In the highly competitive landscape of industrial manufacturing and finishing, selecting the right abrasive paper grit size is a pivotal factor that directly influences product quality, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of abrasive grit sizes is essential to meet diverse application requirements and regional market standards.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of abrasive paper grit size, tailored to empower procurement professionals and technical buyers with actionable insights. It delves into the various grit classifications, explains how different materials and grit sizes affect performance outcomes, and highlights critical manufacturing and quality control considerations that ensure consistent product reliability.
Beyond technical details, the guide provides an in-depth overview of global supplier landscapes, cost factors, and sourcing strategies that address the unique challenges faced by buyers in emerging and established markets alike. Whether you are sourcing for automotive finishing in the UK, precision tooling in Saudi Arabia, or heavy-duty applications in South America, this resource equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions that optimize value and reduce supply chain risks.
Key areas covered include:
By integrating technical expertise with global market intelligence, this guide serves as an indispensable tool for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance their abrasive paper procurement strategy and achieve superior operational outcomes.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse Grit (40-60) | Large abrasive particles, rough surface finish | Heavy material removal, initial sanding stages | + Fast stock removal – Rough finish, not for fine work |
| Medium Grit (80-120) | Balanced particle size, moderate surface smoothness | General-purpose sanding, surface preparation | + Versatile use – May require follow-up with finer grit |
| Fine Grit (150-180) | Smaller abrasive grains, smoother finish | Final sanding before finishing, light surface prep | + Produces smooth surfaces – Slower material removal |
| Very Fine Grit (220-400) | Very fine particles, ultra-smooth surface finish | Polishing, finishing coats, delicate surfaces | + Ideal for polishing – Not suitable for heavy sanding |
| Extra Fine Grit (600+) | Extremely fine abrasive, near-polish quality | Automotive, electronics finishing, high-precision | + Superior finish quality – High cost, limited material removal |
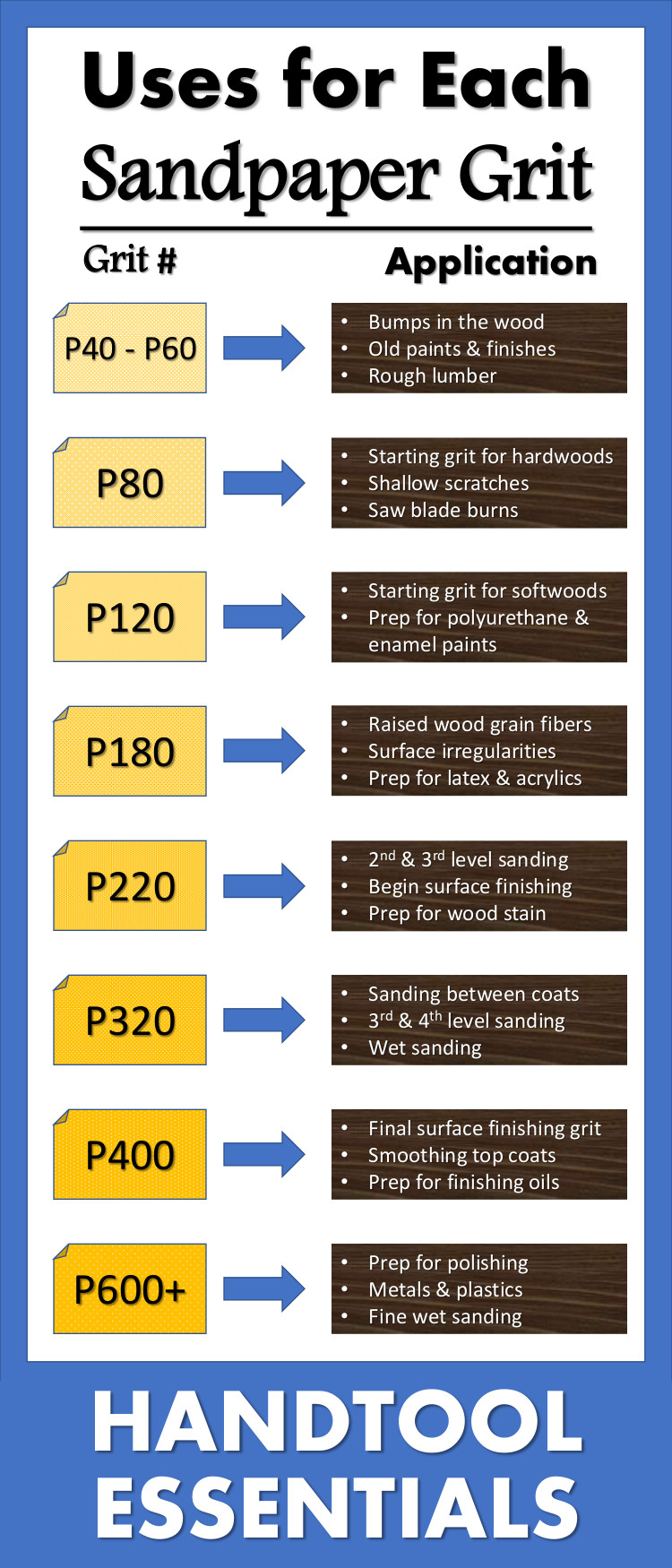
Coarse Grit (40-60):
Coarse grit abrasive papers feature large abrasive particles designed for aggressive material removal and rapid sanding. They are ideal for initial surface preparation, such as stripping paint or shaping wood and metal. For B2B buyers in industries like construction, shipbuilding, or heavy manufacturing, coarse grit abrasives are essential for reducing processing time. However, they produce rough finishes that require subsequent sanding with finer grits. Buyers should consider grit consistency and backing durability to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Medium Grit (80-120):
Medium grit abrasives offer a balance between material removal speed and surface smoothness. This type is widely used for general-purpose sanding and surface preparation, making it a versatile choice for diverse industries including furniture manufacturing and metal fabrication. Buyers should evaluate grit uniformity and adhesion quality to ensure consistent results. Medium grit papers often serve as a transition between coarse and fine sanding stages, so availability in bulk and compatibility with existing equipment are key purchasing factors.
Fine Grit (150-180):
Fine grit abrasive papers are characterized by smaller abrasive grains that produce smoother finishes suitable for final sanding before painting or sealing. Industries such as woodworking, automotive refinishing, and metalworking rely on fine grit abrasives to achieve surface uniformity without deep scratches. When sourcing fine grit abrasives, buyers should prioritize papers with strong abrasive bonding to prevent premature wear, and consider the backing material for flexibility versus durability based on application needs.
Very Fine Grit (220-400):
Very fine grit abrasives are designed for polishing and finishing delicate surfaces, offering ultra-smooth finishes. These are crucial in sectors like aerospace, electronics, and luxury goods manufacturing where surface perfection is critical. Buyers must assess factors like grit size precision and paper consistency to avoid surface defects. While these abrasives have slower material removal rates, their ability to refine surfaces justifies their use in high-value finishing processes.
Extra Fine Grit (600+):
Extra fine grit abrasive papers provide near-polish quality finishes, essential for precision industries such as automotive detailing, electronics assembly, and optical manufacturing. They enable the highest level of surface refinement but are not intended for material removal. For B2B buyers, cost considerations and supplier reliability are paramount since these abrasives are typically more expensive and require stringent quality control. Compatibility with polishing compounds and specific finishing equipment also influences purchasing decisions.
Related Video: Grit Blasting process Vs Sand Blasting process, Types of Grit Blasting abrasive materials
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of abrasive paper grit size | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Surface preparation for paint and coating application | Ensures smooth finish, improves paint adhesion, reduces defects | Consistent grit size, durability under high-volume use, availability of varied grit sizes |
| Metal Fabrication | Deburring, polishing, and finishing of metal parts | Enhances product quality, prevents corrosion, meets industry standards | Abrasive material compatibility, grit size uniformity, supplier reliability for bulk orders |
| Woodworking & Furniture | Sanding and finishing wood surfaces | Achieves fine surface texture, improves stain absorption, reduces rework | Wide grit range availability, dust control features, eco-friendly options for export markets |
| Aerospace & Defense | Precision surface finishing of components | Meets strict tolerance levels, enhances component lifespan, ensures safety compliance | High-quality grit standards, certification compliance, supplier capacity for specialized grits |
| Construction & Renovation | Surface smoothing and preparation of walls, floors, and fixtures | Accelerates project timelines, improves surface durability, reduces labor costs | Availability of coarse and fine grits, compatibility with power tools, logistics for remote locations |
In automotive manufacturing, abrasive paper grit size is critical for surface preparation before paint and coating application. Coarser grits remove old paint and surface imperfections, while finer grits create an ideal smooth surface for new coatings. This process reduces defects and enhances paint adhesion, improving the overall vehicle finish. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East where automotive quality standards are stringent, sourcing abrasives with consistent grit size and high durability is essential to maintain production efficiency and product quality.
Metal fabrication industries rely heavily on abrasive paper grit size for deburring and polishing metal parts to achieve smooth edges and surfaces. Proper grit selection prevents damage to sensitive components and ensures compliance with industry standards, such as corrosion resistance and surface finish quality. Buyers from Africa and South America must consider abrasive material compatibility with different metals and ensure suppliers can provide uniform grit sizes in bulk to support large-scale manufacturing without interruptions.
Woodworkers use a range of abrasive paper grit sizes to sand and finish wood surfaces, from rough sanding with coarse grits to fine finishing with very fine grits. This ensures a flawless texture that enhances stain absorption and reduces the need for rework. International buyers, particularly in Europe and South America, should prioritize suppliers offering a broad grit range and dust control features to comply with environmental regulations and improve workplace safety during sanding operations.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In aerospace and defense sectors, abrasive paper grit size plays a vital role in precision finishing of components where strict tolerance and surface integrity are mandatory. Fine and ultra-fine grits are used to achieve smooth surfaces that extend component lifespan and meet rigorous safety standards. Buyers in regions like the UK and Saudi Arabia must source abrasives that meet high-quality standards and certification requirements, ensuring reliable supplier capacity for specialized grit sizes tailored to aerospace specifications.
Construction and renovation projects utilize abrasive paper grit size for smoothing and preparing surfaces such as walls, floors, and fixtures. Coarser grits enable rapid removal of rough materials, while finer grits provide a polished finish, accelerating project timelines and improving surface durability. For B2B buyers in Africa and the Middle East, sourcing abrasives that are compatible with common power tools and available in both coarse and fine grits is crucial, particularly when managing logistics for remote or challenging locations.
Related Video: Abrasive grit sizes (sanding/grinding/polishing)
Key Properties:
Aluminum oxide is a widely used abrasive material known for its high hardness and excellent durability. It offers good temperature resistance up to approximately 1200°C and moderate corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various industrial applications. Its sharp, angular grit structure ensures efficient cutting and long-lasting performance.
Pros & Cons:
Pros include strong durability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility across multiple substrates such as metals, wood, and plastics. However, it can wear faster when used on extremely hard materials like ceramics. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, with well-established production processes ensuring consistent grit size and quality.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum oxide grit is highly compatible with both wet and dry sanding media, making it adaptable for diverse finishing and surface preparation tasks. It performs well under medium to high pressure conditions, suitable for heavy-duty industrial use.
International B2B Considerations:
For buyers in Africa, South America, the the Middle East, and Europe, aluminum oxide abrasives typically comply with ASTM and DIN standards, which are widely recognized internationally. European buyers, especially in the UK, often require certification for environmental compliance and worker safety. In the Middle East and South America, sourcing from suppliers with ISO 9001 certification ensures quality consistency. Cost sensitivity in developing markets like parts of Africa may favor aluminum oxide for its balance of price and performance.
Key Properties:
Silicon carbide is an extremely hard abrasive with high thermal conductivity and excellent chemical inertness. It withstands temperatures up to 1600°C and is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, making it ideal for precision grinding and finishing of hard materials.
Pros & Cons:
Its main advantage is superior cutting ability on hard, brittle materials such as glass, ceramics, and stone. However, silicon carbide is more brittle and less durable on softer metals, leading to quicker grit breakdown. It is generally more expensive and involves more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Silicon carbide grit is preferred in applications requiring fine finishes and high precision, especially in industries like electronics and automotive parts manufacturing. It works best with dry sanding media but can also be used in wet applications to reduce dust and heat buildup.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East often require compliance with JIS and DIN standards for silicon carbide abrasives, particularly for high-precision industrial applications. South American markets may prioritize suppliers offering traceability and batch testing due to import regulations. In Africa, availability and cost can be limiting factors, so buyers may negotiate bulk orders or regional partnerships to optimize pricing.
Key Properties:
Garnet is a natural abrasive material prized for its moderate hardness and environmentally friendly profile. It has good corrosion resistance and performs well under low to medium temperature conditions, typically below 800°C.
Pros & Cons:
Garnet is renewable and biodegradable, making it attractive for eco-conscious industries. It produces less dust and has a smoother finish compared to synthetic abrasives. However, garnet's durability is lower, and it wears out faster under heavy industrial use. Its natural variability can affect grit consistency.
Impact on Application:
Garnet is ideal for applications requiring gentle abrasion such as wood finishing, waterjet cutting, and surface preparation for coatings. It is compatible with wet media, enhancing dust suppression and reducing clogging.
International B2B Considerations:
European and UK buyers favor garnet for sustainable manufacturing initiatives and often require compliance with REACH and RoHS regulations. Middle Eastern buyers may seek garnet with certification of origin due to import restrictions on natural minerals. South American and African buyers might focus on local sourcing opportunities to reduce logistics costs and ensure supply chain stability.
Key Properties:
Ceramic alumina is a high-performance abrasive known for its extreme hardness and toughness. It offers excellent heat resistance up to 1400°C and superior wear resistance, maintaining sharpness longer than traditional abrasives.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage is its exceptional durability and ability to maintain cutting efficiency under high pressure and temperature conditions. It is more expensive and complex to manufacture, requiring advanced sintering techniques. Ceramic alumina is less suitable for softer materials due to its aggressive cutting action.
Impact on Application:
This material is favored in heavy industrial applications such as aerospace, automotive, and metal fabrication where long-lasting abrasive performance is critical. It works well with both dry and wet sanding media and is effective in high-speed grinding operations.
International B2B Considerations:
European and Middle Eastern buyers often require compliance with stringent ASTM and DIN standards for ceramic alumina abrasives, especially in aerospace sectors. South American buyers may look for suppliers offering technical support and customization options. African markets may face higher costs but benefit from the material’s longevity, reducing total cost of ownership.
| Material | Typical Use Case for abrasive paper grit size | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | General-purpose sanding on metals, wood, plastics | Durable and cost-effective | Less effective on very hard materials | Low |
| Silicon Carbide | Precision grinding of glass, ceramics, stone | Superior hardness and chemical resistance | Brittle and less durable on soft metals | Medium |
| Garnet | Eco-friendly sanding for wood finishing, waterjet cutting | Renewable and produces less dust | Lower durability and grit variability | Medium |
| Ceramic Alumina | Heavy-duty industrial grinding in aerospace and automotive | Exceptional durability and heat resistance | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
The production of abrasive paper involves a series of meticulously controlled stages to ensure the grit size is consistent, durable, and suitable for various industrial applications. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes helps in evaluating suppliers and ensuring the product meets specific operational needs.
1. Material Preparation
2. Coating and Forming
3. Assembly and Finishing
Robust quality control (QC) is critical in abrasive paper manufacturing to maintain grit size consistency and product performance. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers adhering to recognized standards and transparent QC processes.
Relevant International and Industry Standards
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Common Testing Methods
For buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC processes is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
1. Supplier Audits
2. Review of Quality Documentation
3. Third-Party Inspections and Testing
Consider Regional Regulatory Requirements
Language and Documentation
Logistics and Handling
By understanding the intricate manufacturing and quality assurance processes behind abrasive paper grit size, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that reduce risk, ensure compliance, and optimize operational performance.
When sourcing abrasive paper grit sizes, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. Key cost components include:
Pricing for abrasive paper grit sizes is affected by several dynamic factors:
For buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating abrasive paper grit size pricing requires strategic considerations:
All pricing insights are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, raw material fluctuations, geopolitical factors, and supplier policies. Buyers should request detailed, updated quotations and conduct due diligence before finalizing procurement decisions.
Understanding the technical specifications of abrasive paper grit size is crucial for international B2B buyers to ensure product suitability, performance consistency, and cost-effectiveness. Below are the most critical properties to consider:
Grit Size Number
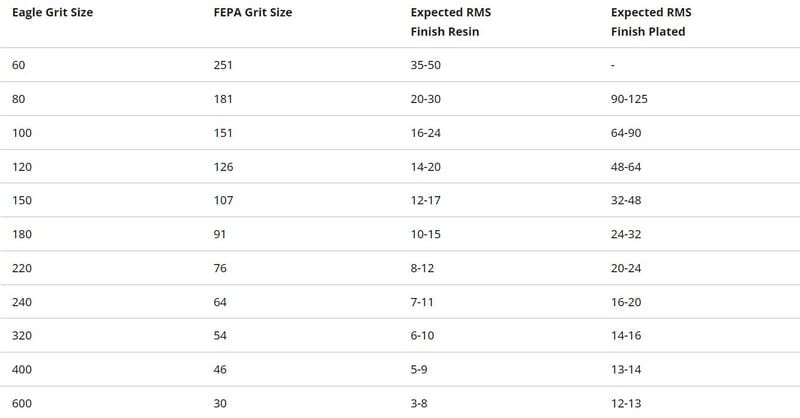
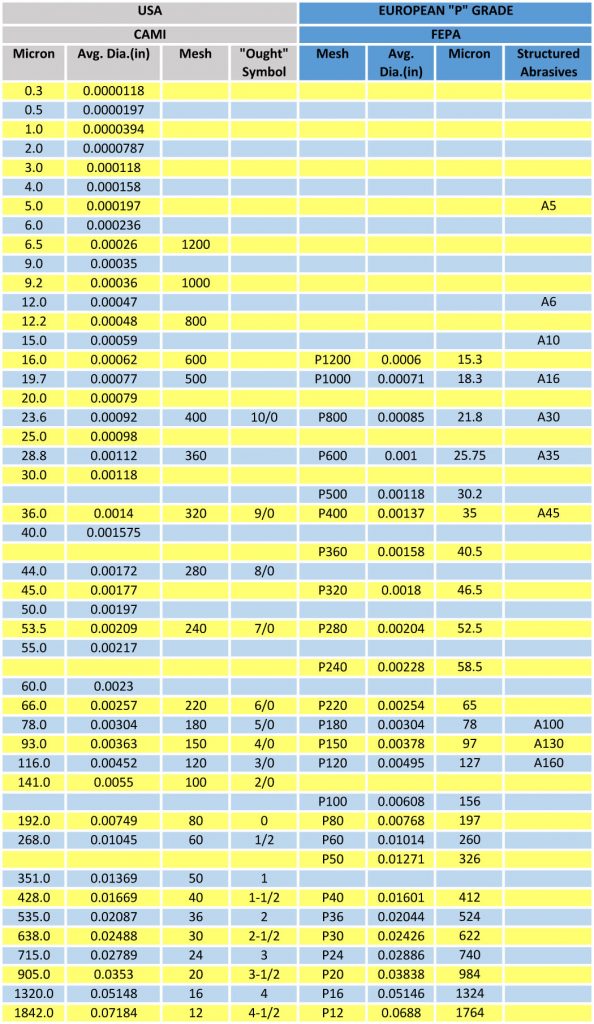
This number represents the size of abrasive particles embedded in the paper. It typically follows standardized scales such as FEPA (Fédération Européenne des Fabricants de Produits Abrasifs) or CAMI (Coated Abrasive Manufacturers Institute). Lower numbers (e.g., 40, 60) indicate coarser grit for aggressive material removal, while higher numbers (e.g., 400, 600) denote finer grit for polishing. Buyers must select the correct grit size to match their surface finishing requirements and avoid underperformance or excessive wear.
Material Grade (Abrasive Type)
Common abrasive materials include aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, garnet, and ceramic alumina. Each type offers distinct hardness, durability, and application suitability. For instance, aluminum oxide is versatile and cost-effective, ideal for wood and metal, whereas silicon carbide excels in harder materials like glass or stone. Specifying the right abrasive material ensures optimal efficiency and longevity, minimizing downtime and replacement costs.
Backing Material
The backing can be paper, cloth, or film, influencing flexibility, strength, and water resistance. Paper backing is economical and suitable for flat sanding tasks, while cloth backing offers enhanced durability for heavy-duty or curved surface applications. Buyers should consider backing type based on the intended use environment and equipment compatibility to maximize operational efficiency.
Tolerance and Consistency
This refers to the uniformity of grit size distribution and adherence to specified particle size ranges. Tight tolerance ensures consistent surface finish quality and predictable wear rates. Variability can lead to uneven abrasion, product defects, or rework. Reliable suppliers provide certification or testing data to confirm tolerance levels, a key factor for quality-conscious buyers.
Bonding Type
The adhesive or bonding method that holds the abrasive grains to the backing affects durability and performance. Resin bonds are common for their strength and heat resistance, making them suitable for high-speed applications. Buyers should verify bonding types to ensure compatibility with operational conditions, such as wet sanding or high-pressure use.
Sheet Dimensions and Thickness
Precise sizing and thickness impact fitment in sanding machines and overall handling. Standard sheet sizes facilitate compatibility with automated equipment, while thickness affects flexibility and wear resistance. International buyers must confirm these specs to avoid logistical and operational issues.
Navigating B2B transactions in abrasive paper requires familiarity with specific trade terminology to streamline communication and procurement processes:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce abrasive papers under their brand, often specifying custom grit sizes or formulations. Partnering with OEMs can offer buyers tailored solutions, quality assurance, and after-sales support, crucial for maintaining competitive advantage.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest volume a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. MOQs impact inventory management and pricing. Buyers from regions like Africa or South America should negotiate MOQs that align with their storage capacity and market demand to optimize cash flow and reduce waste.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent to suppliers to obtain pricing, lead times, and technical details. Well-prepared RFQs specifying grit size, abrasive type, backing, and bonding reduce misunderstandings and accelerate the sourcing process, enabling buyers to compare offers effectively.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities, risks, and costs between buyers and sellers during shipment (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP). Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers, especially in the Middle East and Europe, to negotiate favorable delivery terms and control import expenses.
FEPA and CAMI Standards
These are grit size classification systems widely recognized globally. FEPA is common in Europe, while CAMI is prevalent in the US. Awareness of these standards helps buyers specify grit size accurately and ensures compatibility with supplier offerings from different regions.
Batch Number / Lot Number
Identifies a specific production run of abrasive paper. Tracking batch numbers aids quality control, traceability, and inventory management. For large-scale buyers, requesting batch information can prevent inconsistencies across orders.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, negotiate effectively, and maintain consistent product quality across diverse markets. This knowledge is especially valuable for businesses operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where supplier standards and logistical challenges vary.
The abrasive paper grit size sector is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by evolving industrial needs, technological advancements, and regional market demands. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these market forces is critical to optimizing procurement strategies and maintaining competitive advantage.
Global Drivers: The rise of advanced manufacturing, automotive refinishing, aerospace maintenance, and electronics production fuels demand for precision abrasives with tailored grit sizes. Europe’s mature industrial base, particularly in the UK and Germany, demands high-quality, consistent abrasive papers with fine to ultra-fine grits for surface finishing and polishing applications. Conversely, emerging markets in Africa and South America are witnessing growth in construction and metal fabrication sectors, increasing demand for coarser grit sizes suitable for aggressive material removal.
Technological & Sourcing Trends: Digitalization and Industry 4.0 integration are influencing abrasive paper production and procurement. Suppliers now offer enhanced traceability, custom grit formulations, and just-in-time delivery models, enabling buyers to reduce inventory costs and improve process efficiency. Furthermore, online B2B marketplaces and virtual trade shows facilitate cross-border sourcing, allowing buyers from the Middle East and Africa to access global suppliers with greater ease.
Market Dynamics: Price volatility in raw materials like aluminum oxide and silicon carbide affects abrasive paper pricing, compelling buyers to adopt flexible sourcing strategies and long-term supplier partnerships. Additionally, regional trade policies and logistics infrastructure are pivotal; for example, European buyers benefit from streamlined customs procedures within the EU, while Middle Eastern buyers must navigate varied import regulations. Sustainability demands and certifications increasingly influence supplier selection, favoring producers with eco-conscious manufacturing practices.
Sustainability has become a decisive factor in abrasive paper procurement, reflecting broader corporate responsibility goals and regulatory pressures across Europe, the Middle East, and beyond. The environmental impact of abrasive paper production primarily involves energy consumption, chemical usage, and waste generation from grit manufacturing and paper backing processes.
Environmental Considerations: Many suppliers are adopting cleaner production techniques, such as using recycled paper backings and reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in adhesives. The shift towards synthetic, eco-friendly abrasive grains and water-based binders minimizes harmful emissions and improves product lifecycle sustainability.
Ethical Supply Chains: For B2B buyers, especially those in regions with growing regulatory scrutiny like the UK and the EU, ensuring ethical sourcing is paramount. This includes verifying supplier compliance with labor standards, conflict-free raw material sourcing, and transparency throughout the supply chain. Buyers from Africa and South America can leverage certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and SA8000 (Social Accountability) to vet suppliers.
Green Certifications & Materials: Certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for paper backing and REACH compliance for chemical safety enhance buyer confidence. Additionally, innovations like biodegradable abrasive papers and grit sizes optimized for longer tool life reduce waste and operational costs, aligning with corporate sustainability targets.
The abrasive paper grit size sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially dominated by natural abrasives like garnet and emery, the industry transitioned to synthetic materials—aluminum oxide and silicon carbide—in response to industrial demands for greater durability and precision.
Historically, grit size classification followed standardized systems such as FEPA (Federation of European Producers of Abrasives) and CAMI (Coated Abrasive Manufacturers Institute), which remain foundational for global trade and quality assurance. These standards enable B2B buyers to specify exact grit requirements, ensuring compatibility across diverse industrial applications.
Advancements in coating technologies and grit bonding have further refined abrasive paper performance, allowing manufacturers to offer customized grit distributions tailored to specific surface finishing challenges. This evolution supports international buyers in optimizing abrasive solutions for complex manufacturing processes across varied sectors and geographies.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. How should I vet suppliers of abrasive paper grit sizes for international B2B purchases?
Vetting suppliers requires a thorough assessment of their production capabilities, quality certifications, and compliance with international standards such as ISO or ANSI. Request detailed product specifications and samples to verify grit size accuracy and consistency. Check references and reviews from other B2B buyers, especially within your region, to understand supplier reliability and after-sales support. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider suppliers who demonstrate experience exporting to your region and who understand local market requirements and regulatory frameworks.
2. Can abrasive paper grit sizes be customized to specific industrial needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization of grit sizes to meet precise application requirements, such as specific micron ranges or unique abrasive materials. Discuss your technical needs upfront and request product datasheets or testing reports. Custom orders may require minimum order quantities (MOQs) and longer lead times, so plan accordingly. It’s critical to confirm the supplier’s R&D capabilities and whether they can maintain consistent quality during scale-up for repeat orders.
3. What are typical MOQs and lead times for abrasive paper grit size orders in international trade?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier and customization level but typically range from a few hundred to several thousand units per grit size. Lead times depend on stock availability, customization, and shipping logistics, commonly ranging from 2 to 8 weeks. For buyers in distant markets like Africa or South America, factor in additional transit time and customs clearance. Early communication with suppliers about your expected order volume and delivery schedule is essential to avoid production delays.
4. What payment terms are standard when sourcing abrasive paper grit sizes internationally?
International B2B transactions often use letters of credit (LC), wire transfers (T/T), or trade credit insurance to mitigate payment risks. New buyers might be required to pay a deposit upfront (commonly 30-50%) with the balance upon shipment or delivery. Established relationships can negotiate better terms. Ensure all payment terms are clearly outlined in contracts, and confirm the supplier’s banking details to prevent fraud. Using escrow services or verified payment platforms can add an extra layer of security.
5. How can I ensure quality assurance and product certification compliance for abrasive paper grit sizes?
Demand certificates of analysis (COAs) and quality assurance documentation from suppliers before purchase. Verify compliance with relevant international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and abrasive-specific standards like FEPA or ANSI. Conduct independent laboratory testing if possible, especially for critical applications. Suppliers with third-party audits and transparent quality control processes provide higher assurance. For buyers in regulated industries or regions, ensuring compliance with local import regulations is equally important.
6. What logistics considerations should international buyers keep in mind when importing abrasive paper grit sizes?
Abrasive paper products are generally lightweight but bulky; optimize shipping by consolidating orders and selecting appropriate packaging to prevent damage. Choose reliable freight forwarders familiar with your destination’s customs processes to minimize delays. Understand Incoterms clearly to determine responsibility for shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Buyers in Africa, the Middle East, and South America should anticipate longer transit times and potential port congestion. Collaborate closely with suppliers to plan shipments around seasonal demand and regional holidays.
7. How should disputes related to abrasive paper grit size quality or delivery be managed in international B2B contracts?
Establish clear dispute resolution mechanisms within contracts, such as arbitration clauses or jurisdiction agreements in neutral locations. Maintain detailed records of communications, contracts, and product inspections. In case of quality disputes, request third-party inspections or involve independent laboratories to provide unbiased assessments. Promptly notify suppliers of issues and seek amicable solutions before escalating. For recurring problems, consider renegotiating terms or switching suppliers, but always balance cost, quality, and reliability.
8. Are there regional differences in abrasive paper grit size standards that international buyers should consider?
Yes, grit size grading can differ between regions, with FEPA (Europe) and CAMI (USA) standards being the most common. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, FEPA standards (P-scale) are often preferred, while South America and Africa may encounter both FEPA and CAMI standards. Clarify with suppliers which standard they follow and request grit size conversions if necessary. Understanding these differences ensures compatibility with your machinery and end-use requirements, avoiding costly mismatches or rework.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of abrasive paper grit size is a critical factor in optimizing manufacturing processes and ensuring product quality across diverse industrial applications. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of grit size selection can lead to significant cost efficiencies and enhanced operational performance. Prioritizing suppliers who offer consistent grit grading, reliable supply chains, and compliance with international standards will minimize production downtime and improve end-product consistency.
Key takeaways include the importance of aligning grit size choices with specific application requirements, leveraging supplier partnerships for technical support, and considering regional market dynamics such as import regulations and logistics infrastructure. Strategic sourcing should also incorporate risk mitigation strategies, including supplier diversification and quality assurance protocols, to navigate fluctuating global trade conditions effectively.
Looking ahead, buyers are encouraged to adopt a proactive sourcing approach by engaging with innovative manufacturers who invest in advanced abrasive technologies and sustainable materials. Embracing digital procurement platforms can further streamline supplier evaluation and contract management. By taking these steps, international B2B buyers will not only secure competitive advantages today but also position themselves to capitalize on emerging trends in abrasive material performance and supply chain resilience.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina