towards environmentally responsible manufacturing and supply chain transparency. The production of SiC rods involves energy-intensive processes and raw material extraction that can have significant environmental impacts if not managed properly.
Key sustainability considerations for B2B buyers:
Incorporating sustainability criteria into supplier evaluations not only mitigates reputational risks but also aligns with increasing regulatory requirements in Europe and progressive markets in South America. Buyers benefit from enhanced supply chain resilience and can meet growing customer demand for eco-friendly products.
Silicon carbide’s journey from a synthetic abrasive material discovered in the late 19th century to a high-tech industrial staple underscores its evolving strategic importance. Initially valued for its hardness and thermal stability, SiC rods were primarily used in grinding and cutting applications. The transition to electronic and power device manufacturing in the late 20th century marked a significant shift, as SiC’s superior electrical properties became critical for semiconductor substrates and high-voltage components.
For B2B buyers today, this evolution highlights the necessity of sourcing SiC rods that meet stringent technical specifications driven by advanced manufacturing processes. Understanding the material’s historical development helps buyers appreciate quality differentials and invest in suppliers who innovate to meet modern industrial demands.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How can I effectively vet suppliers of SiC rods to ensure product quality and reliability?
To vet suppliers, start by requesting detailed product specifications, including material composition and manufacturing processes. Verify certifications such as ISO 9001, REACH, or RoHS compliance to ensure quality standards. Ask for sample products to conduct in-house testing or third-party lab analysis. Check the supplier’s track record through client references and industry reputation, focusing on their experience with international shipments. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s crucial to assess the supplier’s ability to meet your regulatory and quality requirements while ensuring consistent delivery performance.
What customization options are typically available for SiC rods, and how should I communicate my specific needs?
SiC rods can be customized in terms of diameter, length, density, and surface finish to meet specific industrial applications such as high-temperature furnaces or semiconductor manufacturing. When engaging suppliers, provide detailed technical drawings or specifications, including tolerances and performance criteria. Clarify the intended use to help suppliers recommend the best grade and formulation. Early communication about customization reduces lead times and avoids costly revisions. International buyers should also inquire about minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products, as these can vary significantly.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for SiC rods, especially for international buyers?
MOQs for SiC rods depend on the supplier’s production capacity and customization level but generally range from 100 to 500 units per order. Lead times can vary from 3 to 8 weeks, influenced by product complexity and shipping logistics. For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, longer lead times may apply due to customs and transit delays. To optimize supply chain efficiency, negotiate MOQs that align with your inventory turnover and confirm lead times upfront. Planning orders well in advance can mitigate risks related to production bottlenecks or shipping disruptions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
What payment terms are commonly accepted in international trade for SiC rods, and how can I mitigate payment risks?
Common payment terms include Letters of Credit (LC), Telegraphic Transfers (TT), and open account arrangements for trusted partners. Letters of Credit offer high security by involving banks in transaction verification, which is ideal for first-time international buyers. For established relationships, suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 payment terms. To mitigate risks, use escrow services or partial payments upfront combined with milestone-based payments. Always verify supplier credentials and avoid full prepayment without guarantees, especially when sourcing from new or unverified suppliers in emerging markets.
Which quality assurance certifications and testing standards should I request when sourcing SiC rods?
Request certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and material-specific certificates like ASTM or DIN standards relevant to SiC rods. Additionally, compliance with environmental and safety standards such as REACH (EU) or RoHS is important for international shipments. Ask suppliers for test reports on mechanical strength, purity, thermal conductivity, and dimensional accuracy. Regular audits or third-party inspections can further ensure compliance. These measures are critical for buyers in regulated markets such as Europe and the Middle East, where product certification impacts customs clearance and end-use approval.
What logistical considerations should international buyers keep in mind when importing SiC rods?
SiC rods are typically shipped via sea freight due to weight and volume, but air freight is an option for urgent orders despite higher costs. Packaging should protect against moisture and mechanical damage during long transit times. Understand import regulations, tariffs, and customs documentation requirements for your country to avoid clearance delays. Engage freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial ceramics and negotiate Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) that clarify cost and risk responsibilities. Planning for potential delays at ports, especially in Africa and South America, helps maintain supply chain reliability.
How should disputes or quality issues be managed in international SiC rod transactions?
Establish clear contractual terms addressing quality standards, inspection rights, and dispute resolution methods before placing orders. Include clauses for product returns, replacements, or refunds if products fail to meet agreed specifications. Utilize third-party inspection agencies to verify quality prior to shipment. In case of disputes, attempt mediation or arbitration as specified in the contract, preferably under internationally recognized frameworks like ICC rules. Maintaining open communication with suppliers facilitates quicker resolutions and preserves long-term business relationships.
Are there any region-specific considerations when sourcing SiC rods from or to Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Yes, regional factors such as local regulatory compliance, import duties, and currency fluctuations can impact procurement. For example, African and South American buyers should account for longer shipping times and potential customs bureaucracy. Middle Eastern buyers must consider strict quality certifications due to industrial standards. European buyers often require adherence to stringent environmental and safety regulations. Understanding these nuances enables better negotiation of terms, selection of compliant suppliers, and smoother logistics planning tailored to each region’s unique challenges.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
The procurement of SiC rods demands a strategic approach that balances quality, cost-efficiency, and supplier reliability. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of supplier markets and technological specifications is crucial. Prioritizing suppliers with proven expertise in SiC rod manufacturing and robust logistics capabilities will mitigate risks and enhance supply chain resilience.
Key takeaways include the importance of thorough supplier vetting, leveraging regional trade agreements to optimize costs, and investing in long-term partnerships to secure favorable terms and consistent product quality. Additionally, staying informed about advancements in SiC rod applications can unlock new opportunities and competitive advantages in industries like electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
Looking ahead, the global SiC rod market is poised for growth driven by increasing demand for high-performance materials. Buyers are encouraged to adopt a proactive sourcing strategy—incorporating market intelligence, sustainability considerations, and flexible procurement models—to stay ahead of supply fluctuations and technological shifts. By doing so, companies from Colombia to the UAE can confidently navigate the complexities of the SiC rod supply chain and capitalize on emerging market trends.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina