Carborundum, also known as silicon carbide, stands as a cornerstone material in numerous industrial applications worldwide. Its exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability make it indispensable for sectors ranging from abrasives and refractories to electronics and automotive components. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key hubs like Thailand and South Africa—understanding the nuances of sourcing high-quality carborundum is critical to maintaining competitive advantage and operational excellence.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower procurement professionals and industrial buyers with actionable insights into the global carborundum market. It covers essential aspects such as the various types and grades of carborundum, key raw materials, and state-of-the-art manufacturing and quality control processes that ensure product consistency and performance. Additionally, the guide provides a detailed overview of reputable global suppliers, cost factors, and regional market trends that influence pricing and availability.
By leveraging this resource, international buyers can navigate complex supply chains, evaluate supplier reliability, and optimize sourcing strategies tailored to their regional market conditions. Whether you are seeking to enhance your product portfolio or secure cost-effective, high-performance materials, this guide offers a structured approach to informed decision-making and risk mitigation in the evolving global carborundum landscape.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Silicon Carbide | High purity, crystalline structure, green/black color | Abrasives, refractories, semiconductor substrates | Pros: High thermal conductivity, chemical stability; Cons: Higher cost, brittle nature |
| Sintered Silicon Carbide | Manufactured via sintering, dense and strong | Mechanical seals, wear parts, high-performance ceramics | Pros: Excellent mechanical strength, corrosion resistance; Cons: More expensive, limited shapes |
| Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide | Produced by reacting silicon with carbon preform | Heat exchangers, kiln furniture, chemical processing | Pros: Cost-effective, good thermal shock resistance; Cons: Lower strength than sintered |
| Silicon Carbide Powder | Fine granular form, varying mesh sizes | Polishing, grinding, additive manufacturing | Pros: Versatile particle sizes, easy integration; Cons: Requires proper handling, dust control |
| Silicon Carbide Fibers | High tensile strength, lightweight | Composite reinforcements, aerospace, automotive | Pros: Enhances material strength, lightweight; Cons: High production cost, specialized use |
Fused Silicon Carbide is characterized by its high purity and crystalline structure, typically appearing in green or black hues. It excels in applications demanding high thermal conductivity and chemical inertness, such as abrasives and semiconductor substrates. For B2B buyers, this type offers durability and performance but comes at a premium price and requires careful handling due to its brittleness. Buyers should evaluate cost-benefit based on application criticality, particularly in high-temperature environments.
Sintered Silicon Carbide is produced through a sintering process that results in a dense, mechanically robust material. It is widely used in mechanical seals and wear-resistant components where strength and corrosion resistance are essential. While more costly, its superior durability justifies investment for industries like chemical processing and heavy machinery. Buyers should consider long-term operational savings against upfront costs and assess supplier capabilities for custom shapes.
Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide involves reacting molten silicon with a carbon preform, offering a cost-effective option with good thermal shock resistance. This variant suits applications such as heat exchangers and kiln furniture where moderate strength suffices. B2B purchasers should weigh its lower mechanical strength against budget constraints and operational demands, ensuring compatibility with the intended chemical environment.
Silicon Carbide Powder is available in various particle sizes, making it highly adaptable for polishing, grinding, and additive manufacturing processes. It enables precise control over surface finishes and material properties. Buyers must prioritize quality control, particle size distribution, and supplier reliability, as inconsistencies can affect end-product performance. Proper handling protocols for dust and safety are also critical considerations.
Silicon Carbide Fibers provide exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, making them ideal for reinforcing composites in aerospace and automotive sectors. Although their production cost is high, they contribute significantly to material performance enhancements. B2B buyers should focus on supplier expertise in fiber processing and integration, as well as compatibility with matrix materials to maximize composite benefits.
Related Video: The Genius Behind Bach's Goldberg Variations: CANONS
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of carborundums | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Metalworking | Abrasive grinding wheels and cutting tools | Enhances precision and durability in metal fabrication | Consistent grit size, high purity, and reliable supply chain |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Heat sinks and semiconductor substrate materials | Improves thermal management and device longevity | High thermal conductivity grade, contamination-free material |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Brake pads and high-performance friction components | Provides superior wear resistance and heat dissipation | Certification compliance, performance consistency, and bulk availability |
| Construction & Building Materials | Polishing and surface finishing of ceramics and stones | Delivers smooth finishes and extends tool life | Particle size uniformity, abrasion resistance, and import logistics |
| Renewable Energy | Silicon wafer slicing in solar panel manufacturing | Increases efficiency and reduces material waste | Ultra-fine grit quality, supply reliability, and cost-effectiveness |
Manufacturing & Metalworking
Carborundum's primary role in manufacturing is as an abrasive for grinding wheels and cutting tools. It enables precise shaping and finishing of metals, crucial for sectors requiring tight tolerances such as machinery production and tooling. For international buyers in Africa and South America, ensuring consistent grit size and material purity is vital to maintain product quality. Reliable supply chains help avoid production delays, especially where local alternatives are limited.
Electronics & Semiconductors
In electronics, carborundum is used for heat sinks and substrates due to its excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties. This application is critical for semiconductor devices to prevent overheating and enhance longevity. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East must prioritize contamination-free, high-grade carborundum to meet stringent industry standards and support advanced manufacturing processes.
Automotive & Aerospace
Carborundum is integral in producing brake pads and friction components, offering superior wear resistance and efficient heat dissipation under high stress. This extends component life and safety in vehicles and aircraft. For buyers in regions like South Africa and Thailand, verifying certification compliance and consistent performance is essential to meet regulatory requirements and maintain end-product reliability.
Construction & Building Materials
The abrasive qualities of carborundum make it ideal for polishing ceramics, stones, and other construction materials. It ensures smooth surface finishes and prolongs tool life. Importers in Africa and South America should focus on particle size uniformity and abrasion resistance, alongside efficient import logistics, to optimize cost and supply continuity.
Renewable Energy
In solar panel manufacturing, carborundum is used for slicing silicon wafers with ultra-fine abrasives, enhancing efficiency and reducing material waste. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East must secure ultra-fine grit quality and dependable supply to keep pace with the growing renewable energy market while managing costs effectively.
Related Video: Uses Of Polymers | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Key Properties: Silicon carbide is renowned for its exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, and excellent resistance to thermal shock. It withstands temperatures up to approximately 1600°C and exhibits strong chemical inertness, particularly against acids and alkalis. Its resistance to wear and corrosion makes it ideal for abrasive environments.
Pros & Cons: SiC offers outstanding durability and performance in high-temperature and high-wear applications. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials and requires specialized manufacturing processes such as sintering or chemical vapor deposition, which can increase lead times and costs. Its brittleness can be a limitation in applications involving mechanical shock.
Impact on Application: Silicon carbide carborundums are well-suited for abrasive machining, high-temperature filtration, and chemical processing industries. They perform exceptionally in environments involving corrosive media or extreme thermal cycling, making them ideal for chemical reactors and heat exchangers.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with ASTM C799 (Standard Specification for Dense Silicon Carbide) and DIN EN 62864 standards is common. European buyers often demand certifications related to REACH and RoHS compliance. In regions like South Africa and Brazil, local standards may align with ASTM or ISO norms, but verifying supplier certifications is crucial. Given the higher cost, buyers should balance performance requirements with budget constraints and consider local manufacturing capabilities to reduce import costs.
Key Properties: Alumina is characterized by excellent hardness, high melting point (~2072°C), and good electrical insulation properties. It offers strong resistance to chemical attack from acids but is less resistant to alkaline environments. Alumina exhibits moderate thermal conductivity and good wear resistance.
Pros & Cons: Alumina is more cost-effective than silicon carbide and easier to manufacture, with widespread availability. However, it has lower thermal shock resistance and can be prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Its chemical resistance is not as broad, limiting its use in highly alkaline or reducing environments.
Impact on Application: Alumina carborundums are commonly used in grinding, polishing, and abrasive blasting applications. They are suitable for media that are acidic or neutral but less ideal for strongly alkaline or corrosive chemical processes. Its electrical insulation properties also make it useful in certain electronic and electrical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Alumina products often adhere to ASTM C799 and ISO 21066 standards. European and Middle Eastern buyers may require compliance with CE marking and RoHS directives, especially for electronic applications. For African and South American markets, alumina’s cost-effectiveness and availability make it a preferred choice, but buyers should confirm the material grade and purity to ensure performance consistency.
Key Properties: Boron carbide is one of the hardest known materials, with excellent abrasion resistance and a melting point around 2763°C. It is chemically inert to most acids and alkalis and exhibits low density, which is advantageous for lightweight applications. Its high neutron absorption capability makes it useful in nuclear industries.
Pros & Cons: Boron carbide offers superior hardness and wear resistance but is brittle and difficult to machine. It is more expensive than alumina but can be cost-competitive with silicon carbide depending on purity and form. Manufacturing complexity and limited supplier availability can pose challenges.
Impact on Application: Boron carbide carborundums are ideal for high-performance abrasive tools, ballistic armor, and nuclear shielding. Their chemical inertness allows use in harsh chemical environments, but brittleness limits their use in impact-prone applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM C799 and ISO 13590 is typical for boron carbide materials. European buyers may require additional certifications for nuclear applications, while Middle Eastern buyers often focus on product traceability and quality assurance. In African and South American markets, the high cost and specialized nature of boron carbide mean it is typically reserved for niche, high-value applications.
Key Properties: Silicon nitride offers excellent fracture toughness, high strength at elevated temperatures (up to 1400°C), and good thermal shock resistance. It is chemically stable in oxidizing and reducing environments and has low thermal expansion.
Pros & Cons: Silicon nitride balances toughness and hardness better than many ceramics, reducing the risk of catastrophic failure. It is more expensive than alumina but generally less costly than boron carbide. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, with processes like hot pressing or gas pressure sintering required.
Impact on Application: Silicon nitride carborundums are used in precision bearings, cutting tools, and high-temperature components exposed to thermal cycling. Their resistance to oxidation and corrosion makes them suitable for automotive and aerospace applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East often require compliance with ISO 20507 and ASTM standards related to silicon nitride ceramics. In Africa and South America, silicon nitride’s balance of cost and performance is attractive for industrial tooling and automotive sectors. Buyers should verify supplier quality certifications and consider logistics costs when sourcing from distant suppliers.
| Material | Typical Use Case for carborundums | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide | Abrasive machining, chemical reactors, heat exchangers | High thermal resistance and chemical inertness | Brittleness and high manufacturing cost | High |
| Alumina | Grinding, polishing, abrasive blasting | Cost-effective with good hardness | Lower thermal shock resistance and limited chemical resistance | Low |
| Boron Carbide | High-performance abrasives, ballistic armor, nuclear shielding | Exceptional hardness and chemical inertness | Brittleness and limited availability | High |
| Silicon Nitride | Precision bearings, cutting tools, high-temp components | Excellent toughness and thermal shock resistance | Moderate cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
Carborundum, a synthetic abrasive material primarily composed of silicon carbide, is widely used in industrial applications for grinding, cutting, and polishing. Understanding its manufacturing process is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers that meet stringent quality and performance standards.
1. Raw Material Preparation
The production begins with sourcing high-purity raw materials such as silica sand, petroleum coke, and carbon. These are carefully weighed and blended to achieve the desired chemical composition. The quality of raw materials significantly impacts the final product’s hardness and abrasive properties, so suppliers often use advanced material analysis techniques at this stage.
2. Formation (Synthesis of Silicon Carbide)
The core manufacturing step involves the Acheson process, where the raw material mixture is heated in an electric resistance furnace at temperatures exceeding 2,000°C. This high-temperature reaction produces crystalline silicon carbide grains. Manufacturers control parameters like temperature, heating duration, and furnace atmosphere to optimize grain size and purity, directly influencing the abrasive quality.
3. Crushing and Milling
After synthesis, the silicon carbide mass is cooled and crushed into coarse grains. These grains are then milled to specific size distributions depending on the intended application. Precision in grain size control is essential, especially for applications requiring uniform abrasiveness, such as precision grinding in automotive or aerospace industries.
4. Assembly and Bonding
For finished abrasive products such as grinding wheels or sandpapers, the carborundum grains are bonded with materials like resins, vitrified ceramics, or rubber. The bonding process affects product durability and performance under different operational conditions. Advanced techniques, including hot pressing and isostatic pressing, are employed to ensure uniform bonding and product consistency.
5. Finishing and Treatment
The final stage includes surface treatments such as coating or impregnation to enhance wear resistance and reduce heat generation during use. Some manufacturers also apply grading and packaging processes designed to preserve product integrity during transit, which is a critical consideration for international B2B shipments.
Ensuring high-quality carborundum products requires rigorous quality control (QC) integrated throughout the manufacturing process. International buyers must prioritize suppliers adhering to recognized standards and implement robust QC systems.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
Quality control is typically implemented at multiple stages, ensuring defects are detected early and products meet stringent specifications.
For international buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC practices is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
Selecting carborundum suppliers with robust manufacturing processes and quality assurance systems is vital for operational success. Buyers should prioritize:
By integrating these insights into procurement strategies, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can secure high-quality carborundum products tailored to their industry needs.
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of carborundums is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies and ensure competitive advantage. Carborundums, primarily used as abrasive materials and in industrial applications, have a multi-faceted cost composition influenced by raw materials, manufacturing complexity, and global trade considerations.
Prices for carborundums vary widely based on specifications, order size, supplier location, and market conditions. The insights provided serve as a strategic framework rather than exact price quotations. Buyers should request detailed quotations from multiple suppliers and factor in all cost components and local market variables before finalizing procurement decisions.
This comprehensive cost and pricing analysis equips international B2B buyers with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of sourcing carborundums efficiently, ensuring optimal cost control and supply chain resilience across diverse global markets.
Understanding the technical specifications of carborundums is vital for international B2B buyers to ensure the product meets their operational requirements and quality standards. Here are key properties to consider:
Material Grade
Carborundums vary by purity and crystalline structure, commonly classified into grades such as electronic grade, metallurgical grade, and abrasive grade. Higher purity grades are essential for applications requiring precision and durability, such as semiconductor manufacturing or fine abrasive work. For buyers, specifying the correct grade prevents costly mismatches in performance.
Particle Size and Grit
Particle size directly influences the abrasive effectiveness and surface finish quality. Grit size ranges from coarse to ultra-fine, with smaller particles used for polishing and larger for heavy material removal. Accurate specification of particle size ensures compatibility with the intended machinery and process, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in dimensions or particle size distribution. Tight tolerances are critical in precision industries to maintain consistent product quality and avoid operational disruptions. Buyers should verify tolerance standards to align with their manufacturing or processing requirements.
Hardness
Measured on the Mohs scale, carborundum’s hardness typically ranges around 9-9.5, making it one of the hardest industrial abrasives. This property determines its wear resistance and cutting ability. For B2B buyers, understanding hardness helps in selecting carborundum for high-durability applications, such as grinding wheels or cutting tools.
Thermal Stability
Carborundum’s ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading is crucial for applications involving heat generation, like metalworking or refractory products. Buyers in regions with high ambient temperatures or demanding industrial environments should prioritize thermal stability to ensure longevity and safety.
Bulk Density
This affects the volume-to-weight ratio, impacting shipping costs and storage requirements. Knowing bulk density helps buyers optimize logistics and inventory management, especially important for international shipments where freight charges can be significant.
Familiarity with industry jargon streamlines communication and negotiation between suppliers and buyers, particularly across diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to suppliers who produce carborundum components that are incorporated into another company’s final products. Buyers working with OEMs benefit from tailored specifications and quality assurances aligned with their product lines.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount of carborundum a supplier is willing to sell per order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning, especially for smaller businesses or those testing new products before scaling up.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent by buyers to suppliers to obtain pricing and delivery terms for specified quantities and grades of carborundum. Crafting clear RFQs helps buyers receive accurate, comparable offers and accelerates procurement cycles.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs between buyers and sellers. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Understanding Incoterms empowers buyers to negotiate favorable shipping arrangements and control costs.
Lead Time
The period between order placement and delivery. In international trade, lead time affects production schedules and market responsiveness. Buyers should confirm realistic lead times to avoid supply chain disruptions.
Certification and Compliance
Refers to adherence to international standards such as ISO, REACH, or RoHS, often required for import/export and quality assurance. Verifying certifications ensures product legitimacy and smooth customs clearance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, optimize supply chain efficiency, and build reliable partnerships with carborundum suppliers worldwide.
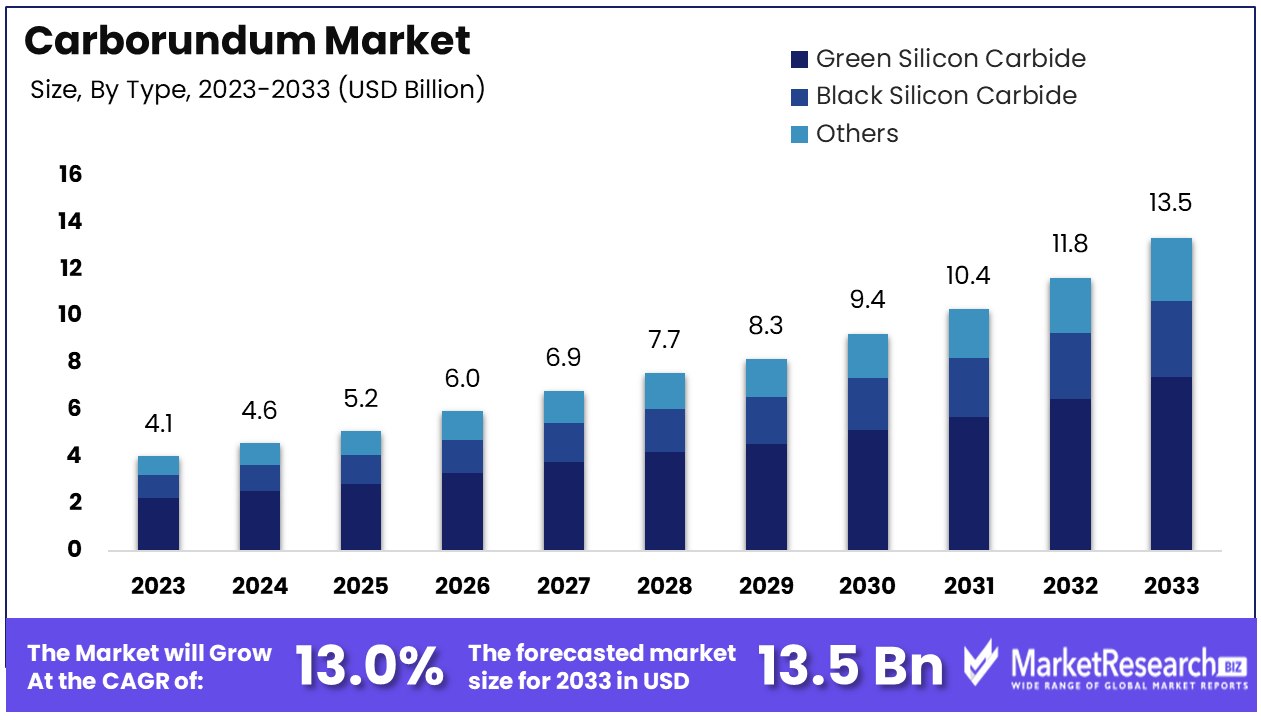
The global carborundum market, driven by its extensive applications in abrasives, refractories, and semiconductor industries, is experiencing dynamic growth fueled by industrial expansion in emerging economies. Key regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing increased demand, with countries like South Africa, Brazil, Saudi Arabia, and Germany playing pivotal roles as both consumers and producers. The rise of manufacturing sectors, particularly in automotive, electronics, and construction, is a significant driver for carborundum consumption.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
For international B2B buyers, understanding regional supply chain nuances is critical. Africa and South America are becoming attractive sourcing hubs due to their expanding mineral resources and improving industrial infrastructure, though buyers must navigate logistical challenges and regulatory variability. Europe continues to be a leader in high-quality carborundum production with advanced technological capabilities, offering premium products but often at higher price points.
Emerging sourcing trends include increased adoption of digital procurement platforms that enable transparent supplier evaluation and real-time pricing, which is especially beneficial for buyers operating across diverse geographies. Moreover, strategic partnerships and long-term contracts are gaining traction to mitigate supply volatility caused by geopolitical tensions and raw material price fluctuations. Buyers from the Middle East are leveraging these trends to secure consistent supply chains while optimizing costs.
Technological innovation is shaping product differentiation, with manufacturers focusing on enhanced purity and particle size control to meet the demanding specifications of semiconductor and precision engineering industries. Additionally, modular and customizable carborundum products are becoming more prevalent, allowing buyers to tailor materials to specific industrial applications, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste.
Sustainability is increasingly central to procurement strategies in the carborundum sector. The environmental impact of mining and processing silicon carbide, the primary component of carborundum, includes energy-intensive operations and potential ecological disruption. For B2B buyers, prioritizing suppliers that implement energy-efficient manufacturing processes and adhere to stringent environmental standards can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of their supply chains.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, particularly for buyers in regions with heightened regulatory scrutiny and consumer demand for responsible supply chains. Ensuring transparency through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI), and adherence to local and international labor laws helps mitigate risks related to human rights abuses and environmental degradation.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Green certifications for carborundum products, including those verifying recycled content or low-emission production methods, are gaining market value. Buyers should engage suppliers who invest in circular economy practices, such as reclaiming and reprocessing scrap materials, which reduce waste and lower resource consumption. Collaborative initiatives between buyers and suppliers to establish traceability systems enhance accountability and foster long-term sustainability.
For international buyers, especially from Africa and South America, integrating sustainability criteria into supplier selection not only aligns with global regulatory trends but also opens access to premium markets in Europe and the Middle East, where end-users increasingly demand eco-friendly products. Transparent communication about sustainability initiatives can strengthen buyer-supplier relationships and differentiate offerings in competitive markets.
The development of carborundum dates back to the late 19th century when Edward G. Acheson discovered silicon carbide’s abrasive properties, leading to its commercial production. Initially used primarily for grinding and cutting applications, carborundum’s role expanded with industrialization, especially in refractory materials and electronics.
Over the decades, advancements in synthetic production methods have improved product quality and scalability, enabling global supply chains to develop. The sector’s evolution reflects broader industrial trends toward precision manufacturing and environmental stewardship, making it a critical component in modern industrial ecosystems.
For B2B buyers, understanding this history underscores the importance of selecting suppliers with proven technical expertise and the ability to innovate in response to evolving industrial demands and sustainability imperatives.
How can I effectively vet carborundum suppliers from different regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
Vetting suppliers requires a multi-step approach: start with verifying business licenses and certifications relevant to carborundum manufacturing and export. Request samples to assess product quality firsthand. Utilize third-party inspection services or factory audits to confirm manufacturing capabilities and compliance with international standards. Check references and customer reviews, especially from buyers within your region or industry. Establish clear communication channels to evaluate responsiveness and transparency. Platforms like Alibaba or global trade directories can be initial sources but always complement online data with direct interactions.
Is customization of carborundums available, and how should I approach this with international suppliers?
Many suppliers offer customization in terms of grit size, shape, bonding material, and packaging to meet specific industrial needs. When negotiating customization, provide detailed technical specifications and expected performance criteria. Confirm minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom batches, as these are often higher than standard products. Request prototypes or samples before committing to large orders. Clarify intellectual property rights and confidentiality to protect proprietary designs or formulations. Timelines for custom production may be longer, so plan procurement schedules accordingly.
What are typical MOQ and lead times for carborundum orders, and how can I manage them effectively?
MOQs vary significantly by supplier and product type but generally range from 500 kg to several tons for industrial-grade carborundum. Lead times depend on stock availability, production schedules, and shipping logistics, typically spanning 3 to 8 weeks. To manage these factors, negotiate flexible MOQs if possible, especially when testing new suppliers or products. Establish clear production and delivery timelines in contracts. Consider buffer stock to mitigate delays caused by customs clearance or transport disruptions, which are common in cross-border trade.
What payment terms are standard in international carborundum transactions, and how can buyers protect their interests?
Common payment methods include Letters of Credit (LC), Telegraphic Transfers (T/T), and escrow services. LCs provide security by involving banks in payment release upon document verification, suitable for new or large suppliers. T/T is faster but riskier without a trusted relationship. Negotiate partial payments—such as 30% upfront and 70% upon shipment—to balance risk. Always request pro forma invoices detailing costs and terms. Engage trade finance specialists or use trade credit insurance to mitigate financial risks in unfamiliar markets.
What quality assurance certifications should I look for when sourcing carborundums internationally?
Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, REACH compliance for chemical safety in Europe, and sometimes specific industry certifications like ASTM standards for abrasives. Suppliers should provide test reports confirming physical and chemical properties, such as hardness, purity, and particle size distribution. Request certificates of analysis (COA) with each batch. Verifying third-party lab testing enhances reliability. Ensuring compliance with your country’s import regulations and environmental standards is critical to avoid customs delays or product rejection.
How do I handle logistics and shipping challenges when importing carborundums from diverse regions?
Carborundum is typically shipped in bulk or palletized bags, requiring careful packaging to prevent moisture damage and contamination. Work with freight forwarders experienced in handling abrasive materials and customs regulations of your target markets. Plan for potential delays caused by port congestion, documentation issues, or geopolitical factors. Utilize Incoterms clearly in contracts to define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. For regions with less-developed infrastructure, consider multimodal transport solutions and warehouse partnerships to optimize delivery times.
What steps should I take if there is a dispute over carborundum quality or delivery terms?
First, document all communications, contracts, and inspection reports. Engage in direct dialogue with the supplier to clarify issues and seek amicable resolution. Employ third-party inspection or arbitration services if necessary. Clearly define dispute resolution mechanisms in contracts, such as mediation or international arbitration under ICC or UNCITRAL rules. Understand local legal frameworks and consider hiring legal counsel familiar with international trade law. Maintaining a professional relationship can often lead to quicker settlements than litigation.
Are there regional considerations for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe when sourcing carborundums?
Yes, regional factors include import tariffs, certification requirements, and preferred payment methods. For example, African buyers may face higher logistics costs and longer lead times due to port infrastructure constraints. South American buyers should verify compliance with Mercosur or Andean trade bloc regulations. Middle Eastern buyers often prioritize suppliers with ISO and Halal certifications. European buyers must ensure REACH compliance and sustainability standards. Understanding local market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and political stability is crucial for effective sourcing and risk mitigation.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of carborundums demands a nuanced understanding of market dynamics, supplier capabilities, and regional considerations. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, embracing a data-driven approach to supplier evaluation is critical. This involves assessing supplier reliability, product quality certifications, and logistical efficiency to mitigate risks and optimize cost-effectiveness.
Key takeaways include:
Looking ahead, the carborundum market is expected to evolve with increasing demand for sustainable production methods and enhanced product performance. International buyers should proactively engage with suppliers embracing green technologies and advanced manufacturing processes to maintain competitive advantage.
Actionable insight: Begin strategic sourcing initiatives today by conducting comprehensive supplier audits and exploring collaborative opportunities that align with your operational goals. This forward-thinking approach will secure supply chains and drive growth in an increasingly complex global marketplace.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina