硅粉, or silicon powder, stands as a cornerstone material across diverse industrial sectors including electronics, metallurgy, chemical manufacturing, and renewable energy. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in dynamic markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—securing high-quality 硅粉 is critical to ensuring product performance, regulatory compliance, and competitive advantage.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into every essential aspect of 硅粉 sourcing to empower buyers with actionable insights. You will gain clarity on the various types and grades of 硅粉, tailored to specific industrial applications, along with detailed information on raw materials and manufacturing processes that influence quality and consistency. Rigorous quality control standards and certifications are also unpacked, enabling you to distinguish reputable suppliers and mitigate supply chain risks.
Understanding the pricing dynamics and market trends is crucial for strategic procurement. This guide provides up-to-date analysis on cost drivers, regional market variations, and supply-demand forecasts that impact your sourcing decisions. Additionally, an extensive directory of verified global suppliers is included, highlighting those with proven reliability and compliance in key regions such as South Africa and Spain.
Finally, a curated FAQ section addresses common concerns and technical queries, streamlining your evaluation process. By leveraging this guide, international buyers will be equipped to navigate the complexities of the global 硅粉 market with confidence—securing the right product at the right price, from the right partner, to fuel sustainable business growth.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fumed Silica (Pyrogenic Silica) | Ultra-fine particles, high purity, hydrophobic or hydrophilic variants | Electronics, coatings, adhesives, sealants | + High purity and surface area; - Higher cost, handling requires care |
| Precipitated Silica | Spherical particles, moderate purity, cost-effective | Rubber reinforcement, food additives, cosmetics | + Cost-effective and versatile; - Lower purity, variable particle size |
| Silica Gel | Porous, granular form, high absorption capacity | Desiccants, chromatography, pharmaceuticals | + Excellent moisture adsorption; - Not suitable for structural use |
| Colloidal Silica | Stable suspension of silica nanoparticles | Polishing, catalysts, inks, paints | + Uniform particle size, stable dispersion; - Requires specialized storage |
| Microcrystalline Silica | Crystalline structure, larger particle size | Construction, fillers, abrasives | + Strong mechanical properties; - Less reactive, heavier |
Fumed Silica (Pyrogenic Silica)
Fumed silica is produced via flame hydrolysis, resulting in ultra-fine, highly pure particles with a large surface area. It is available in hydrophobic and hydrophilic variants, making it highly adaptable. This type is ideal for high-performance applications such as electronics insulation, adhesives, and advanced coatings. Buyers should consider its higher price point and the need for specialized handling to avoid dust-related issues. Its purity and performance justify the investment for industries demanding precision.
Precipitated Silica
Manufactured through chemical precipitation, precipitated silica consists of spherical particles with moderate purity. It is widely used in rubber manufacturing, food processing, and cosmetics due to its cost efficiency and versatility. For B2B buyers, evaluating particle size distribution and purity levels is crucial, as these impact product performance. This type offers an excellent balance between cost and functionality, making it a preferred choice for bulk industrial applications.
Silica Gel
Silica gel is a porous, granular form of silica known for its exceptional moisture absorption properties. It is predominantly used as a desiccant in packaging, pharmaceuticals, and chromatography. Buyers seeking silica gel should focus on pore size and adsorption capacity to match specific moisture control requirements. While it is not suitable for structural or filler applications, its moisture regulation capabilities are indispensable for supply chains sensitive to humidity.
Colloidal Silica
Colloidal silica is a stable dispersion of silica nanoparticles suspended in a liquid medium. Its uniform particle size and stability make it ideal for polishing agents, catalyst supports, and specialty inks. B2B buyers must ensure proper storage conditions to maintain dispersion stability and prevent agglomeration. This type is favored in precision industries where surface finish and chemical reactivity are critical.
Microcrystalline Silica
Characterized by its crystalline structure and larger particle size, microcrystalline silica is commonly used in construction materials, fillers, and abrasives. It offers robust mechanical properties but is less reactive than amorphous forms. Buyers should assess particle size and crystallinity to optimize performance in structural applications. Its cost-effectiveness and durability make it a staple in heavy industry sectors.
Related Video: The Genius Behind Bach's Goldberg Variations: CANONS
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 硅 粉 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Deoxidizer in Steel and Ferroalloy Production | Enhances metal purity and mechanical properties; reduces production defects | High purity and consistent particle size; reliable supply to prevent production delays |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Raw material for silicon-based components and powders | Enables production of high-performance semiconductors and photovoltaic cells | Ultra-high purity, low contamination levels; certification compliance with international standards |
| Chemical Industry | Raw material for silicone production and catalysts | Improves catalyst efficiency and silicone product quality | Consistent chemical composition; availability of technical data sheets for process integration |
| Rubber & Plastics | Filler and reinforcing agent in rubber and plastic composites | Enhances mechanical strength, heat resistance, and durability of products | Particle size distribution and surface treatment; compatibility with polymer matrices |
| Construction & Ceramics | Additive in refractory materials and ceramics | Increases thermal stability and abrasion resistance of construction materials | Thermal stability, chemical inertness; compliance with regional environmental regulations |
硅 粉 plays a critical role in metallurgy, particularly as a deoxidizer in steel and ferroalloy production. It effectively removes oxygen impurities during smelting, improving the purity and mechanical strength of metals. For international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing high-purity 硅 粉 with consistent particle size is essential to maintain product quality and avoid costly production interruptions. Reliable logistics and supplier certifications are also vital to ensure uninterrupted supply chains.
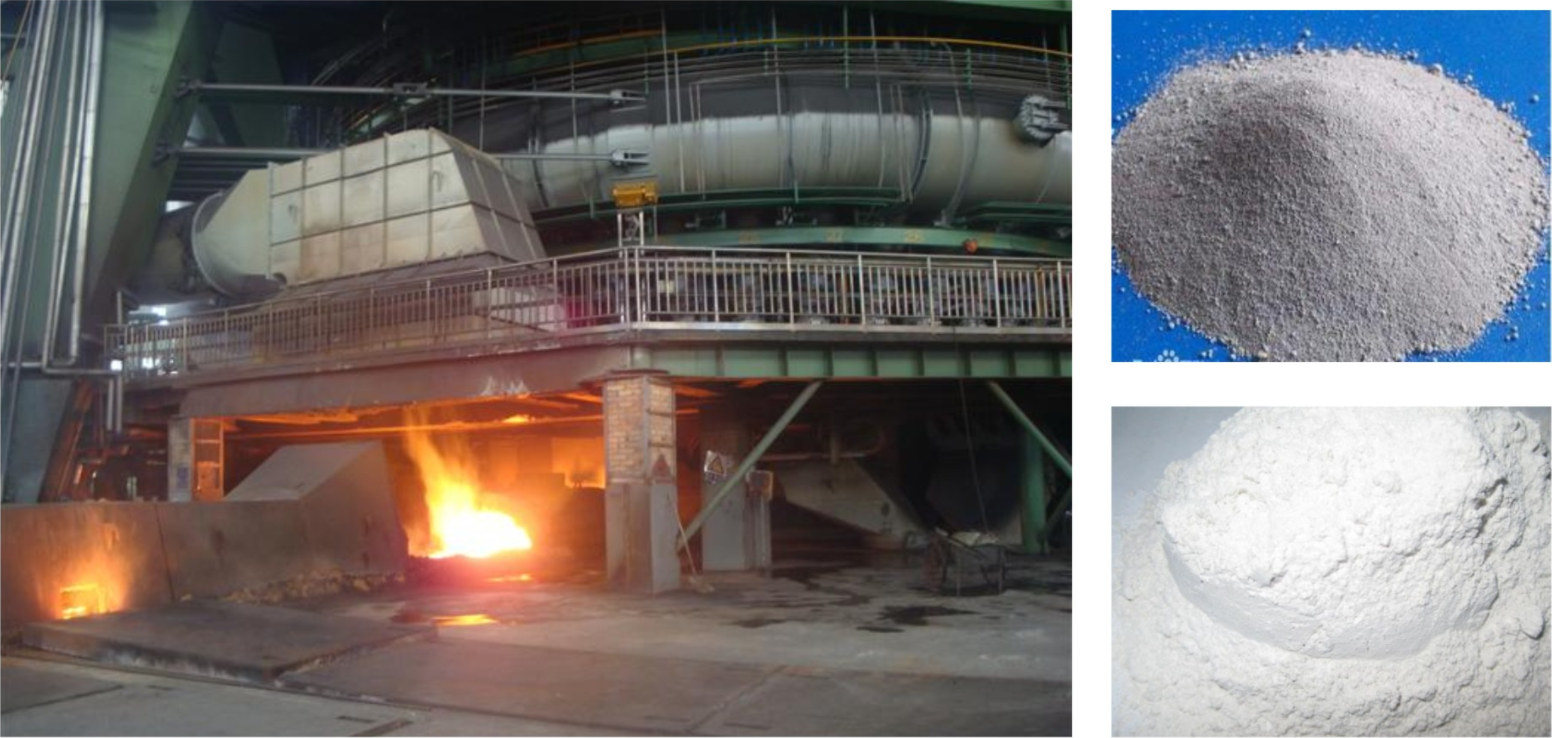

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In the electronics and semiconductor industry, 硅 粉 serves as a fundamental raw material for manufacturing silicon wafers and powders used in photovoltaic cells and semiconductor devices. Here, the demand for ultra-high purity and minimal contamination is stringent to meet the performance requirements of advanced electronic components. Buyers from technologically advanced markets such as Spain or South Africa must prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive quality certifications and meet international semiconductor-grade standards.
The chemical industry utilizes 硅 粉 extensively as a precursor for silicone production and as a catalyst component. Its chemical consistency directly influences catalyst activity and the overall quality of silicone-based products used across various sectors. International B2B buyers should seek 硅 粉 with stable chemical composition and detailed technical documentation to facilitate smooth integration into existing chemical processes, especially in regions where regulatory compliance is critical.
For the rubber and plastics sector, 硅 粉 acts as a reinforcing filler that significantly improves the mechanical strength, heat resistance, and durability of rubber and plastic products. It is widely used in manufacturing tires, seals, and various polymer composites. Buyers from emerging and mature markets alike must consider the particle size distribution and surface treatment of 硅 粉 to ensure compatibility with polymer matrices, which affects the final product performance and longevity.
In construction and ceramics, 硅 粉 is added to refractory materials and ceramic products to enhance thermal stability and abrasion resistance. This application is particularly relevant for manufacturers producing high-performance building materials and industrial ceramics. International buyers should evaluate thermal properties and chemical inertness of the 硅 粉, along with compliance with environmental standards, to meet both performance and sustainability goals in their regional markets.
When selecting materials for 硅 粉 (silicon powder) applications, international B2B buyers must consider various material options that influence product performance, manufacturing efficiency, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in conjunction with 硅 粉, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and relevance to buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties:
Quartz is prized for its exceptional thermal stability, withstanding temperatures above 1,000°C without degradation. It offers excellent chemical inertness and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-purity silicon powder production and applications requiring contamination-free environments.
Pros & Cons:
Quartz is highly durable and chemically stable, which supports long-term reliability. However, its brittleness can pose challenges during handling and processing. Manufacturing complexity is moderate due to the need for precise purification and milling processes. Quartz-based silicon powder is ideal for electronics and optical industries but may be costlier than other materials.
Impact on Application:
Quartz-based 硅 粉 is compatible with high-temperature processes and aggressive chemical environments, making it suitable for semiconductor and photovoltaic applications. It ensures minimal contamination, critical for high-specification end products.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Europe (e.g., Spain) often require compliance with ASTM C778 and ISO 9001 standards for purity and consistency. African and Middle Eastern buyers should verify supplier certifications to meet local import regulations and quality standards. Quartz’s relatively higher cost may impact procurement strategies in price-sensitive markets like South America.
Key Properties:
This material features silicon powder with a purity of about 98-99%, suitable for metallurgical and chemical industries. It has good thermal conductivity and moderate resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures.
Pros & Cons:
Metallurgical grade silicon is cost-effective and widely available, making it attractive for large-scale industrial applications such as alloy production and silicones manufacturing. However, its lower purity limits its use in high-tech sectors. Manufacturing processes are less complex, supporting faster turnaround times.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for applications where ultra-high purity is not critical, such as aluminum-silicon alloys or silicone rubber production. Its compatibility with diverse chemical media makes it versatile but unsuitable for electronics or solar-grade silicon needs.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Africa and South America benefit from metallurgical grade silicon’s affordability and availability. Compliance with regional standards like DIN EN 16785-1 (Europe) or ASTM F123 is advisable to ensure material consistency. Logistics considerations, including shipping bulk quantities, are important for cost optimization.
Key Properties:
Fumed silica is an ultra-fine, amorphous silicon dioxide powder with a high surface area and excellent dispersibility. It exhibits outstanding thermal stability and chemical inertness, often used as a reinforcing agent.
Pros & Cons:
Its fine particle size enhances product performance in composites and coatings but increases manufacturing complexity and handling challenges due to dust control requirements. The cost is relatively high due to specialized production methods.
Impact on Application:
Fumed silica is preferred in high-performance applications such as adhesives, sealants, and advanced ceramics where improved mechanical strength and thermal resistance are needed. Its compatibility with organic and inorganic media broadens its industrial use.
Considerations for International Buyers:
European buyers often require compliance with REACH regulations and ISO 14001 environmental standards. Middle Eastern and African buyers should assess supplier safety data sheets (SDS) carefully due to handling risks. Import tariffs and transportation safety for fine powders must be factored into procurement plans.
Key Properties:
This material involves silicon powder treated with silane coupling agents to improve surface properties, enhancing adhesion and dispersion in polymer matrices. It maintains good thermal and chemical stability.
Pros & Cons:
Silane treatment significantly improves compatibility with organic polymers, making it valuable for composite materials and silicone elastomers. The treatment adds cost and requires specialized manufacturing steps, increasing lead times.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for high-performance composites, sealants, and coatings where enhanced bonding between silicon powder and polymer is critical. It supports improved mechanical properties and durability in end products.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in South America and Europe should verify compliance with local chemical safety standards such as REACH and OSHA. In Africa and the Middle East, ensuring access to technical support for handling and application is important. The higher price point necessitates careful cost-benefit analysis for volume purchases.
| Material | Typical Use Case for 硅 粉 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Semiconductor, photovoltaic, optics | High thermal stability and chemical inertness | Brittleness and higher cost | High |
| Metallurgical Grade Silicon | Alloy production, silicones manufacturing | Cost-effective and widely available | Lower purity limits high-tech applications | Low |
| Fumed Silicon Dioxide | Reinforcement in composites, coatings | Ultra-fine particles improve mechanical strength | Handling complexity and dust control risks | High |
| Silane-Treated Silicon Powder | Polymer composites, sealants, elastomers | Enhanced adhesion and dispersion in polymers | Added cost and specialized manufacturing | Medium |
This guide assists B2B buyers in making informed decisions by balancing performance requirements, regulatory compliance, and cost considerations tailored to their regional markets.
Manufacturing and quality assurance of 硅 粉 (silicon powder) are critical to ensure high purity, consistent particle size, and performance tailored to industrial applications such as electronics, solar panels, and specialty alloys. For international B2B buyers—particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding these processes and quality controls is essential for selecting reliable suppliers and ensuring compliance with regional standards.
The production of high-quality 硅 粉 typically involves several carefully controlled stages, each contributing to the powder’s purity and physical properties:
Ensuring consistent quality requires rigorous QA/QC protocols aligned with international standards and industry-specific requirements.
Given the critical nature of quality in 硅 粉, buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verifying supplier quality systems:
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the following when evaluating 硅 粉 suppliers:
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing stages and quality assurance frameworks for 硅 粉, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their technical needs and compliance obligations, minimizing risks and ensuring reliable supply chains.
When sourcing 硅粉 (silicon powder) for industrial or manufacturing applications, understanding the detailed cost and pricing structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This section breaks down the key cost components, price influencers, and practical buyer strategies to optimize procurement, especially for international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Raw Materials
The primary cost driver is the quality and purity of the silicon source. Higher-grade silicon powders with specific particle sizes and purity levels command premium prices. Variations in raw material costs stem from sourcing locations and market demand for silicon feedstock.
Labor Costs
Labor expenses include skilled workforce wages involved in processing, milling, and packaging the silicon powder. These costs fluctuate significantly depending on the country of manufacture and automation levels in production.
Manufacturing Overhead
Overhead covers utilities, plant maintenance, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. Efficient production lines with modern machinery reduce overhead per unit, impacting final pricing.
Tooling and Equipment
Specialized milling and classification equipment used to achieve precise particle size distribution and surface characteristics add upfront tooling costs. These are typically amortized over production volumes.
Quality Control (QC) and Certification
Rigorous testing to ensure particle size uniformity, chemical composition, and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, RoHS) is vital. Certification costs are included in pricing, reflecting reliability and traceability.
Logistics and Shipping
International freight, customs duties, insurance, and inland transportation significantly affect landed costs. Silicon powder’s bulk and sensitivity to moisture may require special packaging, increasing logistics expenses.
Supplier Margin
Suppliers incorporate profit margins that vary by market competition, order size, and contract terms. Margins tend to be lower for large-volume buyers or long-term agreements.
Order Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Bulk purchases typically reduce unit costs. Many suppliers offer tiered pricing, rewarding higher volumes with discounts, which is advantageous for buyers consolidating orders.
Product Specifications and Customization
Tailored particle sizes, surface treatments, or blends affect price. Custom specifications often require additional processing steps, tooling, or QC measures.
Material Quality and Certifications
Certified high-purity powders for sensitive applications (electronics, solar cells) command premium pricing compared to industrial-grade silicon powder.
Supplier Location and Reliability
Suppliers from regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive prices but consider reliability, lead times, and after-sales support. Established suppliers with strong reputations may charge more but provide consistency and compliance assurance.
Incoterms and Payment Terms
Pricing varies depending on delivery terms such as FOB, CIF, or DDP. Buyers should clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs to accurately assess total costs.
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Look beyond the unit price to include logistics, customs, warehousing, and potential rework costs. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, factoring in import duties and local regulations is critical.
Leverage Volume Consolidation
Pool orders with other departments or partners to meet MOQs and unlock better pricing tiers. This is particularly effective for buyers in regions with smaller individual demand but collective purchasing power.
Request Samples and Certifications Early
Ensure material quality matches application needs by verifying certificates and testing samples before committing to large orders. This reduces the risk of costly quality issues.
Assess Supplier Flexibility and Lead Times
Prioritize suppliers who can adapt to specification changes and offer reasonable lead times to mitigate supply chain disruptions, which are common in international trade.
Consider Incoterm Implications
Choose delivery terms that balance cost savings with control over shipment. For example, CIF terms can simplify logistics for buyers unfamiliar with international freight but may increase costs.
Prices for 硅粉 vary widely depending on grade, supplier, volume, and market conditions. The information provided here is indicative and should be used as a framework to guide negotiations and sourcing strategies rather than fixed cost expectations. Buyers are encouraged to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence tailored to their specific requirements and regional considerations.
By carefully analyzing these cost components and price influencers, international B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of 硅粉 procurement, optimize expenditure, and secure reliable supply chains suited to their industrial needs.
When sourcing 硅 粉 for industrial or manufacturing purposes, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for ensuring product quality and compatibility with your applications. Below are the primary properties you should evaluate:
Purity (%)
This indicates the percentage of silicon content in the powder. Higher purity (typically above 99%) is essential for applications such as electronics, solar panels, and high-performance alloys. Lower purity grades may be suitable for less critical uses like metallurgical additives. Purity directly impacts the efficiency and reliability of your end product.
Particle Size (Microns)
Particle size distribution affects the surface area and reactivity of the powder. Finer particles (below 10 microns) offer better dispersion and reactivity, which is vital in chemical processes or coatings. Coarser powders may be preferred for bulk materials or certain metallurgical processes. Consistent particle size ensures uniformity in production.
Specific Surface Area (m²/g)
This measures the total surface area per gram of powder, influencing chemical activity and bonding characteristics. A higher specific surface area enhances reaction rates and sintering behavior, important for advanced material manufacturing. It also affects flowability and packing density.
Moisture Content (%)
Silicon powder should have low moisture content to prevent clumping and degradation. Moisture can adversely affect storage, handling, and chemical reactions. Typically, moisture below 0.5% is recommended for industrial-grade powders.
Bulk Density (g/cm³)
Bulk density impacts packaging, transportation, and mixing ratios in formulations. Knowing this helps in calculating volume requirements and optimizing logistics costs. Variations can affect dosing accuracy in production.
Crystallinity and Phase Composition
Silicon powder may be amorphous or crystalline. Crystalline silicon is preferred in electronics and photovoltaics, while amorphous silicon finds use in coatings and chemical applications. Confirming phase composition ensures the powder meets your process needs.
Navigating international procurement and trade contracts for 硅 粉 involves understanding key industry jargon. Below are terms frequently encountered in supplier negotiations and contracts:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce components or materials that are used in another company’s final product. When dealing with OEM suppliers of 硅 粉, ensure their product specifications align with your manufacturing standards and certifications.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount a supplier is willing to sell in one order. MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier and product grade. Understanding MOQ helps you balance inventory costs with production needs, especially for buyers in emerging markets where storage space may be limited.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers to obtain pricing, availability, and terms for 硅 粉. An effective RFQ should clearly specify technical requirements, delivery timelines, and payment conditions to receive accurate and comparable bids.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), and EXW (Ex Works). Knowing these helps clarify cost allocation and risk during transport.
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Lead times for 硅 粉 may vary based on production capacity, shipping distance, and customs clearance. Accurate lead time estimates are critical for production planning and avoiding downtime.
Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
A document provided by the supplier detailing the batch-specific technical data of the 硅 粉 shipment, including purity, particle size, and moisture content. Always request a CoA to verify product compliance with your specifications before acceptance.
By focusing on these technical properties and mastering essential trade terminology, international B2B buyers—from Africa to Europe—can optimize their procurement strategy for 硅 粉. This approach minimizes risks, ensures quality consistency, and fosters stronger supplier relationships, ultimately supporting reliable supply chains and competitive manufacturing outcomes.
The global 硅粉 (silicon powder) market is experiencing robust growth driven by expanding applications across the electronics, solar energy, automotive, and chemical industries. Key demand centers include Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where industrial modernization and renewable energy investments are accelerating. For instance, South Africa’s growing manufacturing sector and Spain’s commitment to solar power are boosting regional consumption of high-purity silicon powders used in semiconductors and photovoltaic cells.
Market dynamics for international B2B buyers are shaped by several factors:
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these trends can help identify reliable suppliers who align with evolving technical requirements and regional market conditions. Building partnerships with suppliers committed to innovation and supply chain resilience is essential to maintaining competitive advantage.
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the 硅粉 supply chain. The environmental impact of silicon powder production involves significant energy consumption, primarily due to high-temperature processing and purification steps. For B2B buyers prioritizing sustainability, engaging suppliers who implement energy-efficient manufacturing practices and utilize renewable energy sources can substantially reduce the carbon footprint of their procurement.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, especially for buyers in regions with increasing regulatory scrutiny and consumer demand for responsible products. Ensuring traceability in the supply chain helps mitigate risks related to labor practices and environmental compliance. Many forward-looking suppliers now pursue certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adhere to international labor standards, enhancing transparency and accountability.
In addition, the emergence of green silicon powders—produced using cleaner technologies and sustainable raw materials—offers buyers a way to meet corporate social responsibility goals. These materials often come with third-party verification and can be leveraged in marketing to environmentally conscious end-users.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, incorporating sustainability and ethical criteria into supplier selection not only supports global environmental objectives but also aligns with regional policies promoting green industrial growth. Collaborating with suppliers who demonstrate commitment to these principles can reduce supply chain risks and open access to new market opportunities driven by sustainability mandates.
硅粉 production has evolved significantly over the past decades, transitioning from rudimentary grinding methods to sophisticated chemical vapor deposition and plasma synthesis techniques. Historically, silicon powder was primarily used in metallurgical applications, but its role expanded with the semiconductor revolution in the late 20th century.
The advent of solar photovoltaics and lithium-ion battery technologies further transformed the market, driving demand for ultra-pure, nano-sized silicon powders with precise particle size control. This evolution reflects broader industrial trends toward miniaturization, energy efficiency, and high-performance materials.
Understanding this historical progression helps B2B buyers appreciate the technical complexities and quality benchmarks now expected in the 硅粉 sector. It also underscores the importance of sourcing from suppliers with advanced manufacturing capabilities and a proven track record of innovation to meet the sophisticated demands of modern industries.
How can I effectively vet suppliers of 硅粉 to ensure reliability and quality?
Start by requesting detailed company profiles, including business licenses and export certifications relevant to your region (e.g., EU REACH compliance for Europe). Verify their production capabilities, quality control processes, and client references, preferably from your continent or industry. Utilize third-party inspection services or audits to assess factory standards. Also, evaluate their communication responsiveness and willingness to provide samples for testing. A reliable supplier will be transparent about their certifications and quality assurance measures, helping mitigate risks in international transactions.
Is it possible to customize 硅粉 specifications to meet specific industrial requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization such as particle size distribution, purity levels, and packaging formats tailored to your application needs. When negotiating, clearly specify your technical requirements and intended use cases. Confirm that the supplier has R&D capabilities or technical support to accommodate custom formulations or adjustments. Custom orders may affect lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs), so clarify these aspects upfront to align expectations and avoid delays.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times when sourcing 硅粉 internationally?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier’s scale and product type but often start from one metric ton for bulk industrial orders. Lead times generally range from 2 to 6 weeks, considering production, quality checks, and shipping. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, factor in additional time for customs clearance and inland logistics. Negotiate MOQs based on your consumption forecasts, and consider consolidated shipments or long-term contracts to optimize costs and supply chain stability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Which payment terms are commonly accepted for international 硅粉 transactions?
Suppliers typically accept Letters of Credit (L/C), Telegraphic Transfers (T/T), and sometimes open account terms for established buyers. L/Cs offer security for both parties but involve bank fees and paperwork. T/T payments often require a 30%-50% deposit upfront with the balance paid before shipment or upon receipt. Negotiate terms that balance risk and cash flow, and ensure contracts clearly define payment schedules, penalties for late payments, and currency considerations to avoid disputes.
What quality assurance certifications should I look for when buying 硅粉?
Look for ISO 9001 certification indicating robust quality management systems, and industry-specific standards such as REACH compliance in Europe or RoHS for electrical applications. Certificates of Analysis (CoA) should accompany each batch, detailing chemical composition and physical properties. For food or pharmaceutical-grade silicon powder, additional certifications like FDA approval or GMP compliance may be necessary. Confirm that testing laboratories are accredited and that the supplier provides traceability documentation to ensure consistent quality.
How can I optimize logistics and shipping for 硅粉 imports to my region?
Choose suppliers experienced in exporting to your region who understand local customs regulations and documentation requirements. Consolidate shipments when possible to reduce freight costs and consider multimodal transport options combining sea, air, and land. Clarify Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to understand responsibility and cost allocations. Engage reliable freight forwarders and customs brokers familiar with your market to expedite clearance. Also, plan for potential delays due to seasonal factors or geopolitical issues and build buffer time into your supply chain.
What steps should I take if there is a quality dispute or shipment issue with 硅粉 suppliers?
Immediately document the issue with photographs, sample testing results, and detailed descriptions. Notify the supplier in writing and refer to the contractual terms regarding quality standards and dispute resolution. Engage third-party inspection or testing agencies for impartial verification if necessary. Many suppliers prefer negotiation or arbitration before legal action; therefore, maintain open communication to seek amicable solutions. Retain all correspondence and contracts for reference. Establish clear dispute resolution clauses during contract negotiation to streamline future conflicts.
Are there specific considerations for sourcing 硅粉 from suppliers in different continents?
Yes, regional differences affect regulatory compliance, quality standards, pricing, and logistics. For example, European suppliers often adhere to stricter environmental and safety regulations, which may increase costs but assure higher quality. Suppliers in South America or Africa might offer competitive pricing but require thorough vetting and due diligence. Time zone differences and language barriers can impact communication, so consider using local agents or translators. Understand import duties, taxes, and certification requirements specific to your country to avoid unexpected costs or delays.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Effective strategic sourcing of 硅粉 (silicon powder) is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize cost-efficiency, quality, and supply chain resilience. Key considerations include evaluating supplier reliability, assessing product specifications aligned with industry standards, and leveraging global trade dynamics to secure competitive pricing. For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, cultivating diversified supplier relationships while navigating regional logistics and regulatory environments can unlock significant advantages.
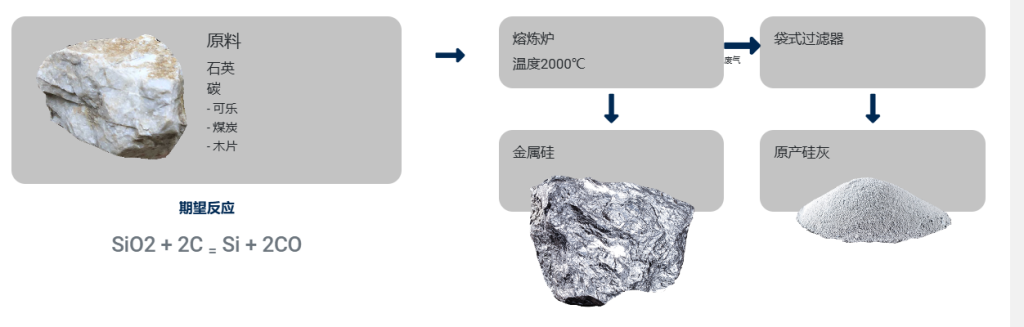
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Critical takeaways for buyers include:
Looking ahead, the 硅粉 market is expected to evolve with innovations in material science and increasing demand across electronics, energy, and manufacturing sectors. Buyers who adopt a proactive, informed sourcing strategy will be well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities and mitigate risks.
Actionable next steps: Engage with verified suppliers early, conduct comprehensive due diligence, and remain agile to adapt sourcing strategies as market conditions shift. This approach will ensure sustained competitive advantage and supply stability in a dynamic global landscape.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina