Alumina’s position on the Mohs hardness scale is a fundamental attribute that directly impacts its performance in industrial applications ranging from abrasives to electronics. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding alumina’s hardness characteristics is crucial for selecting the right grade and form to meet specific operational demands. This guide demystifies the complexities surrounding alumina’s Mohs hardness, providing a clear pathway to smarter sourcing decisions.
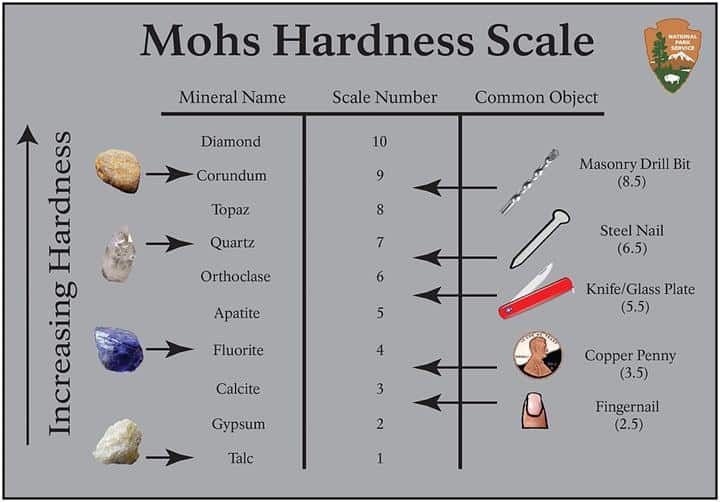
The Mohs hardness of alumina, typically ranging around 9, signifies its exceptional resistance to scratching and wear, making it indispensable for high-precision, durability-critical applications. However, variations in purity, particle size, and manufacturing processes can influence this hardness and, by extension, the material’s suitability for different industrial uses. Buyers must therefore evaluate these parameters alongside cost, supplier reliability, and quality control measures.
This comprehensive guide covers:
- Types of alumina and their Mohs hardness implications
- Material specifications and manufacturing processes influencing hardness
- Quality control standards ensuring consistent performance
- Profiles of global suppliers with a focus on emerging and established markets
- Cost factors and market trends shaping procurement strategies
- Frequently asked questions addressing common buyer concerns
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By equipping B2B buyers with this knowledge, the guide empowers you to navigate the global alumina market confidently, optimize product selection, and foster supplier partnerships that align with your operational and budgetary goals. Whether sourcing for abrasive manufacturing in Brazil, electronics in Europe, or industrial components in the Middle East or Africa, this resource is designed to enhance your strategic procurement and competitive advantage.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha Alumina (Corundum) | Highest purity alumina with Mohs hardness ~9, crystalline structure | Cutting tools, abrasives, wear-resistant coatings | Pros: Extremely hard and durable; Cons: Higher cost, brittle under impact |
| Gamma Alumina | Transitional phase alumina, slightly lower hardness (~8-8.5), porous | Catalyst supports, adsorbents, polishing powders | Pros: High surface area, cost-effective; Cons: Lower hardness limits heavy abrasion use |
| Nano Alumina | Alumina particles at nanoscale, enhanced surface reactivity and hardness | Electronics, advanced ceramics, coatings | Pros: Superior mechanical properties, improved wear resistance; Cons: Higher processing complexity and cost |
| Tabular Alumina | Dense, fused alumina with controlled particle size and shape | Refractories, kiln furniture, high-temperature applications | Pros: Excellent thermal stability and hardness; Cons: Requires precise handling, moderate cost |
| Activated Alumina | Porous alumina with high absorption capacity, moderate hardness (~8) | Water purification, desiccants, gas drying | Pros: Effective moisture and contaminant removal; Cons: Not suitable for abrasive applications |
Alpha Alumina (Corundum) is the most widely recognized form of alumina with a Mohs hardness close to 9, making it one of the hardest materials available after diamond. Its crystalline structure lends exceptional wear resistance, ideal for cutting tools and abrasive materials. For B2B buyers in industries such as mining or manufacturing in Africa, Europe, and South America, alpha alumina offers longevity and performance but at a higher price point. Consideration should be given to its brittleness under impact, necessitating careful handling during transport and application.
Gamma Alumina represents a transitional phase alumina with a slightly lower hardness but significantly higher porosity and surface area. This makes it valuable for catalytic applications and polishing powders, especially in chemical industries prevalent in the Middle East and Brazil. Buyers should weigh its cost-effectiveness and functional versatility against its reduced hardness, which limits its use in heavy abrasion environments.
Nano Alumina features alumina particles engineered at the nanoscale, enhancing mechanical strength and surface reactivity. This type is increasingly favored in advanced ceramics and electronics manufacturing sectors in regions like Europe and Vietnam. While offering superior wear resistance and improved coating performance, nano alumina demands more sophisticated processing techniques and investment, which buyers must factor into procurement decisions.
Tabular Alumina is produced by fusing alumina at very high temperatures, resulting in a dense, stable form with excellent thermal and mechanical properties. It is extensively used in refractory applications such as kiln linings and furnace components. Buyers in heavy industries across Africa and the Middle East will find tabular alumina beneficial for its durability under extreme conditions, though it requires precise handling and moderately higher costs.
Activated Alumina is distinct for its porous structure and high absorption capacity rather than extreme hardness. It is primarily utilized in water purification, gas drying, and as a desiccant, serving environmental and industrial needs globally. While its moderate hardness (~8) limits abrasive uses, activated alumina offers significant value to B2B buyers focused on filtration and purification technologies, especially in markets emphasizing sustainable practices.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of alumina mohs hardness | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Substrates and insulating components in microelectronics | High wear resistance and electrical insulation improve device reliability and lifespan | Consistent purity and particle size distribution; supplier certifications for quality and supply chain transparency |
| Abrasives & Cutting Tools | Manufacture of grinding wheels, cutting tools, and polishing agents | Enhances durability and cutting precision, reducing downtime and operational costs | High hardness grade alumina with uniform hardness; bulk supply capability and compliance with environmental standards |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Engine components, wear-resistant coatings, and thermal barriers | Improves component longevity under extreme mechanical stress and high temperatures | Proven material performance under harsh conditions; compliance with international material standards and certifications |
| Chemical Processing | Linings for reactors, pumps, and pipes exposed to abrasive fluids | Protects equipment from erosion and corrosion, extending maintenance intervals | Chemical purity and resistance to specific corrosive agents; availability of custom shapes and sizes |
| Medical Devices | Components in surgical tools and implants requiring high hardness | Ensures precision and durability for critical medical applications | Biocompatibility certification; traceability and adherence to medical-grade material standards |
Electronics & Semiconductors
In this sector, alumina’s Mohs hardness is leveraged for substrates and insulating components where high wear resistance and electrical insulation are critical. The hardness ensures minimal degradation over time, maintaining the performance and reliability of microelectronic devices. International buyers, especially from emerging markets like Brazil or South Africa, should prioritize sourcing alumina with consistent purity and particle size to meet stringent global standards, ensuring compatibility with advanced manufacturing processes.
Abrasives & Cutting Tools
Alumina with high Mohs hardness is essential in producing grinding wheels, cutting tools, and polishing agents. Its hardness directly correlates with tool longevity and cutting precision, which are vital for operational efficiency in industries such as mining or metal fabrication prevalent in regions like the Middle East and Europe. Buyers must consider suppliers who can guarantee uniform hardness grades and sustainable production practices to comply with environmental regulations and ensure steady supply.
Automotive & Aerospace
Alumina’s hardness makes it ideal for engine components, wear-resistant coatings, and thermal barrier applications where resistance to mechanical stress and heat is paramount. For international B2B buyers, particularly from automotive hubs in Europe and emerging aerospace sectors in South America, sourcing should focus on materials that meet international standards like ISO or ASTM, with proven performance data under harsh conditions to avoid costly failures and downtime.
Chemical Processing
In chemical plants, alumina’s hardness is utilized in linings for reactors, pumps, and pipes that handle abrasive or corrosive fluids. This application significantly reduces equipment erosion and corrosion, enhancing uptime and lowering maintenance costs. Buyers from regions with growing chemical industries, such as the Middle East or Vietnam, must ensure the alumina’s chemical purity and resistance characteristics align with the specific chemicals processed, alongside the availability of custom-fabricated shapes.
Medical Devices
Alumina’s Mohs hardness is critical for manufacturing surgical tools and implants that require exceptional durability and precision. The material’s hardness contributes to instrument longevity and patient safety. For international buyers in Europe and Africa aiming to supply medical-grade components, sourcing must include biocompatibility certifications and full traceability to comply with regulatory requirements and quality assurance standards.
Related Video: The Mohs Scale of Hardness Explained
Key Properties:
High-purity alumina exhibits exceptional hardness (Mohs ~9), excellent thermal stability (up to 1750°C), and outstanding chemical inertness, making it highly resistant to corrosion and wear. It has good electrical insulation properties and high compressive strength.
Pros & Cons:
Pros include superior durability, excellent wear resistance, and compatibility with aggressive chemical environments. The main drawbacks are higher cost and manufacturing complexity due to stringent purity requirements and sintering processes. It may require specialized machining techniques, which can impact lead times.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for high-performance components such as cutting tools, wear-resistant linings, and electrical insulators exposed to harsh mechanical and chemical conditions. Its corrosion resistance suits applications involving acids and alkalis, common in chemical processing industries.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers in Africa, South America (e.g., Brazil), the Middle East, and Europe should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM C799 or DIN EN 60672 for electrical and mechanical properties. Import regulations and tariffs on high-purity ceramics may vary, so sourcing from regional suppliers or certified exporters can optimize costs and delivery. Consider local manufacturing capabilities for post-processing.
Key Properties:
Tabular alumina features a dense, angular grain structure with Mohs hardness around 9, excellent abrasion resistance, and high thermal shock resistance. It withstands temperatures up to 1800°C and has good chemical stability.
Pros & Cons:
Pros include excellent mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, making it suitable for refractory applications. It is generally more cost-effective than high-purity alumina but less electrically insulating. The angular grain shape can complicate machining and finishing.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in refractory linings, kiln furniture, and grinding media where mechanical wear and thermal cycling are critical. Its robustness suits heavy industrial environments such as cement plants and steel manufacturing.
International B2B Considerations:
Compliance with international refractory standards (e.g., ASTM C704, ISO 10012) is essential. Buyers in regions with high industrial activity like the Middle East and Europe will benefit from suppliers offering certification and traceability. Logistics considerations include bulk shipping and storage conditions to prevent moisture absorption.
Key Properties:
Fused alumina is produced by melting alumina at very high temperatures, resulting in a hard, dense material with Mohs hardness around 9. It offers excellent abrasion resistance and moderate chemical resistance, with a melting point near 2050°C.
Pros & Cons:
Advantages include affordability and versatility in abrasive applications. It is easier to produce in large volumes compared to sintered alumina. However, fused alumina may have lower purity and slightly reduced corrosion resistance, limiting its use in highly acidic environments.
Impact on Application:
Widely used as an abrasive grain in grinding wheels, sandblasting, and polishing. It is also suitable for wear-resistant coatings and linings where moderate chemical exposure is expected.
International B2B Considerations:
Buyers from South America and Africa should verify compliance with standards such as JIS R 1601 or ISO 11126 to ensure quality consistency. Given its widespread use, multiple suppliers exist globally, but quality variations require careful supplier audits. Import duties and local demand cycles can influence pricing and availability.
Key Properties:
These composites combine alumina with other ceramics (e.g., zirconia) to enhance toughness while maintaining high hardness (Mohs ~8-9). They offer improved fracture resistance, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Pros include enhanced mechanical resilience and tailored properties for specific applications. Cons involve higher production costs and more complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times and require advanced supplier capabilities.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for cutting tools, wear parts in mining and oil & gas industries, and components exposed to cyclic mechanical stresses. Their toughness reduces failure rates in demanding environments.
International B2B Considerations:
European and Middle Eastern buyers often require compliance with EN and ASTM standards for mechanical and thermal properties. For African and South American markets, ensuring supplier capacity for custom composite formulations is critical. Collaboration with suppliers on specifications and testing protocols can mitigate risks.
| Material | Typical Use Case for alumina mohs hardness | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Alumina | High-performance wear parts, electrical insulators | Exceptional hardness and chemical inertness | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Tabular Alumina | Refractory linings, kiln furniture, grinding media | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Difficult machining, moderate cost | Medium |
| Fused Alumina | Abrasives, wear-resistant coatings | Cost-effective, versatile abrasive | Lower purity, moderate corrosion resistance | Low |
| Ceramic Composites with Alumina Matrix | Cutting tools, mining wear parts, cyclic stress components | Enhanced toughness and tailored properties | Higher cost and complex production | High |
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al2O3) is prized in industrial applications for its exceptional hardness, typically rated around 9 on the Mohs scale. Achieving consistent hardness and material integrity requires precise manufacturing methods tailored to the final application, whether in abrasives, ceramics, or advanced engineering components.
The process begins with the selection and purification of raw materials. High-purity alumina powders are sourced, often with controlled particle size distributions to optimize sintering behavior and final mechanical properties. Impurities are minimized to maintain hardness and wear resistance.
Shaping the alumina into the desired form is critical for achieving uniform hardness and structural integrity.
Sintering consolidates the shaped alumina particles into a dense, hard ceramic.
Final treatments enhance surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding supplier quality assurance and control protocols is essential to secure reliable alumina products with consistent Mohs hardness.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
Raw materials, including alumina powders, undergo rigorous testing for purity, particle size, and chemical composition. Suppliers must provide certificates of analysis (CoA) verifying these parameters.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During forming, sintering, and finishing, checkpoints verify dimensional accuracy, density, and surface integrity. Process parameters like sintering temperature and pressure are closely monitored.
Final Quality Control (FQC):
Finished products are subjected to comprehensive testing to confirm hardness, mechanical strength, and defect-free surfaces before shipment.
For buyers in emerging and established markets such as Brazil, Vietnam, South Africa, and the Middle East, ensuring supplier reliability requires proactive verification strategies.
Understanding regional challenges and standards is crucial for buyers across continents:
Africa and South America:
Infrastructure variability means buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust quality management and transparent documentation to mitigate risks of inconsistent product quality.
Middle East:
Compliance with both international standards and regional certifications (e.g., GCC conformity marks) may be required. Suppliers with experience exporting to this market often have streamlined QA processes.
Europe (including countries like Brazil and Vietnam as trading partners):
Stringent regulations require full compliance with EU directives such as REACH and RoHS. Buyers should ensure suppliers maintain updated certifications and can provide detailed environmental and safety data sheets.
Logistics and handling:
Alumina’s hardness does not eliminate sensitivity to mechanical damage during transport. QA protocols should include packaging standards and damage inspection upon receipt.
By comprehensively understanding manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, international B2B buyers can confidently source alumina products with reliable Mohs hardness, ensuring optimal performance in their industrial applications.
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics for alumina with specific Mohs hardness ratings is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize procurement and ensure quality compliance. Below is a detailed breakdown of key cost components, price influencers, and actionable buyer strategies tailored for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Prices for alumina with specific Mohs hardness values fluctuate based on global raw material markets, supplier capacity, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should treat any quoted prices as indicative and conduct thorough market benchmarking and supplier audits prior to contract finalization.
By comprehensively analyzing cost drivers and price influencers while applying strategic procurement practices, international B2B buyers can optimize sourcing of alumina with precise Mohs hardness specifications, achieving cost efficiency without compromising quality or delivery reliability.
Understanding the technical specifications of alumina related to its Mohs hardness is essential for B2B buyers to ensure product suitability and performance in industrial applications. Here are key properties to consider:
Mohs Hardness Value
Alumina typically exhibits a Mohs hardness of around 9, making it one of the hardest commercially available ceramic materials. This high hardness translates to excellent wear resistance and durability, critical for applications such as cutting tools, abrasives, and wear-resistant coatings. Buyers should confirm the exact hardness rating to match application demands.
Material Grade
Alumina is available in various purity grades, commonly ranging from 85% to 99.9% alumina content. Higher purity grades offer superior hardness, chemical stability, and thermal resistance. Selecting the appropriate grade impacts product longevity and performance, especially in harsh environments common in mining, automotive, and electronics sectors.
Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Precise dimensional tolerances are crucial for components where fitting and assembly precision impact performance. Tolerances are typically specified in microns and vary depending on manufacturing processes. Buyers should specify tolerance requirements clearly to suppliers to avoid costly rework or incompatibility in assembly lines.
Density
The density of alumina affects its mechanical strength and thermal conductivity. Standard densities range from 3.8 to 3.95 g/cm³ depending on purity and sintering conditions. Consistent density ensures predictable mechanical behavior, important for structural components and thermal insulation applications.
Surface Finish
The surface quality of alumina parts can affect friction, wear, and bonding with other materials. Surface finishes may vary from rough sintered to polished. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements aligned with end-use—for example, polished surfaces for optical or electronic applications.
Thermal Stability
Alumina maintains hardness and structural integrity at elevated temperatures (up to ~1700°C). This property is vital for applications exposed to heat, such as furnace linings or engine components. Buyers should verify thermal stability specifications when sourcing for high-temperature operations.
Navigating international alumina trade involves familiarity with specific terminology that impacts pricing, delivery, and contractual obligations. Here are essential terms every B2B buyer should know:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce components or products that are purchased by another company and retailed under that purchasing company's brand. Understanding OEM requirements can help buyers source alumina materials that meet strict quality and specification standards demanded by large manufacturers.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest amount of alumina a supplier is willing to sell in one order. MOQs affect inventory planning and cost management. Buyers, especially SMEs from regions like Africa or South America, should negotiate MOQ terms to optimize cash flow and storage capacities.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document sent by buyers to suppliers asking for pricing, availability, and terms for specified alumina products. Preparing detailed RFQs with clear technical requirements ensures accurate and competitive supplier responses, facilitating better procurement decisions.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs between buyers and sellers. Common Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) clarify who bears risks and costs during transit, crucial for international buyers to manage logistics effectively.
Batch Consistency
Refers to the uniformity of alumina quality across production batches. Consistent batches reduce variability in manufacturing processes and product performance. Buyers should request certificates of analysis or quality assurance documents to verify batch consistency.
Lead Time
The time interval between placing an order and receiving the alumina shipment. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan production schedules and manage supply chain risks, particularly when sourcing from overseas suppliers in Europe or the Middle East.
By focusing on these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions, optimize procurement strategies, and secure alumina materials that meet their operational requirements efficiently.
The alumina mohs hardness sector plays a pivotal role in industries requiring high-performance abrasives, refractory materials, and advanced ceramics. Globally, demand is driven by rapid industrialization, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe. Countries like Brazil and Vietnam are notable for their expanding manufacturing bases, which increasingly require alumina materials with precise hardness specifications to enhance product durability and performance.
Key market dynamics reveal a shift toward specialized sourcing strategies. International B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who can guarantee consistent mohs hardness levels, ensuring product reliability in applications such as cutting tools, wear-resistant coatings, and electronic substrates. This demand pushes suppliers to adopt advanced quality control technologies, including laser-based hardness testing and real-time compositional analysis.
Technological innovation is another critical trend. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as IoT-enabled production lines and AI-driven supply chain analytics—enables suppliers to optimize alumina quality and delivery timelines. For buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe, leveraging these innovations means improved transparency and reduced lead times, essential for just-in-time manufacturing processes.
Sourcing trends emphasize regional diversification to mitigate geopolitical risks and supply chain disruptions. African and South American markets, rich in bauxite resources (the primary source of alumina), are becoming more attractive for direct partnerships and joint ventures, fostering local supply chains that reduce dependency on traditional suppliers in Asia and North America.
Sustainability is increasingly a strategic priority in the alumina mohs hardness sector, reflecting global shifts toward environmentally responsible manufacturing. Alumina production is energy-intensive and can generate significant emissions; thus, B2B buyers are scrutinizing suppliers’ environmental footprints more closely. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East, regions with stringent environmental regulations, often require suppliers to adhere to ISO 14001 environmental management standards and demonstrate ongoing carbon reduction initiatives.
Ethical sourcing is critical due to the complex supply chains involving raw bauxite extraction. Buyers from Africa and South America are particularly sensitive to the social and environmental impacts of mining activities, including land degradation, water usage, and community displacement. Partnering with suppliers who comply with certifications such as the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) or who participate in Fair Trade practices ensures supply chain transparency and social accountability.
"Green" certifications and material innovations are gaining traction. For instance, alumina sourced from low-carbon processes or produced using renewable energy appeals to buyers committed to sustainability goals. Additionally, the development of recycled alumina materials and closed-loop production methods reduce waste and enhance circular economy credentials, offering a competitive advantage to suppliers in the global marketplace.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The alumina sector’s evolution is closely linked to advancements in materials science and industrial growth. Historically, alumina’s high mohs hardness value (around 9) made it indispensable for abrasive applications, replacing less durable materials in the early 20th century. The expansion of the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries in the latter half of the century intensified the demand for high-purity, precisely graded alumina powders.
Over recent decades, improvements in refining and processing techniques have allowed for better control of hardness and particle size distribution, enabling broader industrial applications. For B2B buyers today, understanding this evolution highlights the importance of selecting suppliers with a strong technological foundation and a track record of innovation to meet increasingly sophisticated industrial requirements.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Is customization of alumina Mohs hardness possible, and how should I approach it with suppliers?
Customization is often feasible by adjusting the alumina’s purity, grain size, and processing methods. Clearly communicate your specific hardness and performance requirements upfront. Engage suppliers who offer technical consultation and R&D support to tailor products to your application needs. Request prototypes or small trial orders to test suitability before scaling. Ensure customization does not compromise other critical properties like chemical stability or particle size distribution. Establish clear agreements on specs, tolerances, and testing protocols to avoid misunderstandings.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for alumina products with specified Mohs hardness, especially for buyers in emerging markets?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier and alumina grade, often ranging from 500 kg to several tons per order. Lead times can span from 2 to 8 weeks, influenced by production capacity, customization needs, and shipping logistics. Buyers from Africa, South America, and the Middle East should negotiate MOQs that align with their market demand and storage capabilities. Early communication about forecasted volumes can help suppliers plan production and reduce lead times. Consider suppliers with flexible batch sizes or local warehousing options to optimize inventory management.
What payment terms are common in international B2B alumina transactions, and how can I protect my investment?
Standard payment terms include letters of credit (LC), advance payments, or net 30-60 day terms, depending on buyer-supplier trust levels. Letters of credit provide security by ensuring payment only upon fulfillment of contractual delivery and quality terms. For new suppliers, advance payments combined with small initial orders minimize risk. Use escrow services or trade financing solutions available in your region to safeguard transactions. Always request detailed invoices and proof of shipment, and consider insurance for high-value shipments to mitigate financial exposure.
Which quality assurance certifications and documentation should I require to verify alumina Mohs hardness compliance?
Request certificates of analysis (CoA) that detail Mohs hardness testing results, along with batch-specific quality reports. Look for suppliers certified to ISO 9001 and, where applicable, ISO 14001 (environmental management). Compliance with ASTM or equivalent international standards for alumina hardness testing adds credibility. For critical applications, third-party lab verification or witness testing can be arranged. Ensure traceability documentation accompanies shipments to maintain quality control throughout the supply chain.
What logistics considerations should I account for when importing alumina with specific Mohs hardness from global suppliers?
Alumina is generally stable but requires protection from moisture and contamination during transit. Confirm packaging standards meet international shipping requirements, including moisture barriers and robust containers. Choose freight options balancing cost and delivery speed; sea freight is economical but slower, while air freight suits urgent or smaller shipments. Understand import regulations, tariffs, and customs procedures in your country to avoid delays. Partner with freight forwarders experienced in handling mineral imports to streamline clearance and reduce risk.
How can I resolve disputes related to alumina Mohs hardness discrepancies after delivery?
First, review the contract terms detailing hardness specifications, testing methods, and acceptance criteria. Engage independent third-party laboratories to retest samples from the disputed batch. Communicate promptly and transparently with your supplier, providing documented evidence. Most reputable suppliers have dispute resolution procedures, including replacement, refund, or compensation clauses. Maintain detailed records of all correspondence and quality tests. If necessary, involve trade associations or arbitration bodies specializing in international mineral trade to mediate.
Are there regional factors that B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider when sourcing alumina Mohs hardness internationally?
Yes, regional factors such as local regulations, import duties, and quality standards vary significantly. For example, Europe enforces strict REACH compliance, while some African markets may require additional customs documentation. Currency fluctuations and payment system availability can impact pricing and transaction ease. Logistics infrastructure quality affects delivery reliability; remote areas may need longer lead times. Build relationships with suppliers familiar with your region’s market and legal landscape to navigate these challenges effectively and secure consistent supply.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
In today’s competitive global market, understanding the significance of alumina’s Mohs hardness is essential for B2B buyers aiming to optimize material performance and cost-efficiency. The superior hardness of alumina not only ensures durability and resistance to wear but also enhances product longevity across industrial applications—from abrasives to electronics. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing practices can unlock access to reliable suppliers, competitive pricing, and quality certifications that align with regional standards and operational needs.
Key takeaways for effective sourcing include:
Looking ahead, international buyers should adopt a proactive approach by continuously monitoring market trends, investing in supplier development, and exploring technological advancements in alumina processing. This strategic mindset will not only safeguard supply continuity but also enhance competitive advantage in industries demanding high-performance materials. Embrace strategic sourcing today to capitalize on alumina’s exceptional hardness properties and drive sustainable growth across your global operations.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina