Guide to Abrasive Materialien
Understanding the global landscape of abrasive materials is essential for making strategic sourcing decisions that drive efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Abrasive materials are the backbone of countless manufacturing, construction, and finishing processes worldwide, making their reliable supply critical for maintaining operational excellence. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Kenya—navigating this complex market can be challenging without comprehensive insights.
This guide offers an in-depth exploration of the entire abrasive materialien ecosystem, from the different types and raw materials used to manufacturing standards and quality control practices. It also covers how to identify reputable suppliers, evaluate costs, and understand market trends that influence pricing and availability. By equipping you with detailed knowledge, this resource enables smarter sourcing decisions that mitigate risks and optimize supply chains.
Whether you are seeking specialized abrasives for industrial applications or bulk materials for large-scale projects, understanding the nuances of global supply dynamics is vital. This guide aims to empower B2B buyers with actionable insights—helping you navigate international markets confidently, forge strong supplier relationships, and ensure consistent quality in your procurement processes. Ultimately, informed sourcing leads to competitive advantages in today’s interconnected global economy.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | Hard, durable, versatile, relatively low cost | Grinding wheels, sanding belts, abrasive discs | Pros: Widely available, cost-effective, suitable for many materials. Cons: Less aggressive on hard metals, shorter lifespan in high-wear applications. |
| Silicon Carbide | Extremely hard, sharp, brittle, high thermal resistance | Cutting, grinding hard materials like glass, ceramics | Pros: Excellent for cutting tough, brittle materials, produces a fine finish. Cons: More brittle, can wear quickly if not used properly. |
| Zirconia Alumina | Tough, self-sharpening, high resistance to heat and impact | Heavy-duty grinding, rough shaping of metals | Pros: Long-lasting, ideal for demanding applications, reduces downtime. Cons: Higher cost, may be over-spec for softer materials. |
| Ceramic Alumina | Very high hardness, self-sharpening, superior heat resistance | Precision grinding, high-speed applications | Pros: Extended tool life, consistent performance, excellent for high-precision work. Cons: Higher initial investment, requires compatible equipment. |
| Garnet | Natural mineral, coarse, abrasive, eco-friendly | Sanding, polishing, woodworking, finishing | Pros: Cost-effective, environmentally friendly, good for softer materials. Cons: Shorter lifespan, less suitable for heavy-duty industrial use. |
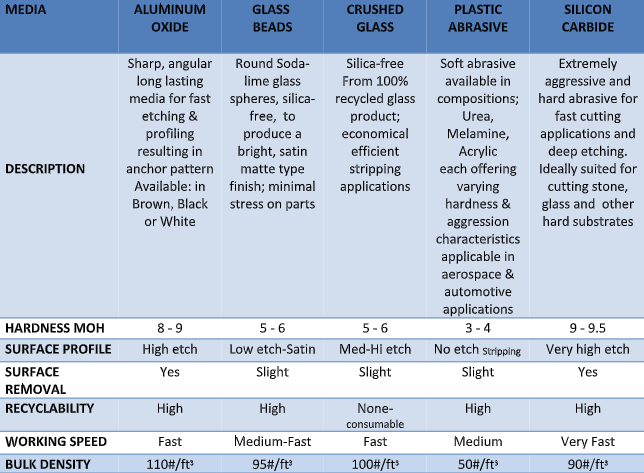
Aluminum Oxide is one of the most common abrasives used globally, known for its durability and versatility across a broad range of materials, including ferrous metals, wood, and plastics. Its moderate cost and availability make it a practical choice for many B2B applications, especially where budget constraints are critical. Buyers should consider its moderate wear rate for high-volume operations and select grit sizes accordingly to optimize lifespan and performance.
Silicon Carbide stands out for its extreme hardness and sharpness, making it ideal for cutting and grinding brittle materials such as glass, ceramics, and non-ferrous metals. Its thermal resistance allows for use in high-temperature processes, but its brittle nature demands careful handling. For buyers, selecting the right grade and ensuring proper equipment compatibility are crucial to maximize efficiency and minimize waste.
Zirconia Alumina offers a tough, self-sharpening surface that withstands heavy-duty grinding tasks. It is highly suitable for rough shaping and aggressive material removal in metal fabrication industries. Its durability reduces the frequency of tool replacements, which can lower operational costs over time. However, its higher price point requires careful cost-benefit analysis, especially for large-scale operations.
Ceramic Alumina is engineered for high-performance applications requiring precision and longevity. Its self-sharpening properties and heat resistance make it suitable for high-speed grinding and finishing tasks. B2B buyers should evaluate initial costs against the potential for reduced downtime and extended tool life, especially in high-volume manufacturing settings.
Garnet is a natural abrasive with eco-friendly appeal, mainly used in woodworking, polishing, and finishing applications. Its lower cost and environmental friendliness make it attractive for companies emphasizing sustainability. However, its shorter lifespan and limited suitability for heavy industrial use mean it is best for light-duty tasks or where environmental considerations are prioritized.
When sourcing abrasive materialien, buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize supplier reliability, material consistency, and compliance with industry standards. For high-volume or critical applications, investing in premium abrasives like ceramic alumina can enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. Conversely, for lighter or more cost-sensitive projects, materials like garnet or aluminum oxide may offer sufficient performance at a lower price point. Understanding the specific material compatibility, grit size, and bonding type ensures optimal selection, leading to improved process efficiency and product quality across various industries.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of abrasive materialien | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metalworking & Manufacturing | Surface finishing, grinding, and polishing of metal components | Achieves high-quality surface finishes, reduces post-processing costs, and enhances product durability | Consistent abrasive quality, particle size control, and compliance with industry standards (ISO, ASTM) |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Cutting, shaping, and smoothing concrete, stone, and ceramics | Improves precision, reduces material waste, and speeds up project timelines | Abrasive hardness suited for tough materials, availability of large quantities, and cost efficiency |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Precision grinding and surface preparation of engine parts and composites | Ensures tight tolerances, reduces defects, and extends component lifespan | Material compatibility with sensitive parts, minimal contamination, and certification requirements |
| Mining & Quarrying | Crushing, grinding, and ore processing | Enhances extraction efficiency, lowers operational costs, and prolongs equipment life | Durability under heavy loads, resistance to wear, and supply chain reliability in remote areas |
| Electronics & Fine Manufacturing | Polishing and lapping of delicate electronic components | Achieves ultra-smooth surfaces critical for performance, reduces defect rates | Fine particle sizes, contamination control, and adherence to cleanroom standards |
Abrasive materials are fundamental in metalworking for tasks such as grinding, cutting, and polishing metal surfaces. They enable manufacturers to achieve smooth, high-quality finishes essential for corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. For international B2B buyers, sourcing abrasives with consistent particle size and hardness ensures predictable results and reduces rework. Especially in regions like Africa and South America, reliable supply chains and adherence to industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) are critical to maintain production efficiency and product quality.
In the construction sector, abrasives are used extensively for cutting concrete, shaping stones, and smoothing ceramic surfaces. These applications demand abrasives that can handle tough materials efficiently, minimizing waste and accelerating project timelines. Buyers should prioritize abrasives with high durability and proven performance in large-scale operations. Sourcing considerations include availability of bulk quantities, cost competitiveness, and compatibility with local construction standards, which vary across regions such as the Middle East and Europe.
Abrasives play a vital role in the automotive and aerospace industries for precision finishing of engine parts, turbine blades, and composite materials. They help achieve tight tolerances and superior surface quality, directly impacting the performance and lifespan of critical components. International buyers must focus on abrasives that are compatible with sensitive materials, free from contamination, and meet stringent certification standards. This is particularly important for European and Middle Eastern aerospace applications where quality assurance is paramount.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In mining, abrasives are integral to crushing, grinding, and mineral processing operations. They contribute to higher extraction efficiency, reduced operational costs, and extended equipment service life. For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing abrasives with exceptional wear resistance and consistent supply in remote or logistically challenging areas is essential. Long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers that can deliver high-performance abrasives under demanding conditions are key to maintaining operational continuity.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In the electronics industry, abrasives are used for polishing and lapping delicate components such as semiconductors and microchips. These applications require ultra-fine abrasives capable of producing mirror-like finishes without introducing contamination. B2B buyers should prioritize abrasives with fine particle sizes, strict contamination controls, and compliance with cleanroom standards. Ensuring supply chain reliability and quality consistency is especially crucial for European and Asian markets with stringent quality requirements.
Key Properties:
Aluminum oxide is one of the most widely used abrasive materials due to its high hardness (9 on Mohs scale), excellent toughness, and thermal stability. It performs well under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, making it suitable for grinding metals and ceramics. Its corrosion resistance is moderate, but it can withstand exposure to many chemicals, especially in dry environments.
Pros & Cons:
Advantages include its durability, availability in various grit sizes, and cost-effectiveness for many applications. Aluminum oxide is relatively easy to manufacture, which keeps costs manageable. However, it can be brittle under certain conditions, leading to potential fracture if mishandled or used improperly. Its end-product suitability is broad, especially for metalworking and surface preparation.
Impact on Application:
This material is compatible with a wide range of media, including metals, ceramics, and composites. Its high hardness makes it ideal for aggressive material removal, but it may generate significant heat, requiring cooling in some applications.
International B2B Considerations:
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS is crucial. Aluminum oxide abrasives are generally standardized, but verifying supplier certifications ensures quality consistency. Cost considerations are important for regions with import tariffs or logistics challenges, and local availability can influence procurement strategies.
Key Properties:
Silicon carbide is a very hard abrasive (9-9.5 Mohs), with excellent thermal conductivity and chemical inertness. It performs well at elevated temperatures and resists corrosion, especially in wet or chemically aggressive environments. Its high hardness and toughness make it suitable for precision grinding and finishing.
Pros & Cons:
Silicon carbide offers superior cutting performance and produces a finer finish compared to aluminum oxide. Its chemical inertness makes it ideal for applications involving reactive media. However, SiC is generally more expensive, and manufacturing complexity can lead to higher costs. It is also more brittle than aluminum oxide, which can result in fracture under impact.
Impact on Application:
Due to its inertness and high thermal stability, silicon carbide is preferred in applications involving reactive chemicals, such as in the electronics or aerospace sectors. Its compatibility with specific media, like acids or alkalis, is a key advantage.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers should ensure suppliers meet relevant standards (e.g., ASTM, JIS). In regions like Europe and Germany, strict compliance with environmental and safety regulations (REACH, RoHS) is essential. In emerging markets such as Kenya or South America, sourcing reliable suppliers with certifications can mitigate risks related to quality and counterfeit products.
Key Properties:
Garnet is a natural mineral abrasive with a Mohs hardness of around 6.5-7. It offers good durability and sharpness. It performs well in dry blasting and is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Garnet’s chemical stability ensures minimal contamination of the work surface.
Pros & Cons:
Garnet is cost-effective, especially in regions where it is locally mined (e.g., India, Australia). It is environmentally friendly and produces less dust compared to synthetic abrasives. Its main limitation is lower hardness compared to synthetic abrasives, which can reduce its lifespan in high-demand applications. It is less suitable for very aggressive or high-precision tasks.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for surface preparation, cleaning, and finishing in industries like construction, shipbuilding, and automotive. Its media compatibility is broad but less effective for heavy material removal compared to synthetic abrasives.
International B2B Considerations:
For buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East, sourcing garnet locally can reduce costs and lead times. Ensuring compliance with environmental standards and verifying quality certifications (ISO, local standards) is vital. European buyers often prefer garnet that meets strict environmental and safety regulations.
| Material | Typical Use Case for abrasive materialien | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | Metal grinding, surface prep, ceramics | Cost-effective, widely available, versatile | Brittle under impact, moderate corrosion resistance | Med |
| Silicon Carbide | Precision grinding, electronics, chemical inertness | High hardness, chemical inertness, high thermal stability | Higher cost, more brittle, limited impact resistance | High |
| Garnet | Surface cleaning, outdoor blasting, finishing | Environmentally friendly, cost-effective, locally available | Lower hardness, less durable for heavy-duty tasks | Low |
This strategic overview helps international B2B buyers evaluate abrasive materials based on application needs, regional considerations, and compliance standards. Selecting the right abrasive material enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures adherence to safety and environmental regulations across diverse markets.
The production of abrasive materials involves a multi-stage process designed to ensure consistency, performance, and safety. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers evaluate supplier capabilities and product quality.
The process begins with selecting and preparing raw materials, which vary based on the type of abrasive (e.g., alumina, silicon carbide, garnet). Raw materials are typically sourced globally, with suppliers adhering to strict quality standards. Pre-processing involves crushing, milling, and sieving to achieve the desired grain size distribution. Precise control during this stage ensures uniformity, which directly impacts the abrasive’s effectiveness.
Forming encompasses shaping the abrasive grains or powders into usable forms. Techniques include:
- Briquetting: Compressing powders into blocks or sticks for easier handling and transportation.
- Sintering: Fusing grains at high temperatures to produce bonded abrasives like grinding wheels or discs.
- Casting: Pouring molten material into molds for specialized shapes.
Advanced forming methods may incorporate binders or bonding agents, especially for coated abrasives, to enhance durability.
Once formed, abrasive components are assembled into final products such as grinding wheels, belts, or discs. Bonding techniques vary:
- Resinoid Bonding: Using synthetic resins for flexible, high-performance abrasives.
- Vitrified Bonding: Ceramic-like bonds offering high thermal resistance.
- Metal Bonding: For superabrasives like diamond or CBN, enabling cutting tools with extreme precision.
This stage often involves curing, baking, or sintering to solidify bonds.
Final processing includes shaping, balancing, and surface finishing to meet precise specifications. Quality control here ensures proper wheel concentricity, surface smoothness, and dimensional accuracy. Additional treatments like coating or impregnating may be applied to improve performance or lifespan.
Maintaining high-quality standards is critical, especially for international B2B transactions. Suppliers typically implement comprehensive quality management systems aligned with recognized standards.
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should pay attention to specific nuances in supplier QC practices:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the supplier’s certifications align with local market requirements, such as CE for Europe or local standards in Kenya.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Verify the origin of raw materials and adherence to environmental and social standards, especially for regions with strict import regulations.
- Quality Consistency: Establish long-term relationships with suppliers demonstrating stable QC records and continuous improvement initiatives.
- Sampling and Testing: Request sample testing reports and consider conducting independent testing or third-party audits before large orders.
- Custom Certifications: For specialized applications (e.g., oil and gas, aerospace), confirm compliance with industry-specific standards like API or AS9100.
A comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices empowers B2B buyers to make informed procurement decisions in the abrasive materials sector. By focusing on transparent supplier certifications, rigorous QC checkpoints, and adherence to international standards, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure they source high-quality, reliable abrasives suitable for their specific industry applications and regional requirements.
Effective sourcing of abrasive materials requires a clear grasp of the key cost components involved. Typically, costs can be segmented into raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margin. Raw materials, such as aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or zirconia, constitute a significant portion of the total cost, with prices fluctuating based on global supply and demand, purity levels, and material grade.
Labor costs vary considerably across regions—generally lower in parts of Africa and South America, higher in Europe and the Middle East—impacting the final price. Manufacturing overhead includes factory expenses, energy, and equipment maintenance, which tend to be higher in developed economies due to stricter standards and higher wages. Tooling costs are largely fixed but can influence unit prices, especially for customized abrasive products. Quality assurance and certifications (ISO, ANSI, etc.) add to costs but are crucial for ensuring product reliability, especially in sectors like aerospace or automotive.
Logistics costs are another critical factor, heavily influenced by geographic location, shipping mode (sea, air, land), and supply chain efficiency. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who bears transportation and insurance costs, directly impacting total landed cost. A comprehensive understanding of these components allows buyers to compare suppliers more accurately and plan budgets effectively.
Several factors influence the final price of abrasive materials in international trade:
Volume and MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger volumes typically lower unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers from Africa and South America should negotiate for favorable MOQs, especially when dealing with smaller or emerging suppliers, to reduce per-unit costs.
Specifications and Customization: Customized abrasives tailored to specific applications (e.g., grain size, bond type, hardness) often command premium prices. Clear communication of exact needs helps avoid unnecessary costs associated with over-specification.
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) often entail additional testing and processing costs, but they are essential for compliance and performance, particularly in regulated industries. European buyers, for instance, might prioritize certifications, influencing cost.
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, proximity, and negotiation power significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers or those with local manufacturing facilities may offer more competitive rates, especially in Europe and the Middle East.
Incoterms and Shipping Arrangements: The choice of Incoterms impacts logistics costs, insurance, and risk allocation. Buyers should evaluate total landed costs, not just product prices, to make informed purchasing decisions.
Negotiate for Better Terms: Leverage volume discounts, flexible MOQs, or long-term contracts to reduce unit prices. For buyers from regions with less bargaining power, establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can foster competitive pricing.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the purchase price but also costs related to transportation, customs, storage, and potential rework due to quality issues. For example, cheaper abrasive materials that require frequent replacement or reprocessing may end up more expensive over time.
Leverage Regional Advantages: Buyers in Africa and South America might benefit from local or regional suppliers, reducing logistics costs and lead times. European buyers, meanwhile, often access high-quality suppliers with established certification standards, justifying higher costs through enhanced reliability.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Prices can vary based on market fluctuations, geopolitical factors, and currency exchange rates. Regular market monitoring and flexible procurement strategies can mitigate risks associated with price volatility.
While prices vary widely based on specifications, origin, and order volume, typical ranges for abrasive materials are approximately:
These figures serve as a general guide; actual prices may differ based on current market conditions and specific supplier arrangements.
By understanding these cost and pricing dynamics, B2B buyers from diverse regions can optimize their procurement strategies, achieve cost efficiencies, and build resilient supply chains in the abrasive materials sector.
1. Material Grade
The grade of an abrasive material indicates its quality level, typically reflecting purity, toughness, and consistency. Higher-grade abrasives, such as premium silicon carbide or diamond, offer superior cutting ability, longer lifespan, and better surface finish. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate grade ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency for specific applications.
2. Grain Size (Mesh or Fineness)
Grain size defines the particle dimensions, influencing the abrasiveness and finish quality. Coarser grains (lower mesh numbers) are used for rapid material removal, while finer grains (higher mesh numbers) provide smoother finishes. Accurate specification of grain size is crucial for achieving desired surface quality and process efficiency.
3. Tolerance and Shape
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in grain size and shape, affecting consistency. Shape—whether angular or rounded—also impacts cutting action and surface finish. Consistent tolerance and shape ensure predictable performance and reduce waste in production processes.
4. Hardness and Toughness
Hardness measures the abrasive’s resistance to wear, while toughness indicates its ability to withstand fracturing under stress. Balancing these properties is vital: harder abrasives last longer but may be more brittle, whereas tougher abrasives are less prone to breakage but may wear faster. These properties directly influence tool life and processing costs.
5. Bonding and Matrix Composition
In bonded abrasives (like grinding wheels), the bonding material holds abrasive grains together. The bond’s hardness and type (resinoid, vitrified, metal) determine the tool’s aggressiveness, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Proper selection of bond properties enhances performance and safety.
6. Tolerance and Density
Density impacts the stability and heat resistance of abrasive tools. Denser materials usually provide better cutting action and longer lifespan, especially under high-pressure conditions. Ensuring the right density aligns with operational demands and product longevity.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce equipment or components that integrate abrasive materials. Understanding OEM specifications is essential for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility, performance, and compliance with industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. Knowledge of MOQ helps buyers plan procurement strategies, negotiate prices, and avoid overstocking, especially when sourcing specialized abrasives or customized products.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit price and delivery terms from suppliers. Crafting clear RFQs with detailed specifications ensures accurate quotes and fosters competitive bidding, leading to better terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Familiarity with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) enables buyers to negotiate delivery conditions, control costs, and mitigate risks during international transactions.
5. Specification Sheets (Tech Data Sheets)
Documents provided by suppliers detailing technical properties, usage guidelines, and compliance standards. Reviewing these sheets ensures that abrasive materials meet application requirements and industry regulations.
6. Certification and Compliance (ISO, REACH, etc.)
Certifications verify that abrasive products adhere to quality, environmental, and safety standards. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with relevant certifications to ensure product reliability and regulatory compliance across different markets.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers buyers to make informed procurement decisions, optimize supply chain efficiency, and ensure product suitability for their specific applications. Clear communication of specifications and familiarity with industry jargon reduce misunderstandings, minimize delays, and foster long-term supplier relationships—crucial factors in competitive international markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The global abrasive materials sector is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by technological innovation, evolving industry demands, and geopolitical factors. Key drivers include increasing automation across manufacturing, automotive, and construction industries, which demand high-performance abrasives for precision and efficiency. Emerging B2B sourcing trends emphasize digital platforms and supply chain transparency, enabling buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Germany and Kenya—to access a broader supplier base with enhanced ease.
For international buyers, understanding regional market nuances is vital. Europe, especially Germany, remains a leader in high-quality, specialized abrasives, driven by stringent standards and technological innovation. Conversely, Africa and South America often seek cost-effective solutions, with sourcing increasingly shifting toward Asian manufacturers due to competitive pricing and expanding manufacturing hubs.
Market dynamics are also shaped by raw material availability and geopolitical stability. For instance, the supply of key minerals like garnet or silicon carbide can fluctuate based on regional policies or resource depletion. This necessitates diversified sourcing strategies, including multi-sourcing and local partnerships, to mitigate risks.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a critical factor influencing procurement decisions. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate adherence to environmental standards, ethical labor practices, and certifications such as ISO 14001 or REACH compliance. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies—like IoT-enabled quality control and supply chain tracking—further enhances market transparency and efficiency, offering buyers real-time insights into product origin and lifecycle.
Overall, the sector's future hinges on balancing innovation, cost efficiency, and sustainability, making strategic sourcing and market intelligence indispensable for international B2B buyers aiming to secure reliable, high-quality abrasive materials.
Sustainability has transitioned from a regulatory requirement to a strategic imperative within the abrasive materials industry. Environmental impacts—such as dust generation, energy consumption during manufacturing, and waste management—are now central considerations for buyers and suppliers alike. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly production methods, such as using renewable energy sources and implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste.
Ethical sourcing is equally vital, especially for buyers from regions like Europe and Africa where regulatory frameworks strongly emphasize human rights and fair labor practices. Suppliers with transparent supply chains and certifications like ISO 26000 or SA8000 demonstrate commitment to social responsibility, reducing reputational risks for buyers. For instance, sourcing abrasives derived from sustainably mined minerals or recycled materials not only aligns with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
The demand for 'green' abrasive materials is growing, driven by certifications such as EU Ecolabel and Cradle to Cradle. These certifications verify that products meet strict environmental standards, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Additionally, innovations like bio-based abrasives or those made from recycled industrial waste are gaining traction, offering eco-efficient alternatives to traditional materials.
For international buyers, establishing relationships with certified suppliers and conducting due diligence on supply chain practices are essential steps. Incorporating sustainability criteria into procurement policies not only ensures compliance but also enhances brand reputation and competitiveness in global markets. As regulatory landscapes tighten, proactive engagement with sustainable sourcing practices will be crucial for long-term success.
The abrasive materials industry has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from natural mineral reliance to sophisticated synthetic and recycled options. Initially, natural abrasives like emery and garnet dominated, sourced from regional deposits with limited environmental considerations. The mid-20th century saw the rise of synthetic abrasives such as silicon carbide and aluminum oxide, driven by industrial needs for consistent quality and performance.
In recent decades, technological advancements have enabled the development of engineered abrasives with tailored properties for specific applications, including nano-structured materials and bio-based alternatives. Simultaneously, increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures have prompted a shift toward sustainable practices and ethical sourcing, shaping industry standards and consumer expectations.
This evolution reflects a broader trend of innovation and responsibility, requiring B2B buyers to stay informed about new materials, certifications, and sourcing strategies. Understanding this historical context helps buyers appreciate the importance of continuous adaptation in a sector where technological and environmental considerations are increasingly intertwined.
Thorough vetting begins with reviewing supplier credentials, including certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) and compliance with international standards. Request samples for testing and verify their quality control processes. Check references from other international buyers, and assess their production capacity and lead times. Consider visiting factories or engaging third-party inspectors for on-site audits, especially for high-volume orders. Establish clear communication channels and ask for detailed documentation on raw material sources, manufacturing practices, and QA procedures to mitigate risks associated with quality inconsistencies.
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options such as grit size, bonding agents, shape, and coating to suit specific applications like grinding, polishing, or cutting. Initiate discussions early to define your technical specifications and desired performance characteristics. Suppliers typically require detailed drawings, sample references, or performance data. Be prepared for potential additional costs and longer lead times. Confirm whether customization involves minimum order quantities (MOQs) or specific testing procedures, and ensure clear communication on lead times, sample approval processes, and quality assurance before placing bulk orders.
MOQs vary depending on the supplier and product complexity but generally range from 500 kg to several tons for bulk orders. Lead times can span from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by raw material availability and manufacturing capacity. Common payment terms include 30% upfront deposit with the balance payable before shipment, or letters of credit for larger transactions. Negotiate flexible terms where possible, especially for trial orders. Establish clear timelines and payment schedules upfront to avoid delays, and consider using escrow or trade finance options to mitigate payment risks across borders.
Request certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), and industry-specific standards relevant to abrasive materials. QA documentation should include test reports, batch traceability, and compliance certificates indicating adherence to international safety and performance standards. For critical applications, ask for third-party lab test results on grit size, hardness, and purity. These documents help validate product consistency, ensure regulatory compliance, and reduce risks of substandard materials affecting your production quality.
Begin by selecting reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial materials. Decide between sea freight (cost-effective for large quantities) and air freight (faster but more expensive). Ensure proper packaging to prevent damage during transit, especially for fragile or abrasive surfaces. Clarify incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to define responsibilities and costs. Track shipments proactively and confirm customs clearance procedures, tariffs, and import regulations in your country. Building strong relationships with logistics providers can streamline customs processes, reduce delays, and optimize delivery schedules.
Establish clear contractual terms covering quality standards, inspection rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms—preferably arbitration or mediation under recognized international frameworks. If quality issues arise, document discrepancies with detailed photos and test reports, and communicate promptly with your supplier. Offer opportunities for corrective actions or rework, and negotiate solutions aligned with contractual terms. Maintaining open, professional communication and involving third-party inspectors or mediators can facilitate fair resolution. Always include clauses for penalty or refund processes in your initial agreements to safeguard your investments.
Trade policies, tariffs, and import/export restrictions can significantly influence costs and supply stability. For example, tariffs on raw materials or geopolitical tensions may cause delays or price fluctuations. Stay informed about trade agreements, sanctions, and regional stability in your sourcing countries. Diversify your supplier base across multiple regions to reduce dependency on a single source. Engage with local trade associations or chambers of commerce for updates on policy changes. Incorporating flexible sourcing strategies and building buffer inventories can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical disruptions.
Prioritize suppliers with environmental management certifications and transparent sustainability practices. Verify compliance with local and international regulations such as REACH, OSHA, or equivalent standards. Incorporate contractual clauses requiring adherence to safety protocols and proper waste disposal. Conduct periodic audits or request third-party audit reports to confirm ongoing compliance. Educate your procurement team on regional environmental laws and import restrictions. Implement quality control checks at multiple stages—raw material sourcing, production, and post-shipment—to ensure products meet safety and environmental standards, reducing legal and reputational risks.
Effective strategic sourcing of abrasive materials is essential for international B2B buyers seeking competitive advantage, quality assurance, and supply chain resilience. By prioritizing supplier diversification, evaluating quality standards, and leveraging technological advancements such as digital procurement platforms, buyers can optimize costs and mitigate risks across diverse markets.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional supply dynamics and fostering strong supplier relationships are critical. Embracing sustainable sourcing practices and staying informed about evolving industry standards will position buyers to adapt swiftly to market shifts and regulatory changes.
Looking ahead, the abrasive materials industry will continue to evolve with innovations in material technology and increased emphasis on environmental responsibility. Buyers should proactively engage in strategic partnerships and leverage data-driven decision-making to secure reliable, high-quality supplies.
Actionable Takeaway: Invest in comprehensive market intelligence, build resilient supplier networks, and harness digital tools to future-proof your sourcing strategy. By doing so, international B2B buyers can unlock new growth opportunities and maintain a competitive edge in the dynamic abrasive materials landscape.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina