In today’s interconnected economy, understanding the multifaceted applications of sic uses is paramount for businesses aiming to secure a competitive edge in global markets. Whether you represent a manufacturing firm in Germany, a trading company in Nigeria, or a procurement division in Brazil or the Middle East, grasping the nuances of sic uses—from material selection to quality control—is essential to optimize supply chains and ensure product excellence.
This guide delivers an exhaustive exploration of sic uses, covering the diverse types available, critical materials involved, and cutting-edge manufacturing and quality assurance practices. It also maps out the global supplier landscape, highlighting key regions and trusted partners to facilitate reliable sourcing. Cost considerations and market trends are dissected to empower buyers with strategic insights tailored to their specific regional contexts and business scales.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those navigating the complex trade environments of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this resource serves as a trusted compass. It demystifies technical jargon, anticipates frequently asked questions, and offers actionable advice to streamline decision-making and mitigate risks.
By leveraging this comprehensive knowledge base, your organization can confidently engage with suppliers, negotiate favorable terms, and integrate sic uses effectively into your product portfolios. This guide is designed not only to inform but to transform your approach to global procurement, ensuring sustainable growth and operational resilience in an evolving marketplace.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Sic Usage | Indicates exact replication of quoted material including errors | Legal documentation, academic citations, contract reviews | + Ensures accuracy and transparency – May confuse non-expert readers |
| Corrective Sic Usage | Highlights intentional retention of errors for emphasis or clarification | Quality control, compliance audits, editorial reviews | + Maintains original context – Requires clear explanation to avoid misinterpretation |
| Contextual Sic Usage | Used to denote errors or unusual phrasing specific to cultural or regional contexts | International communications, translations, market research | + Preserves cultural authenticity – Can complicate understanding across diverse markets |
| Digital Sic Usage | Applied in digital content to flag copied text with errors in software or data processing | Software documentation, data integrity reports | + Supports data traceability – May require technical knowledge to interpret |
| Visual Sic Usage | Involves use of [sic] in visual media or presentations to indicate original text errors | Marketing materials, presentations, training manuals | + Enhances credibility – Visual clutter may distract audience |
Standard Sic Usage
This is the most common form of sic, used to indicate that a quoted text is reproduced exactly as found, including any errors or unusual spellings. It is essential in legal and academic fields where precision and authenticity are critical. For B2B buyers, especially those dealing with contracts or compliance documents, understanding this use ensures that no alterations are made to original texts, preserving legal integrity. Buyers should ensure their teams are familiar with this notation to avoid confusion or misinterpretation during due diligence or audits.
Corrective Sic Usage
Corrective sic usage occurs when errors are intentionally left in the text to emphasize authenticity or to highlight mistakes for further review. This variation is particularly relevant in quality control and editorial processes where transparency is paramount. B2B buyers in manufacturing or publishing sectors can leverage this to maintain audit trails and enhance accountability. However, clear communication is necessary to prevent misunderstandings, especially when dealing with international partners unfamiliar with this notation.
Contextual Sic Usage
This type of sic use focuses on preserving errors or phrasing that reflect cultural, linguistic, or regional specificities. It is especially useful in translation services, international marketing, and ethnographic research where maintaining original context is vital. For B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this usage helps retain authenticity in communications and product materials. Buyers should consider the cultural competence of their teams to interpret these nuances correctly and avoid potential market misalignments.
Digital Sic Usage
In digital environments, sic is used to flag copied or imported text containing errors within software, databases, or documentation. This is crucial for IT vendors, software developers, and data analysts who need to track data integrity and source authenticity. B2B buyers investing in technology solutions must ensure their providers use clear sic notation to facilitate debugging and compliance. Understanding this variation can also help buyers negotiate service level agreements that account for error management and traceability.
Visual Sic Usage
Visual sic usage applies to presentations, marketing collateral, or training materials where original text errors are displayed intentionally. This can enhance credibility by showing transparency or by preserving original quotes in client-facing documents. For B2B buyers in marketing, communications, or training sectors, this use supports brand authenticity and trust-building. However, buyers should balance the benefits against potential visual distraction and ensure that audiences understand the purpose of sic to maintain professionalism.
Related Video: Silicon Carbide Explained - SiC Basics
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sic uses | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Electronics | High-voltage power devices such as inverters and converters | Enables higher efficiency and thermal management; reduces energy loss | Source high-purity SiC wafers with consistent doping; ensure supplier can meet volume and quality standards for industrial-grade components |
| Automotive | Electric vehicle (EV) powertrains and fast-charging stations | Enhances power density and reduces system size; improves reliability under harsh conditions | Look for SiC materials with proven automotive-grade certifications and long-term availability for global supply chains |
| Renewable Energy | Solar inverters and wind turbine power converters | Improves conversion efficiency and operational lifespan | Prioritize suppliers experienced in renewable energy sectors with robust quality control and traceability |
| Industrial Machinery | Motor drives and industrial automation power modules | Increases system efficiency and reduces cooling requirements | Evaluate suppliers’ ability to provide customized SiC solutions tailored to specific voltage and current ratings |
| Telecommunications | High-frequency, high-power RF devices and base station amplifiers | Enables better signal performance and power handling for 5G infrastructure | Ensure compliance with international standards and availability of technical support for integration |
Silicon Carbide (SiC) has become a cornerstone material in power electronics, especially for high-voltage devices like inverters and converters used in industrial power systems. SiC’s wide bandgap allows devices to operate at higher voltages and temperatures than traditional silicon, significantly improving energy efficiency and reducing cooling costs. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and South America where power infrastructure is rapidly evolving, sourcing SiC wafers with consistent purity and doping levels is critical to ensure device reliability and manufacturing yield.
In the automotive sector, SiC is revolutionizing electric vehicle (EV) powertrains and fast-charging infrastructure. SiC-based power modules enable higher power density and better thermal performance, which translates to lighter, more efficient EVs and faster charging times. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe, such as Germany, should prioritize automotive-grade SiC materials that comply with stringent industry standards and come from suppliers with established global logistics to support continuous production.
For renewable energy applications, SiC is integral to solar inverter and wind turbine power converter technology. Its ability to handle high voltages and temperatures improves overall system conversion efficiency and extends equipment lifespan. International B2B buyers should focus on vendors with proven expertise in renewable energy sectors and strong quality assurance processes to meet the demanding operational environments typical in Africa and Europe.
In industrial machinery, SiC power devices are used in motor drives and automation modules to boost efficiency and reduce the need for bulky cooling systems. This is particularly valuable for industries in South America and Africa where energy costs and space constraints are significant concerns. Buyers need to seek suppliers capable of providing tailored SiC solutions that match specific voltage and current requirements to optimize system performance.
Finally, in telecommunications, SiC enables high-frequency, high-power RF devices essential for 5G base stations and other communication infrastructure. The material’s superior power handling and thermal stability improve signal quality and device lifespan. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure that SiC components comply with international standards and that suppliers offer robust technical support for seamless integration into complex telecom systems.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a versatile material widely used in high-performance industrial applications due to its exceptional thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties. For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, selecting the right SiC material variant is crucial to optimize product performance, cost-efficiency, and compliance with regional standards.
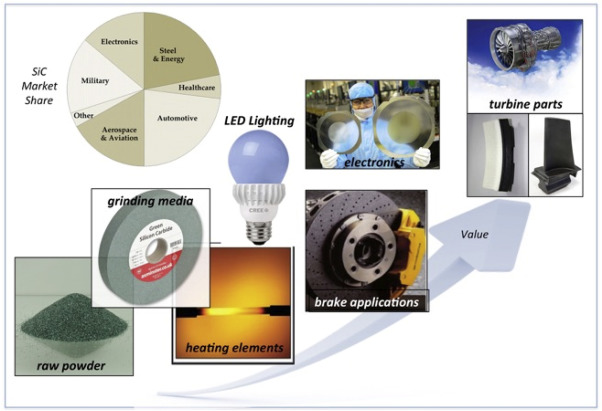
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Properties:
Monocrystalline SiC exhibits outstanding thermal conductivity (up to 490 W/mK) and high breakdown electric field strength, making it ideal for high-power electronics and semiconductor devices. It has excellent mechanical hardness and can operate at temperatures exceeding 600°C.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Superior electrical properties for power devices, excellent thermal stability, and minimal defects.
- Cons: High manufacturing complexity and cost due to crystal growth processes; limited wafer sizes can constrain large-scale production.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for high-frequency, high-voltage power electronics and harsh environment sensors. Its high purity and uniformity ensure reliable performance in power modules and automotive applications.
Considerations for Buyers:
European buyers (e.g., Germany) often require compliance with IEC and DIN standards for semiconductor-grade SiC wafers. Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should verify supplier certifications and ensure material traceability, as power electronics are increasingly vital for renewable energy projects. South American buyers should consider import tariffs and logistics costs, balancing quality and price.
Key Properties:
Polycrystalline SiC ceramics feature high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and thermal shock resistance. They typically withstand temperatures up to 1600°C and exhibit good chemical inertness against acids and alkalis.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Cost-effective compared to monocrystalline SiC, excellent mechanical durability, and suitable for abrasive environments.
- Cons: Lower electrical conductivity and less uniformity; potential brittleness under extreme mechanical stress.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in mechanical seals, pump components, kiln furniture, and abrasive media handling. Its corrosion resistance suits chemical processing industries and harsh environmental conditions.
Considerations for Buyers:
In regions like the Middle East and Africa, where chemical industries are growing, polycrystalline SiC offers a balance of durability and cost. Compliance with ASTM C799 or ISO 9001 quality standards is critical for ensuring material reliability. European buyers should verify adherence to EN standards and request detailed material certifications.
Key Properties:
SiC composites combine SiC matrix with reinforcing fibers, offering enhanced fracture toughness, thermal shock resistance, and mechanical strength. Operating temperatures can reach above 1400°C with improved damage tolerance.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Superior mechanical resilience, lightweight compared to monolithic ceramics, and excellent thermal stability.
- Cons: Higher production complexity and cost; requires specialized manufacturing capabilities.
Impact on Application:
Used in aerospace components, heat exchangers, and high-performance automotive parts where weight reduction and durability are critical. The composite structure improves lifespan under cyclic thermal and mechanical loads.
Considerations for Buyers:
European buyers prioritize composites for advanced engineering applications and expect compliance with aerospace material standards like AMS or DIN EN. Buyers in developing markets should assess supplier capabilities and after-sales support, as composite fabrication demands precise quality control.
Key Properties:
SiC powders vary in particle size and purity, influencing sintering behavior and final product properties. High-purity powders (>99%) are essential for electronic-grade materials, while coarser grades serve abrasive and refractory applications.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Versatile feedstock for various SiC products; cost-effective for mass production.
- Cons: Requires downstream processing expertise; inconsistent powder quality can impact final product performance.
Impact on Application:
Crucial for manufacturers producing SiC ceramics, coatings, and composites. Powder selection directly affects sintering temperature, density, and mechanical properties.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers in South America and Africa should ensure powder suppliers provide consistent quality and comply with ISO/ASTM powder standards. Logistics and storage conditions are important to prevent contamination. European buyers often demand traceability and batch testing reports.
| Material | Typical Use Case for sic uses | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline Silicon Carbide | Power electronics, high-frequency semiconductors | Superior electrical and thermal properties | High manufacturing cost and limited wafer size | High |
| Polycrystalline Silicon Carbide | Mechanical seals, chemical processing components | Excellent wear and corrosion resistance | Lower electrical conductivity, brittle under stress | Medium |
| Silicon Carbide Composites | Aerospace parts, heat exchangers, automotive | Enhanced toughness and thermal shock resistance | Complex manufacturing and higher cost | High |
| Silicon Carbide Powders | Raw material for ceramics, coatings, composites | Versatile and cost-effective feedstock | Requires precise processing and quality control | Low to Medium |
This guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on application requirements, regional standards, and cost considerations. Selecting the appropriate SiC material variant is pivotal for optimizing product performance and ensuring compliance across diverse industrial sectors worldwide.
The production of silicon carbide (SiC) components, widely used in high-performance electronics, abrasives, and automotive parts, involves a series of precise and controlled manufacturing stages. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—evaluate supplier capabilities and ensure product reliability.
SiC manufacturing begins with raw material sourcing and preparation. High-purity silicon and carbon are the primary inputs, often derived from quartz and petroleum coke. The materials undergo:
Material quality at this stage directly impacts the performance of the final product, making supplier transparency about material sourcing critical.
After preparation, SiC materials are shaped into the desired forms using several advanced techniques:
Each technique requires specialized equipment and expertise, which can vary significantly between suppliers.
In applications like power electronics, SiC components are often integrated with other materials:
This stage demands stringent process control to avoid defects that could compromise performance.
Final finishing ensures the product meets exact specifications:
Finishing is essential for meeting customer requirements and facilitating downstream use.
Quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) are integral to SiC manufacturing, ensuring products meet international standards and function reliably in demanding environments.
Ensuring suppliers adhere to these certifications reduces risk and facilitates smooth import/export procedures.
Each checkpoint involves specific tools and methodologies to maintain high standards throughout the manufacturing cycle.
B2B buyers should request detailed test reports and certificates of analysis for these parameters.
For buyers across diverse regions like Germany, Nigeria, Brazil, or the UAE, verifying supplier QC practices is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product integrity.
Audits help verify claims about certifications, equipment, and process adherence.
Ensuring transparency in documentation supports informed purchasing decisions.
This extra layer of verification is particularly valuable for buyers in regions where local enforcement of standards may vary.
By proactively addressing these factors, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can secure high-quality SiC products that meet their operational demands.
This comprehensive understanding of manufacturing and quality assurance for SiC applications empowers B2B buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions. Thorough evaluation of supplier processes, adherence to international standards, and robust QC verification are key pillars for successful procurement in global markets.
When sourcing sic uses products, international B2B buyers must carefully analyze the various cost components to accurately assess pricing and ensure competitive procurement. The primary cost drivers include:
Pricing for sic uses products is not static; it is influenced by several critical factors that buyers must evaluate:
Navigating the complexities of sic uses sourcing requires strategic approaches tailored to diverse regional markets:
The pricing insights provided are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and logistical factors. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and request detailed quotations reflecting their specific requirements and regional considerations.
By carefully dissecting these cost elements and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions for sic uses, optimize procurement costs, and build resilient supply chains across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Understanding the critical technical specifications of products labeled for "sic uses" is essential for international B2B buyers to ensure quality, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness in procurement. Here are some of the most important properties to consider:
Material Grade
This refers to the classification of the base material used, often denoting purity, composition, or manufacturing standards. For sic uses, selecting the correct material grade affects durability and performance, especially in demanding industrial environments. Buyers from regions like Nigeria or Germany should verify that the grade meets both local regulatory standards and their specific application needs.
Dimensional Tolerance
Dimensional tolerance defines the allowable deviation from specified measurements. Tight tolerances ensure parts fit precisely in complex assemblies, reducing waste and rework. For buyers in South America or the Middle East, understanding tolerance levels can prevent costly returns or production delays.
Thermal Stability
This indicates how well a product maintains its properties under temperature variations. High thermal stability is critical for sic uses in sectors like electronics or automotive, where temperature fluctuations are common. Buyers should confirm thermal specifications to avoid failures in end-use environments.
Chemical Resistance
The ability to withstand exposure to chemicals without degradation is vital, especially for industrial or manufacturing applications. Knowing the chemical resistance helps buyers in Africa or Europe ensure longevity and safety in harsh operational settings.
Surface Finish
Surface finish impacts both the aesthetics and functional performance, such as friction or corrosion resistance. In B2B transactions, specifying the required finish can influence pricing and supplier selection, especially when products interface with other components.
Mechanical Strength
This property defines the product’s ability to withstand mechanical forces such as tension, compression, or impact. Understanding mechanical strength helps buyers assess suitability for heavy-duty applications and compliance with safety standards.
Familiarity with industry jargon and trade terms streamlines communication and negotiation between buyers and suppliers across continents. Here are some key terms relevant to sic uses procurement:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or products that are used in another company’s end products. Knowing whether a supplier is an OEM or a reseller helps buyers assess authenticity, warranty, and support options.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. MOQ influences pricing and inventory decisions. Buyers from emerging markets, such as in Africa or South America, should negotiate MOQs carefully to balance cost with storage capabilities.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit detailed price and delivery information from suppliers. Issuing clear RFQs with technical specs reduces misunderstandings and expedites supplier evaluation.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyer and seller. Understanding Incoterms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for buyers in regions with diverse logistics infrastructures, ensuring clarity in cost and risk allocation.
Lead Time
The period between order placement and product delivery. Accurate lead time estimates help buyers plan production schedules and manage supply chain risks, particularly important for time-sensitive projects.
Certificate of Compliance (CoC)
A document confirming that the product meets specified standards or regulations. For international buyers, especially in regulated markets like Europe, obtaining a CoC ensures product legitimacy and facilitates customs clearance.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, optimize supply chain efficiency, and foster strong supplier relationships tailored to the unique demands of sic uses.
The sic uses sector is experiencing dynamic growth driven by increasing global demand for innovative, efficient, and sustainable solutions across multiple industries. Key markets in Europe—particularly Germany—alongside emerging economies in Africa (e.g., Nigeria), South America, and the Middle East, are fueling diverse sourcing needs and supply chain strategies. Buyers from these regions seek to balance cost-effectiveness with quality and compliance, navigating complexities such as varying regulatory environments, trade policies, and logistics challenges.
Current trends emphasize digital transformation in procurement and supply chain management, leveraging technologies like AI-powered analytics, blockchain for traceability, and IoT-enabled monitoring. These advancements help B2B buyers optimize supplier selection, reduce lead times, and enhance transparency. Additionally, nearshoring and regional sourcing hubs are gaining traction as companies aim to mitigate risks from global disruptions and reduce dependency on distant suppliers.
For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, increasing local production capabilities combined with access to international quality standards present unique opportunities to diversify sourcing and foster regional partnerships. In the Middle East, investments in infrastructure and innovation hubs are creating new supply chain nodes. European buyers, especially from Germany, continue to prioritize suppliers with strong compliance credentials and innovation capacity, reflecting the region’s stringent quality and environmental standards.
Sustainability is no longer optional but a critical component of procurement strategies in the sic uses sector. Environmental impacts such as carbon emissions, waste generation, and resource depletion are under scrutiny by regulators and end-customers alike. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship to safeguard brand reputation and ensure long-term supply chain resilience.
Key actionable insights include adopting green certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for sustainable materials, and compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations prevalent in Europe. These certifications provide assurance of responsible sourcing and product safety. Additionally, integrating lifecycle assessments (LCA) into procurement decisions enables buyers to quantify environmental impacts and select suppliers with lower carbon footprints.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East where regulatory frameworks may be evolving, partnering with suppliers who adhere to global sustainability standards can facilitate access to European and South American markets with stringent import requirements. Transparent supply chains supported by blockchain and traceability technologies further enhance ethical sourcing by enabling verification of labor practices and environmental compliance.
The sic uses sector has evolved from traditional, often fragmented supply chains into a highly interconnected, technology-driven ecosystem. Historically, sourcing focused primarily on cost and availability, with limited visibility into supplier practices or environmental impacts. Over the last two decades, globalization and digitalization have transformed procurement into a strategic function emphasizing agility, transparency, and sustainability.
In regions like Europe, early adoption of environmental regulations and quality standards shaped market expectations and supplier capabilities. Emerging markets such as Nigeria and South America are rapidly catching up, investing in infrastructure and capacity building to meet international demand. This evolution reflects a broader shift toward responsible business practices and collaborative supply networks, enabling B2B buyers worldwide to make more informed, sustainable sourcing decisions in the sic uses sector.
How can I effectively vet suppliers of sic uses to ensure reliability and quality?
To vet suppliers, request detailed company profiles, certifications, and client references. Verify their manufacturing capabilities through virtual tours or third-party audits. Check their compliance with international standards relevant to sic uses and inquire about their quality control processes. Engaging with suppliers who participate in recognized trade fairs or industry associations can provide additional assurance. For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, partnering with local trade chambers or export promotion agencies can also help validate supplier credibility.
Is customization available for sic uses, and how should I approach it in negotiations?
Most reputable suppliers offer customization to meet specific technical or regulatory requirements. Clearly define your specifications, including dimensions, materials, and performance criteria, before discussions. Negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) and additional costs associated with custom tooling or design changes. Ensure that customization options comply with your target market’s standards, especially if exporting to Europe or the Middle East, where regulations may be stringent. Request prototypes or samples to verify customization before full-scale production.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for sic uses, especially for international buyers?
MOQs vary widely depending on the product complexity and supplier scale but typically range from hundreds to thousands of units. Lead times can span from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by customization, production capacity, and shipping logistics. For buyers in Africa or South America, additional time should be considered for customs clearance and inland transportation. Discuss flexible MOQs with suppliers if your initial order volume is limited, and confirm lead times upfront to align with your project timelines.
Which payment terms are standard when purchasing sic uses internationally, and how can I protect my transaction?
Common payment terms include advance payments (30%), letters of credit (L/C), or net terms (30-60 days) after shipment. Using L/Cs provides secure, bank-backed payment guarantees, minimizing risks. For new suppliers, consider escrow services or partial upfront payments to mitigate exposure. Always ensure payment terms are clearly documented in the contract, alongside dispute resolution clauses. Engage with banks experienced in international trade from your region (e.g., Nigerian or German banks) to facilitate smooth transactions.
What quality assurance certifications should I look for when sourcing sic uses?
Seek suppliers with ISO 9001 certification for quality management systems as a baseline. Depending on your industry, additional certifications like CE marking (Europe), UL listing (North America), or specific industry standards (e.g., IEC for electrical components) may be necessary. Request product test reports, inspection certificates, and compliance declarations. For buyers in the Middle East, check if suppliers meet GCC or SASO standards. Independent third-party inspections before shipment can further ensure product conformity.
How can I optimize logistics and shipping when importing sic uses internationally?
Choose suppliers with experience in exporting to your region to leverage their knowledge of customs and shipping routes. Decide between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-efficiency based on order urgency and volume. Ensure clear Incoterms are agreed upon—FOB, CIF, or DDP—to define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Collaborate with reliable freight forwarders and customs brokers familiar with your country’s regulations to minimize delays and unexpected costs.
What steps should I take if there is a dispute regarding product quality or delivery of sic uses?
First, document all communications and discrepancies with evidence such as photos or inspection reports. Refer to your purchase contract’s dispute resolution clause, which may specify negotiation, mediation, or arbitration. Engage the supplier promptly to seek amicable resolution, possibly involving third-party inspectors. If unresolved, consider international arbitration bodies like ICC or trade-specific ombudsmen. Maintaining clear contracts and communication from the outset reduces dispute risks.
How can I ensure compliance with import regulations for sic uses in my country?
Research your country’s import requirements, including customs duties, product standards, labeling, and documentation needed (e.g., certificates of origin, safety data sheets). Engage local customs authorities or trade consultants for guidance. For buyers in regions like Europe or the Middle East, compliance with REACH, RoHS, or local certification schemes is critical. Work closely with your supplier to obtain all necessary certifications and ensure accurate shipment documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of sic uses presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers to optimize supply chains, reduce costs, and enhance product innovation. By leveraging diverse suppliers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses can capitalize on regional strengths, secure reliable sourcing channels, and foster sustainable partnerships. Prioritizing quality, compliance, and adaptability in vendor selection is essential to mitigate risks and meet evolving market demands.
Key takeaways include the importance of comprehensive market intelligence, supplier diversification, and embracing digital tools to streamline procurement processes. Strategic sourcing not only drives cost efficiency but also unlocks value through innovation and agility, positioning companies for long-term competitive advantage.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, buyers are encouraged to deepen collaboration with global suppliers, invest in transparent supply networks, and explore emerging markets to future-proof their sourcing strategies. The dynamic global landscape calls for proactive engagement and continuous improvement to harness the full potential of sic uses. Embrace strategic sourcing as a transformative lever to elevate your business performance and sustainably expand your international footprint.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina