In today’s interconnected economy, understanding the properties of sic (silicon carbide) is pivotal for B2B buyers aiming to secure competitive advantages in diverse industrial sectors. Silicon carbide’s exceptional thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties make it indispensable across applications ranging from abrasives and refractories to semiconductor devices and automotive components. For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions experiencing rapid industrial growth—leveraging these properties effectively can drive innovation and operational efficiency.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of silicon carbide’s varied types, material grades, and manufacturing processes, alongside stringent quality control measures vital for consistent performance. It delves into sourcing strategies by profiling reputable global suppliers and analyzing cost structures to enable buyers to negotiate favorable terms. Additionally, it provides market insights tailored to emerging and established economies, highlighting regional trends and demand drivers.
By integrating technical knowledge with practical procurement advice, this resource empowers international buyers to make informed, strategic decisions when selecting silicon carbide products. Whether you are sourcing for high-volume manufacturing in South Africa or specialized applications in Vietnam, this guide equips you with the expertise to navigate complexities, mitigate risks, and optimize your supply chain. Unlock the potential of silicon carbide by mastering its properties and market dynamics, ensuring your business stays ahead in a competitive global landscape.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A Properties | High durability, thermal stability, and chemical resistance | Industrial manufacturing, electronics, automotive | Pros: Long lifecycle, reliability in harsh environments; Cons: Higher upfront cost, may require specialized handling |
| Type B Variations | Lightweight, flexible, moderate strength | Packaging, consumer goods, lightweight structures | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to process; Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity, less resistant to chemicals |
| Type C Variants | Enhanced conductivity, customizable surface properties | Electrical components, sensors, energy storage | Pros: Tailored functionality, improved performance; Cons: Complexity in specification, potential supply chain variability |
| Type D Forms | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, sourced from renewable materials | Sustainable packaging, green construction | Pros: Environmentally responsible, regulatory compliance; Cons: May have shorter lifespan, variability in quality |
| Type E Specialized | High precision, engineered for extreme conditions | Aerospace, defense, advanced technology sectors | Pros: Superior performance under extreme stress; Cons: High cost, limited availability |
Type A Properties
These properties are characterized by their exceptional durability and resistance to heat and chemicals, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. B2B buyers in sectors like automotive and electronics benefit from their reliability in extreme conditions. When purchasing, consider the higher initial investment and potential need for specialized storage or handling to maximize lifecycle value.
Type B Variations
Known for their lightweight and flexible nature, these variations are widely used in packaging and consumer goods where ease of processing and cost-efficiency are critical. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between affordability and mechanical strength, especially for applications requiring structural integrity or chemical exposure resistance.
Type C Variants
These properties offer enhanced electrical conductivity and can be customized with specific surface treatments to meet precise functional requirements. They are essential for B2B buyers in electronics and energy sectors aiming to improve device performance. However, buyers must navigate complex specifications and potential supply chain challenges to ensure consistency.
Type D Forms
Eco-friendly and biodegradable, these forms cater to the growing demand for sustainable materials in packaging and construction. B2B buyers focused on environmental compliance and corporate social responsibility will find value here. Yet, they should be mindful of potential compromises in durability and quality consistency when sourcing.
Type E Specialized
Engineered for precision and extreme operational environments, these specialized properties serve high-tech industries such as aerospace and defense. Buyers benefit from unmatched performance but must prepare for significantly higher costs and limited supplier options. Strategic sourcing and long-term supplier relationships are key considerations.
Related Video: Silicon Carbide Explained - SiC Basics
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of properties of SiC | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Electronics | High-efficiency power semiconductors and switches | Enhanced energy efficiency, reduced heat loss, and smaller device size | Quality certification, thermal conductivity specs, supplier reliability |
| Automotive | Electric vehicle (EV) powertrain components and inverters | Increased durability under high temperatures, improved vehicle range | Compliance with automotive standards, scalability, and after-sales support |
| Renewable Energy | Solar inverters and wind turbine power converters | Improved conversion efficiency, longer system lifespan | Availability of custom designs, durability under harsh climates |
| Aerospace & Defense | High-temperature sensors and RF devices | Reliable performance in extreme environments, lightweight | Stringent quality control, traceability, and certifications |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Abrasive tools and wear-resistant coatings | Extended tool life, reduced downtime, and maintenance costs | Material purity, abrasion resistance ratings, and supplier technical support |
Power Electronics
Silicon carbide (SiC) is widely used in power electronics for manufacturing high-efficiency semiconductors and switches. Its superior thermal conductivity and high breakdown electric field enable devices to operate at higher voltages and temperatures with lower energy losses. This translates to smaller, more efficient power modules that are crucial for industrial applications in Africa, South America, and Europe where energy efficiency is a growing priority. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer certified materials with consistent thermal and electrical specifications to ensure reliability in demanding environments.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, SiC components are pivotal for electric vehicle (EV) powertrains and inverters. SiC’s ability to withstand high temperatures and switch frequencies allows EVs to achieve better energy efficiency and longer driving ranges. For B2B buyers in emerging markets like South Africa and Vietnam, sourcing SiC parts that meet automotive quality standards (e.g., AEC-Q101) is essential. Additionally, scalability and supplier support for integration into existing production lines can significantly impact project success.
Renewable Energy
SiC is increasingly employed in solar inverters and wind turbine power converters due to its high efficiency and durability. These properties help renewable energy systems maintain optimal performance even in harsh climatic conditions common in the Middle East and parts of South America. International buyers should seek suppliers capable of providing tailored SiC solutions that withstand environmental stressors and deliver long-term operational stability, which is critical for reducing maintenance costs and maximizing return on investment.
Aerospace & Defense
The aerospace and defense industries leverage SiC for high-temperature sensors and radio frequency (RF) devices that must perform reliably under extreme conditions. SiC’s robustness and lightweight nature are advantageous for applications such as satellite components and military electronics. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing from vendors with rigorous quality control systems, traceability, and the necessary certifications to comply with stringent aerospace standards.
Industrial Manufacturing
SiC’s hardness and thermal stability make it ideal for abrasive tools and wear-resistant coatings used in heavy manufacturing and mining operations prevalent in Africa and South America. These properties reduce tool wear and extend operational life, minimizing downtime and maintenance expenses. When procuring SiC materials for this sector, international buyers should evaluate material purity, abrasion resistance ratings, and the availability of technical support to optimize tool performance and lifecycle management.
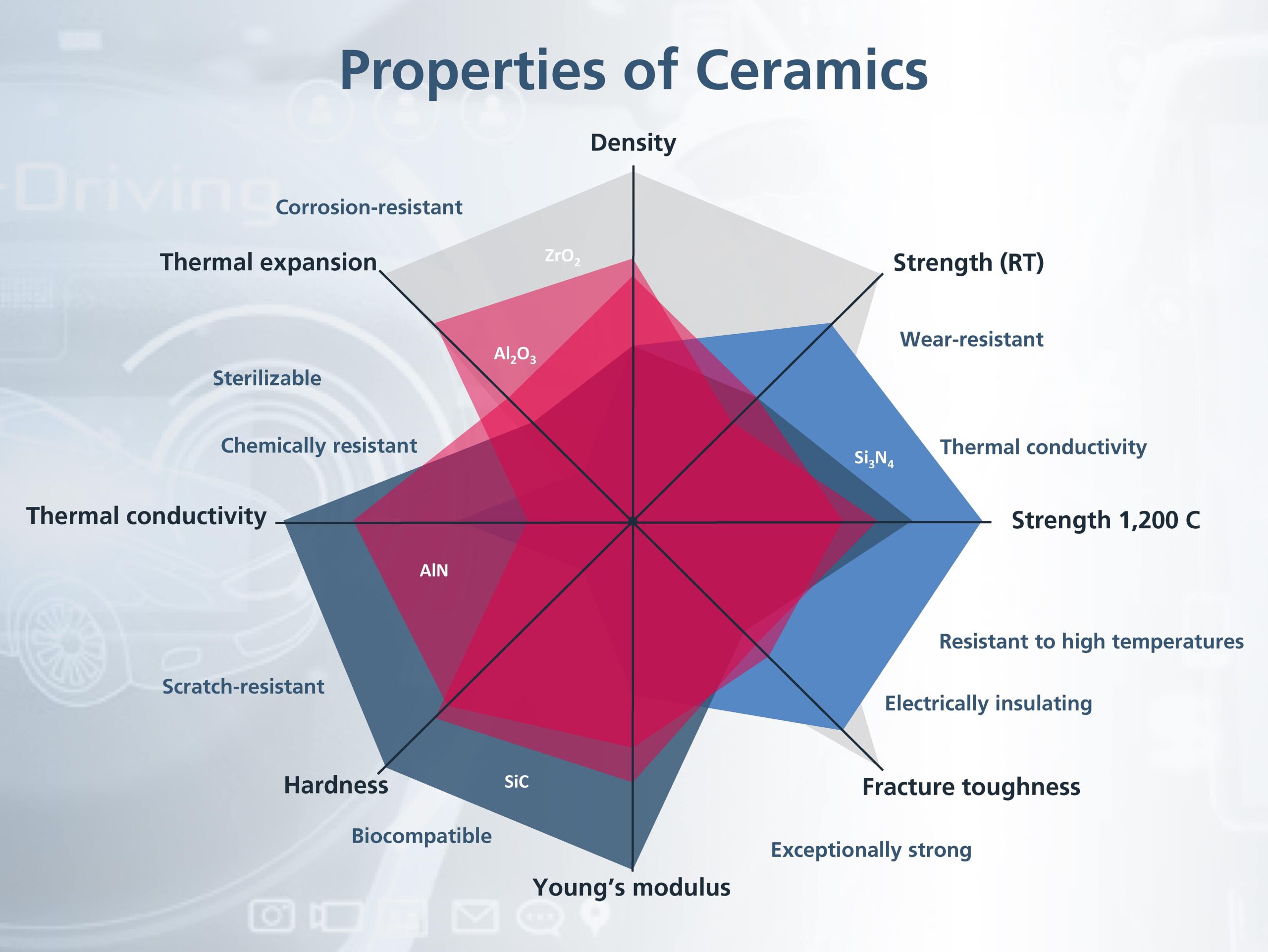
Key Properties:
Silicon carbide ceramics exhibit exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, and excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. They can operate reliably at temperatures exceeding 1600°C and withstand high pressures, making them ideal for harsh environments. Their inertness to acids and alkalis enhances their suitability in corrosive media.
Pros & Cons:
SiC ceramics are highly durable and maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions. However, their manufacturing process is complex and costly due to the high purity and precise sintering required. While the upfront cost is high, the long service life often justifies the investment for demanding applications.
Impact on Application:
SiC ceramics are widely used in mechanical seals, wear-resistant parts, and high-temperature components in chemical processing. Their resistance to aggressive chemicals makes them suitable for pumps and valves handling corrosive fluids. In high-temperature environments, they outperform many metals and other ceramics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like South Africa, Brazil, or the Middle East should verify compliance with international standards such as ASTM C799 or DIN EN 60672 to ensure material quality and compatibility. Local suppliers may have limited stock, so planning for lead times is critical. Preference is often given to suppliers that provide detailed material certifications and traceability.
Key Properties:
Single crystal SiC offers superior electronic properties, including high electron mobility and wide bandgap, making it essential for semiconductor devices. It withstands high voltage and temperature, with excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
Pros & Cons:
This material enables high-performance power electronics and LEDs but is expensive and requires sophisticated manufacturing techniques like chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The production yield can be lower compared to polycrystalline forms, impacting cost and availability.
Impact on Application:
Single crystal SiC is critical in power devices, high-frequency transistors, and sensors used in automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy sectors. Its robustness in harsh environments supports applications in electric vehicles and industrial automation.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with semiconductor industry standards such as JEDEC or IEC is vital. Buyers from Europe and Vietnam should consider suppliers with strong R&D capabilities and after-sales support. Import regulations and tariffs on semiconductor-grade materials may affect total cost and delivery schedules.
Key Properties:
SiC fibers provide high tensile strength, thermal stability, and oxidation resistance. They maintain mechanical properties at temperatures above 1400°C and are chemically inert, making them ideal for composite reinforcement.
Pros & Cons:
SiC fibers enhance composite materials’ performance but are relatively costly and require careful handling during manufacturing to avoid fiber damage. Their integration into composites demands specialized expertise and equipment.
Impact on Application:
Used primarily in aerospace, automotive, and defense industries, SiC fibers improve the thermal and mechanical properties of composites for engine parts, heat shields, and structural components. They enable weight reduction while maintaining strength and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in South America and the Middle East should ensure fiber quality meets ASTM D4018 or ISO 2076 standards. Availability can be limited outside major industrial hubs, so establishing relationships with reliable global suppliers is advantageous. Consideration of customs and import duties is essential for cost management.
Key Properties:
SiC coatings provide a hard, wear-resistant, and chemically inert surface layer that protects substrates from corrosion, erosion, and high temperatures. They exhibit excellent adhesion and thermal stability.
Pros & Cons:
Applying SiC coatings is cost-effective compared to bulk SiC components and extends the life of base materials. However, coating uniformity and thickness control require advanced deposition techniques such as plasma spraying or CVD, which can be capital intensive.
Impact on Application:
SiC coatings are widely used in turbine blades, heat exchangers, and chemical reactors to improve surface durability. They allow the use of less expensive base materials while achieving SiC’s protective benefits.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In Europe and Africa, adherence to ISO 14919 or ASTM B487 standards for coating quality is common. Buyers should assess suppliers’ technical capabilities and post-coating testing services. Regional environmental regulations may influence coating process choices and disposal of waste materials.
| Material | Typical Use Case for properties of sic | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide Ceramics | Mechanical seals, wear parts, high-temp components | Exceptional hardness and chemical resistance | High manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Silicon Carbide Single Crystal | Power electronics, semiconductors | Superior electronic and thermal properties | Expensive, complex production, lower yield | High |
| Silicon Carbide Fibers | Composite reinforcement in aerospace and automotive | High tensile strength and thermal stability | Costly and requires specialized handling | Medium to High |
| Silicon Carbide Coatings | Surface protection for turbines, reactors | Cost-effective surface durability enhancement | Requires advanced deposition technology | Medium |
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a high-performance material widely used in semiconductor, automotive, and industrial applications due to its exceptional thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties. Understanding its manufacturing processes is critical for B2B buyers aiming to source high-quality SiC products tailored to their technical and commercial requirements.
The manufacturing journey begins with the synthesis of high-purity SiC powder. Raw materials typically include silica sand and carbon sources (e.g., petroleum coke). The preparation involves:
Depending on the intended application, SiC powder is shaped into various forms using:
In semiconductor-grade SiC, wafers are diced, cleaned, and integrated into devices. For structural applications, shaped parts may be assembled with other components using brazing or adhesive bonding, requiring compatible thermal and mechanical properties.
Finishing steps are crucial to achieving the desired surface quality and dimensional accuracy:
Robust quality assurance (QA) frameworks are essential to ensure that SiC products meet stringent international standards and client specifications. Buyers should be familiar with the following QA aspects:
For international buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, due diligence in supplier quality verification is crucial to mitigate risks and ensure product compliance.
By understanding the intricate manufacturing processes and rigorous quality assurance frameworks governing silicon carbide production, international B2B buyers can make informed procurement decisions. Leveraging factory audits, certification verification, and third-party inspections empowers buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to secure SiC products that meet global standards and their specific application needs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
When sourcing properties of SIC (Silicon Carbide) materials and products, understanding the detailed cost structure is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement strategies. The primary cost components include:
Pricing in SIC properties sourcing is dynamic and influenced by multiple factors beyond base costs:
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like South Africa and Vietnam, the following actionable insights can enhance sourcing outcomes:
Prices for properties of SIC are indicative and subject to change based on market demand, raw material availability, and geopolitical conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and obtain formal quotations tailored to their specific technical and logistical requirements before finalizing procurement decisions.
Understanding the critical technical specifications of Silicon Carbide (SiC) is essential for international B2B buyers to ensure compatibility with their industrial applications and to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Material Grade
SiC is available in different grades that reflect purity, crystal structure, and particle size. High-purity grades (e.g., semiconductor-grade) are vital for electronic applications, while lower grades suit abrasives or refractory uses. Selecting the correct grade impacts product quality, lifespan, and suitability for your specific manufacturing needs.
Particle Size and Distribution
The size of SiC particles (ranging from micron-sized powders to larger grit) directly affects surface finish, machining precision, and thermal properties. Buyers should specify particle size distribution to match their process requirements, such as polishing, grinding, or sintering, to achieve optimal results and minimize waste.
Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Tolerance refers to allowable deviations in dimensions of SiC components or powders. Precise tolerance is critical in semiconductor and automotive industries where tight specifications ensure product reliability. Vendors typically provide tolerance ranges; negotiating these terms can affect pricing and lead times.
Purity and Impurity Content
Purity levels (usually expressed as a percentage) indicate the presence of unwanted elements. High purity enhances electrical and thermal conductivity, essential for power electronics. Buyers should request detailed impurity profiles to avoid performance degradation or incompatibility in sensitive applications.
Thermal Conductivity
SiC’s high thermal conductivity makes it ideal for heat dissipation in electronics. Buyers should verify thermal specifications to ensure components meet operational temperature requirements, especially in high-power or harsh environments common in Africa, the Middle East, and industrial sectors in Europe.
Mechanical Strength and Hardness
The hardness and fracture toughness of SiC influence its wear resistance and durability in abrasive environments. This property is crucial for buyers in mining, machining, and construction sectors, common in South America and Africa, where material longevity reduces maintenance costs.
Grasping common industry terms helps international buyers navigate procurement processes efficiently, avoid misunderstandings, and establish clear communication with suppliers.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment used in another company’s end products. For SiC buyers, understanding if the supplier is an OEM or a distributor affects warranties, customization options, and pricing structures.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. MOQ impacts inventory management and cash flow. Buyers from emerging markets or smaller enterprises should negotiate MOQs to avoid overstocking or capital lockup.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document issued to suppliers asking for price, delivery, and terms based on specified technical requirements. Clear, detailed RFQs help buyers receive accurate quotes and compare suppliers effectively, reducing procurement cycle times.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs between buyer and seller. Examples include FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Understanding Incoterms is vital for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East to control logistics costs and risks.
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For SiC products, lead time affects production schedules and project timelines. Buyers should confirm lead times upfront, especially when sourcing from overseas suppliers.
Batch Number / Lot Number
A unique identifier for a production batch. This facilitates traceability and quality control, crucial for industries requiring certification and compliance with international standards.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, streamline procurement, and foster successful partnerships in the global Silicon Carbide market.
The global market for properties of sic (silicon carbide) is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand in sectors such as electronics, automotive, and renewable energy. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is critical for strategic sourcing and investment decisions.
Global Drivers:
Silicon carbide’s superior thermal conductivity, electrical properties, and durability make it indispensable in high-performance applications, including power electronics, LED lighting, and electric vehicle components. The surge in electric vehicle adoption and renewable energy infrastructure development worldwide is fueling demand. Additionally, industrial automation and semiconductor innovation are pushing suppliers to innovate with high-quality, application-specific sic materials.
Emerging Sourcing Trends:
- Localization and Diversification: Buyers in emerging markets, such as South Africa and Vietnam, are actively seeking to diversify their supplier base to mitigate geopolitical risks and supply chain disruptions. This includes partnerships with suppliers in Asia and Europe known for advanced manufacturing capabilities.
- Technology Integration: Adoption of digital procurement platforms and AI-driven analytics is improving transparency and efficiency in sourcing sic properties. These technologies enable better quality control, predictive demand forecasting, and supplier risk assessment.
- Customization and Value-Added Services: Suppliers increasingly offer tailored sic products with specific properties optimized for client applications, supported by technical consultation and after-sales services, enhancing value for B2B buyers.
Market Dynamics:
The market is characterized by moderate supplier consolidation, with leading manufacturers investing heavily in R&D and capacity expansion. International buyers must navigate fluctuating raw material prices, trade regulations, and logistics complexities. Regulatory frameworks in Europe and the Middle East emphasize compliance with safety and environmental standards, shaping sourcing strategies. Emerging economies prioritize cost-efficiency and supply reliability, influencing negotiation approaches and contract structures.
Sustainability is becoming a decisive factor in the procurement of silicon carbide properties, as environmental concerns rise globally. B2B buyers, especially from regions emphasizing green growth, are prioritizing ethical sourcing and sustainability credentials in their supplier evaluations.
Environmental Impact:
Silicon carbide production involves energy-intensive processes and the use of raw materials that can have significant ecological footprints. Buyers should assess suppliers based on their carbon emissions, waste management practices, and energy efficiency initiatives. Companies adopting renewable energy in manufacturing and closed-loop recycling systems stand out as sustainable partners.
Ethical Supply Chains:
Transparency and traceability in the supply chain are essential to ensure compliance with international labor standards and avoid sourcing from conflict-affected regions. Ethical sourcing policies not only mitigate reputational risks but also align with increasing regulatory demands in Europe and the Middle East.
Green Certifications and Materials:
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Management): Widely recognized certification indicating a supplier’s commitment to reducing environmental impact.
- REACH and RoHS Compliance: Critical for buyers in Europe to ensure materials meet chemical safety and hazardous substances regulations.
- Eco-friendly Product Lines: Some suppliers are innovating with bio-based binders and less toxic processing agents in sic manufacturing, enabling buyers to meet corporate sustainability goals.
For B2B buyers, integrating sustainability into sourcing decisions enhances long-term supply chain resilience and opens access to markets with stringent environmental regulations.
Silicon carbide was first synthesized in the late 19th century and initially found use as an abrasive material due to its hardness. Over time, advances in material science have transformed sic into a critical semiconductor material, especially since the late 20th century. The development of high-purity sic crystals and wafers has enabled its use in power electronics, replacing traditional silicon in high-temperature and high-voltage applications.
This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers as it underscores the transition from commodity-grade materials to highly engineered products. Understanding this progression helps buyers appreciate the complexity and value embedded in modern sic properties, informing procurement strategies that prioritize quality, innovation, and supplier expertise.
How can I effectively vet suppliers of properties of SIC to ensure reliability and quality?
Begin by conducting thorough due diligence, including verifying company registration, financial stability, and reputation through trade references and online reviews. Request detailed product specifications and samples to assess quality firsthand. Use third-party inspection services or local agents to audit manufacturing processes and compliance with international standards. Engage in direct communication to evaluate responsiveness and transparency. Prioritize suppliers with certifications relevant to properties of SIC and those who demonstrate consistent delivery performance. This approach minimizes risks and builds a foundation for a trustworthy business relationship.
Is customization of properties of SIC feasible for international B2B buyers, and what are the typical processes involved?
Yes, customization is often available but varies by supplier capabilities. Buyers should clearly communicate their technical requirements, including chemical composition, physical properties, and packaging preferences. Expect to negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times, as customization usually requires adjustments in production lines. Detailed technical drawings or specifications may be needed. Confirm the supplier’s flexibility and experience with custom orders before committing. Additionally, discuss intellectual property protection if your specifications are proprietary, ensuring confidentiality agreements are in place.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
What are the standard minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms for properties of SIC in international B2B trade?
MOQs typically depend on the supplier’s production scale and customization level, ranging from a few tons to several containers. Lead times can vary from 2 to 8 weeks, influenced by order complexity and supplier location. Payment terms often include a 30% advance deposit with the balance payable upon shipment or after receiving inspection certificates. Letters of credit (LCs) or escrow services are common to secure transactions. Negotiate terms upfront, considering your cash flow and risk tolerance, and always clarify incoterms to understand delivery responsibilities.
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for when sourcing properties of SIC internationally?
Prioritize suppliers with internationally recognized certifications such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management), REACH compliance (for chemical safety in Europe), and relevant local regulatory approvals. Request batch-specific quality certificates, including material safety data sheets (MSDS) and third-party lab test reports confirming physical and chemical properties. Implement pre-shipment inspections or factory audits to verify quality standards are met. Establish clear quality control protocols in your contract, including remedies for non-compliance, to ensure consistent product performance and regulatory adherence.
How can I optimize logistics and shipping for properties of SIC when importing to regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
Work with freight forwarders experienced in handling chemical and industrial materials, ensuring compliance with hazardous material regulations if applicable. Select suitable shipping modes balancing cost and delivery speed—sea freight is cost-effective for bulk orders, while air freight suits urgent or smaller consignments. Clarify incoterms to define responsibilities for customs clearance, insurance, and duties. Plan for potential delays at ports with contingency stock or flexible scheduling. Utilize tracking technologies and maintain close communication with logistics partners to proactively manage shipments.
What strategies can help resolve disputes related to properties of SIC transactions in international B2B trade?
Incorporate clear dispute resolution clauses in contracts, specifying governing law and arbitration venues (e.g., ICC arbitration). Document all communications and maintain records of agreements, specifications, and quality checks. If discrepancies arise, initiate amicable negotiations supported by evidence like inspection reports or third-party assessments. Engage professional mediators or legal counsel familiar with cross-border trade if needed. Proactive communication and transparent processes reduce misunderstandings, fostering long-term partnerships despite occasional conflicts.
Are there any specific regulatory or import restrictions for properties of SIC that B2B buyers from Africa, South America, or the Middle East should be aware of?
Yes, import regulations vary widely by country and may include restrictions on chemical composition, environmental impact, and safety standards. Buyers must verify compliance with local customs, health, and environmental authorities. Some regions require import licenses, product registration, or conformity assessments before clearance. Engage local legal or trade consultants to navigate complex regulations, and ensure suppliers provide all necessary documentation to prevent shipment delays or seizures. Staying informed about evolving policies helps maintain uninterrupted supply chains.
How can I manage payment risks when dealing with international suppliers of properties of SIC?
Mitigate risks by conducting credit checks and choosing reputable suppliers with transparent financial records. Use secure payment methods such as letters of credit, which provide bank guarantees, or escrow accounts to protect funds until contract terms are met. Avoid full upfront payments unless warranted by strong supplier trust or small order sizes. Consider trade credit insurance for larger transactions. Clearly define payment milestones linked to delivery or inspection milestones in contracts. Maintaining open communication and flexibility can also help address unforeseen financial challenges collaboratively.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of properties of SIC offers international B2B buyers a robust pathway to optimize procurement, enhance supply chain resilience, and achieve competitive advantage. Key takeaways emphasize the critical importance of understanding SIC’s unique material characteristics, supplier capabilities, and regional market dynamics to ensure quality, compliance, and cost-efficiency. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize building strong supplier relationships and leveraging localized insights to navigate logistical and regulatory complexities effectively.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The value of strategic sourcing lies not only in cost reduction but also in fostering innovation and sustainability within the supply network. By integrating comprehensive market intelligence and adopting flexible sourcing strategies, businesses can mitigate risks related to geopolitical shifts and fluctuating demand. This approach is particularly vital for emerging markets where infrastructure and supplier maturity vary significantly.
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to adopt digital tools and collaborative platforms to enhance transparency and agility in sourcing SIC properties. Embracing these forward-thinking practices will unlock new opportunities, drive operational excellence, and position organizations at the forefront of their industries. Now is the time to act decisively, leveraging strategic sourcing as a catalyst for long-term growth and global competitiveness.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina