Navigating the complexities of sourcing aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the melting point of aluminum oxide is crucial, as it influences product quality, manufacturing processes, and application suitability across various industries. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global market for aluminium oxide, providing insights into its types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By addressing the key factors that affect purchasing decisions, this guide empowers buyers to make informed choices that align with their specific needs. Whether you are a manufacturer in the UAE seeking high-performance materials or a procurement officer in Mexico evaluating potential suppliers, this resource will help streamline your sourcing process. It highlights essential criteria for selecting reliable suppliers, ensuring compliance with international standards, and optimizing procurement strategies to achieve cost efficiency.
As you delve into the nuances of aluminium oxide melting points and their implications, you will gain actionable insights that enhance your competitive edge in the global market. From understanding product specifications to navigating supplier relationships, this guide serves as a vital tool for fostering successful partnerships and driving business growth in diverse regions.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha-Alumina (α-Al2O3) | High melting point (2054°C), hardness | Ceramics, abrasives, refractories | Pros: Excellent durability and thermal stability. Cons: Higher cost compared to other forms. |
| Gamma-Alumina (γ-Al2O3) | Lower melting point (1100°C), porous | Catalysts, adsorbents | Pros: High surface area, effective for catalysis. Cons: Less stable at high temperatures. |
| Theta-Alumina (θ-Al2O3) | Intermediate phase, transition state | Nanotechnology, coatings | Pros: Useful in specific applications requiring thermal resistance. Cons: Limited availability and higher processing costs. |
| Amorphous Alumina | Non-crystalline, versatile | Pharmaceuticals, fillers | Pros: High reactivity, adaptable to various applications. Cons: Less mechanical strength compared to crystalline forms. |
| Alumina Hydrate (Al(OH)3) | Lower melting point (300°C), hydrated | Water treatment, flame retardants | Pros: Safe and effective for environmental applications. Cons: Lower thermal stability limits high-temperature applications. |
Alpha-Alumina is recognized for its remarkable hardness and high melting point of 2054°C, making it ideal for demanding applications in ceramics, abrasives, and refractories. Its durability and thermal stability are key advantages for industries requiring materials that withstand extreme conditions. B2B buyers should consider the cost implications, as alpha-alumina tends to be more expensive than other types, but the investment often pays off in longevity and performance.
Gamma-Alumina features a lower melting point of around 1100°C and a porous structure, providing a high surface area that is particularly beneficial in catalytic applications and as an adsorbent. This type is frequently utilized in chemical processes where catalytic efficiency is paramount. While gamma-alumina is advantageous due to its reactivity, buyers should note that it is less stable at elevated temperatures, which could limit its use in high-heat environments.
Theta-Alumina serves as an intermediate phase between alpha and gamma forms, often used in specialized applications like nanotechnology and coatings due to its unique thermal resistance properties. Although it can be beneficial in specific scenarios, its limited availability and higher processing costs may deter some buyers. Companies looking for innovative solutions should weigh the potential advantages against these factors.
Amorphous Alumina is a non-crystalline form that offers high reactivity and versatility across various industries, including pharmaceuticals and fillers. Its adaptability allows it to be tailored for specific applications, making it a valuable option for companies needing a flexible material. However, its mechanical strength is lower than that of crystalline forms, which may be a consideration for buyers focused on durability.
Alumina Hydrate is characterized by its lower melting point of approximately 300°C and is primarily used in water treatment processes and as a flame retardant. Its safety profile makes it suitable for environmental applications, appealing to industries focused on sustainability. However, its lower thermal stability may limit its application in high-temperature scenarios, so buyers should assess their specific needs carefully when considering this type.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Thermal Barrier Coatings | Enhances thermal resistance, improving safety and performance | Certifications for aerospace applications, compliance with industry standards |
| Electronics | Insulation in Semiconductor Manufacturing | Increases efficiency and reliability of electronic components | Purity levels, particle size distribution, and sourcing from reputable suppliers |
| Automotive | Lightweight Components in Vehicle Manufacturing | Reduces weight, enhances fuel efficiency, and improves performance | Material specifications, recycling options, and global supply chain logistics |
| Construction | Refractory Materials for High-Temperature Furnaces | Provides durability and heat resistance, leading to lower maintenance costs | Sourcing from local versus international suppliers, lead times, and quality certifications |
| Medical Devices | Biocompatible Coatings for Implants | Ensures safety and compatibility with human tissue, enhancing product acceptance | Compliance with medical regulations, testing for biocompatibility, and sourcing certifications |
In the aerospace industry, aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt is primarily utilized in thermal barrier coatings (TBCs). These coatings are crucial for protecting components from extreme temperatures, thereby enhancing the safety and performance of aircraft engines. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that meet stringent aerospace certifications and standards, ensuring that the TBCs are reliable and effective in high-stress environments.
In electronics manufacturing, aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt serves as an essential insulation material in semiconductor devices. Its high thermal conductivity and electrical insulating properties help improve the efficiency and reliability of electronic components. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should focus on sourcing high-purity aluminium oxide, as impurities can significantly affect performance. Additionally, understanding particle size distribution is vital for ensuring compatibility with manufacturing processes.

A stock image related to aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt.
The automotive industry uses aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt in lightweight components to enhance vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. By reducing weight, these components contribute to lower emissions and improved handling. For international buyers, key considerations include material specifications and the potential for recycling, which can affect both cost and sustainability goals. Sourcing strategies should also account for global supply chain logistics to ensure timely delivery.
In construction, aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt is employed as a refractory material in high-temperature furnaces. Its excellent durability and heat resistance lead to reduced maintenance costs and longer service life. Buyers should consider whether to source materials locally or internationally, as this can influence lead times and overall project timelines. Quality certifications are also essential to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt is increasingly utilized in medical devices, particularly as a biocompatible coating for implants. This application ensures that the materials are safe and compatible with human tissue, which is crucial for product acceptance and regulatory compliance. Buyers must prioritize suppliers that can provide thorough testing for biocompatibility and necessary certifications, as these factors are critical in the highly regulated medical device market.
Related Video: Some Important Properties and Uses of Aluminium
The Problem:
B2B buyers in industries such as ceramics, electronics, and aerospace often face challenges when working with aluminium oxide (Al2O3) due to its high melting point of approximately 2050°C. This characteristic can complicate processing and handling, especially in applications where precise thermal management is crucial. Buyers may struggle to find appropriate equipment and processes that can accommodate such high temperatures without compromising the integrity of the material or their manufacturing processes.
The Solution:
To effectively manage the melting point of aluminium oxide, buyers should invest in high-temperature furnaces specifically designed for materials with elevated melting points. Additionally, it is crucial to work closely with suppliers who can provide guidance on the best practices for thermal processing. For instance, using advanced refractory materials that can withstand high temperatures will enhance furnace efficiency and material durability. Buyers should also consider pre-treatment processes, such as sintering at lower temperatures before reaching the final melting point, which can improve the overall quality of the final product while reducing energy costs.
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face quality inconsistency when sourcing aluminium oxide, particularly from different suppliers or regions. Variations in the purity and crystal structure can lead to significant differences in performance, affecting applications in industries like electronics and automotive. Buyers may find themselves receiving batches of aluminium oxide that do not meet their specifications, resulting in production delays and increased costs.
The Solution:
To ensure consistent quality, buyers should establish stringent quality control measures and select suppliers who adhere to international standards, such as ISO certifications. Implementing a robust incoming material inspection process is essential. Buyers should request detailed certificates of analysis (CoA) with each batch, specifying the material's purity, particle size distribution, and crystal structure. Additionally, developing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can lead to better negotiation of terms and assurance of quality consistency. Regular audits and site visits to suppliers can also help buyers maintain oversight and ensure that their standards are met.
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when processing aluminium oxide due to its hardness and abrasiveness. Industries such as metalworking and abrasives often require precise machining, grinding, or milling of aluminium oxide components. Buyers may find that standard machining tools wear out quickly, leading to increased operational costs and downtime.
The Solution:
To address processing challenges, buyers should invest in specialized tools made from harder materials, such as polycrystalline diamond (PCD) or cubic boron nitride (CBN), which are designed to handle the abrasiveness of aluminium oxide. Additionally, employing advanced machining techniques, such as water jet cutting or laser machining, can significantly enhance precision and reduce tool wear. Collaborating with tool manufacturers who understand the specific requirements for processing aluminium oxide can provide insights into the best practices and tools available. Furthermore, training operators on the proper machining parameters, such as feed rate and cutting speed, can lead to optimized processing and improved tool lifespan.
When selecting materials for applications involving aluminium oxide (Al₂O₃), particularly regarding its melting point (schmelzpunkt), several common materials come into play. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can impact product performance and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four key materials frequently used in conjunction with aluminium oxide.
Key Properties:
High-purity alumina is characterized by its exceptional thermal stability, high melting point (around 2050°C), and excellent electrical insulation properties. It is highly resistant to corrosion and abrasion, making it suitable for harsh environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of high-purity alumina is its durability and reliability in high-temperature applications. However, it can be costly to produce, which may impact overall project budgets. Additionally, manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
High-purity alumina is ideal for applications such as furnace linings and high-temperature insulators. Its compatibility with various media, including aggressive chemicals, enhances its utility in diverse industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. Local sourcing may also affect costs and availability.
Key Properties:
Alumina-silicate composites combine alumina with silica, resulting in materials that exhibit improved thermal shock resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to pure alumina.
Pros & Cons:
These composites are generally more cost-effective than high-purity alumina while still offering good performance in high-temperature applications. However, their mechanical strength may not match that of pure alumina, which could limit their use in specific applications.
Impact on Application:
Alumina-silicate composites are often used in refractory applications, where they can withstand significant temperature fluctuations. Their compatibility with various media makes them suitable for industries such as metallurgy and ceramics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding composite materials, especially in regions like South America, where environmental standards may differ.
Key Properties:
Zirconia toughened alumina features a blend of zirconia and alumina, providing enhanced toughness and wear resistance. This material can withstand high temperatures and has a melting point similar to that of alumina.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of ZTA is its improved fracture toughness, making it suitable for demanding applications. However, the inclusion of zirconia can increase production costs, and the manufacturing process can be more complex.
Impact on Application:
ZTA is particularly effective in applications requiring high wear resistance, such as cutting tools and wear components in industrial machinery. Its compatibility with various media adds to its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers, especially from Europe, should consider the material's compliance with EU regulations and standards, which can be more stringent than in other regions.
Key Properties:
Alumina ceramics are known for their excellent hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. They exhibit a high melting point and are often used in applications requiring high mechanical strength.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of alumina ceramics is their durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. However, they can be brittle, which may lead to failure under certain stress conditions.
Impact on Application:
Alumina ceramics are widely used in electronics, automotive components, and medical devices. Their compatibility with various environments makes them suitable for diverse applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that alumina ceramics meet specific industry standards, such as ISO certifications, to guarantee quality and performance.
| Material | Typical Use Case for aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Alumina | Furnace linings, high-temperature insulators | Exceptional durability and reliability | High production cost | High |
| Alumina-Silicate Composites | Refractory applications | Cost-effective with good performance | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
| Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA) | Cutting tools, wear components | Improved fracture toughness | Higher production costs | High |
| Alumina Ceramics | Electronics, automotive components | Excellent hardness and wear resistance | Brittle nature | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials associated with aluminium oxide melting point applications. Understanding these factors can significantly influence procurement decisions and product performance in international markets.
The manufacturing of aluminium oxide (alumina) involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary quality standards. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers who want to ensure they are sourcing high-quality materials.
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of raw materials. Bauxite ore, which contains aluminium oxide, is mined and then crushed. This material is often treated with sodium hydroxide in a high-pressure digester, which separates the aluminium oxide from impurities. This process, known as the Bayer process, is fundamental in producing alumina with a high level of purity, often above 99%.
Once the aluminium oxide is extracted, it undergoes forming processes. The most common technique is the calcination process, where the hydrated alumina is heated to high temperatures (around 1000°C to 1100°C) to remove water and convert it into anhydrous alumina. This step is crucial as it affects the physical properties of the final product, such as its melting point and reactivity.
In some cases, particularly for specialized applications, alumina may be further processed into specific forms, such as powders, granules, or sintered products. These forms are achieved through techniques like spray drying or pressing, followed by sintering at elevated temperatures. The finishing stage may also include surface treatments to enhance properties such as corrosion resistance or to prepare it for specific applications like ceramics or refractory materials.
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of aluminium oxide, ensuring that the product meets international standards and customer specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding the quality control (QC) measures in place is essential for verifying supplier reliability.
Manufacturers of aluminium oxide typically adhere to several international quality standards, with ISO 9001 being the most recognized. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for the oil and gas sector may be applicable depending on the end-use of the alumina.
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials, such as bauxite, for impurities and compliance with specifications before processing begins.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring occurs to ensure processes remain within defined parameters. This includes temperature checks during calcination and monitoring of material consistency.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the finished aluminium oxide undergoes rigorous testing to confirm it meets required specifications. This includes physical tests (like particle size distribution) and chemical analyses to verify purity levels.
B2B buyers should be aware of the common testing methods that manufacturers use to ensure product quality. These methods not only confirm compliance with specifications but also help in troubleshooting any production issues.
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF): This method is used to determine the elemental composition of the alumina, ensuring that the product meets chemical purity standards.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): SEM provides detailed images of the material's surface, allowing for analysis of morphology and particle size, which are critical for certain applications.
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA): TGA measures changes in weight as the material is heated, providing insights into thermal stability and composition.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR): FTIR is employed to identify functional groups in the alumina, ensuring that the chemical properties align with specifications.
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance with regional standards. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
One of the most effective ways to verify quality control is through supplier audits. These can be conducted in-person or remotely and should focus on reviewing the supplier's quality management systems, production processes, and testing protocols. Ensure that the audit covers compliance with relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 and any applicable industry standards.
Requesting detailed quality control reports from suppliers can provide insights into their testing methods and results. These reports should include data on IQC, IPQC, and FQC, along with any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can perform unannounced inspections and testing to verify that suppliers adhere to their claimed quality standards.
Navigating the landscape of quality assurance and certification can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. Here are key considerations:
Different regions may have specific certification requirements for aluminium oxide. For instance, products destined for the European market may require CE marking, while those for the Middle Eastern market may need to comply with local standards. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure compliance.
Quality assurance processes can significantly impact pricing. Suppliers who maintain rigorous QC standards may charge higher prices, reflecting the costs associated with maintaining compliance and achieving high-quality outputs. Buyers should weigh the cost against the potential risks of sourcing lower-quality materials.
Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who have proven quality control measures can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to innovations in product development. Engage with suppliers to understand their QC processes and commitment to continuous improvement.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance strategies, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed decisions when sourcing aluminium oxide, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
This sourcing guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in effectively procuring aluminium oxide (alumina) with a focus on its melting point characteristics. Understanding the specific requirements and nuances of sourcing this material is essential for ensuring quality, performance, and compliance with industry standards. This checklist will provide a structured approach to streamline your procurement process.
Before initiating the sourcing process, clarify your technical requirements for aluminium oxide, particularly its melting point. This is crucial because different applications may require varying grades and purities of alumina.
Research the market to identify potential suppliers of aluminium oxide. This helps you understand the landscape and ensures you are aware of the most reputable manufacturers.
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. This step is vital to avoid potential disruptions in your supply chain.
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This not only guarantees product quality but also protects your business from legal risks.
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of aluminium oxide to evaluate its quality against your specifications. This helps mitigate risks associated with material performance.
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate pricing and terms. This is a critical step to ensure that you are getting the best value for your investment.
After selecting your supplier, create a communication plan to facilitate ongoing interactions. Effective communication is essential for addressing any issues that may arise during the procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a comprehensive approach to sourcing aluminium oxide, optimizing their procurement process while minimizing risks associated with quality and supplier reliability.
A stock image related to aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt.
When sourcing aluminium oxide (Al2O3), understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The raw material cost is often the most significant portion of the total price. The purity of aluminium oxide, which can vary based on its intended application (e.g., abrasives, ceramics, or refractories), will influence the price. Higher purity levels typically command a premium.
Labor: Labor costs, including the wages of skilled workers involved in the extraction and processing of aluminium oxide, contribute to overall expenses. Regions with higher labor costs will reflect this in the pricing.
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facilities, equipment depreciation, utilities, and other indirect expenses. Efficient production methods can help minimize these costs, making it crucial for buyers to assess suppliers' operational efficiencies.
Tooling: For customized aluminium oxide products, tooling costs can be substantial. Buyers should inquire about these costs upfront, as they can significantly affect the pricing structure, especially for small batch orders.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the aluminium oxide meets specified standards. Suppliers may charge extra for enhanced QC processes, particularly for high-end applications requiring certifications.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the geographical location of the supplier and the buyer. Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, play a crucial role in determining who bears the logistics costs.
Margin: Finally, the supplier's profit margin will influence the final price. Different suppliers may have varying pricing strategies based on their market positioning and operational costs.
Several factors can significantly impact the pricing of aluminium oxide:
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts. Buyers should negotiate terms that maximize their purchase volume to achieve cost savings.
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to unique processing requirements. Buyers should clarify their needs upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
Material Quality and Certifications: Suppliers offering certified high-purity aluminium oxide typically charge a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher quality against their budget constraints.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and proven track record.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. They dictate the division of costs and responsibilities, which can directly impact the total landed cost of aluminium oxide.
For B2B buyers, particularly from emerging markets, effective negotiation strategies can lead to substantial savings:
Negotiate on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational costs, and potential savings from higher-quality materials.
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate purchases to meet or exceed MOQs, enabling access to better pricing.
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Engage with several suppliers to compare offerings and negotiate better terms. This competition can lead to more favorable pricing.
Request Detailed Quotations: Ensure that suppliers provide a comprehensive breakdown of costs to identify areas for negotiation and assess value.
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding market dynamics, including fluctuations in raw material prices and geopolitical factors, can equip buyers with the knowledge needed for effective negotiations.
Prices for aluminium oxide can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and other external factors. Buyers are encouraged to request current quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing for their specific needs.
In today's competitive landscape, international B2B buyers must evaluate various materials and methods to achieve optimal outcomes in their operations. When considering aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt (alumina melting point), it is essential to explore alternative solutions that can meet similar performance standards while potentially offering cost advantages or operational efficiencies. This section compares aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt with two viable alternatives: zirconium oxide and silicon carbide.
| Comparison Aspect | Aluminiumoxid Schmelzpunkt | Zirconium Oxide | Silicon Carbide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High melting point (2050°C) | High melting point (2715°C) | High thermal conductivity and strength |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than alumina | Higher initial investment but long-term savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires specific conditions | Requires specialized handling | Straightforward, but needs precise equipment |
| Maintenance | Low; stable under most conditions | Moderate; can degrade under extreme conditions | Low; highly durable and resistant to wear |
| Best Use Case | Ceramics, abrasives, and refractory applications | High-temperature applications, dental ceramics | High-performance electronics and automotive components |
Zirconium oxide, known for its superior melting point, is often used in high-temperature applications. Its high thermal stability makes it ideal for environments that experience extreme heat. However, the cost of zirconium oxide is typically higher than that of aluminium oxide, which may not be justifiable for all applications. Additionally, while it offers excellent mechanical properties, the need for specialized handling can complicate implementation.
Silicon carbide is another alternative that provides excellent thermal conductivity and strength. It is particularly useful in high-performance electronics and automotive applications where durability is critical. While the initial investment in silicon carbide can be significant, its longevity and resistance to wear often result in lower total cost of ownership. The straightforward implementation process makes it accessible for various applications, although precise equipment is necessary to achieve optimal results.
When selecting between aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors. First, assess the specific application requirements, including temperature ranges and mechanical stresses. Cost considerations should include both initial investments and long-term maintenance expenses. Additionally, evaluate the ease of implementation and maintenance needs, as these factors can impact operational efficiency. By aligning these criteria with organizational goals, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and sustainability in their operations.
When dealing with aluminium oxide (alumina), understanding its critical technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications:
Material Grade
Aluminium oxide is available in various grades, including alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) alumina. Each grade has distinct properties suitable for specific applications. For instance, α-alumina is preferred for high-temperature applications due to its stability. Buyers should select the appropriate grade based on their end-use requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Melting Point
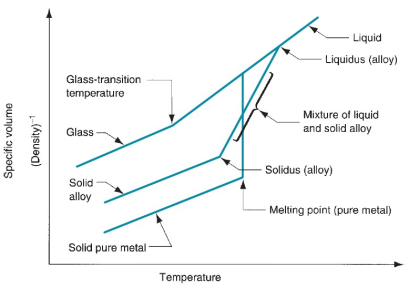
The melting point of aluminium oxide is approximately 2,072°C (3,762°F). This high melting point makes it suitable for applications in environments exposed to extreme heat, such as refractory materials and ceramics. Understanding this property helps buyers assess the material’s suitability for their processes, particularly in industries like metallurgy and ceramics.
Purity Level
Purity levels of aluminium oxide can vary, typically ranging from 99% to 99.99%. Higher purity levels yield better performance in applications like electronics and medical devices. Buyers in these sectors should prioritize high-purity alumina to meet stringent quality standards and ensure product reliability.
Grain Size
The grain size of aluminium oxide can significantly affect its mechanical and thermal properties. Finer grain sizes offer better strength and hardness, making them ideal for abrasives and cutting tools. Buyers need to consider grain size when selecting alumina for specific applications to achieve desired performance characteristics.
Density
The density of aluminium oxide typically ranges from 3.9 to 4.1 g/cm³. This property influences the material’s weight and structural integrity. Buyers should factor in density when designing components that require a balance between strength and weight, especially in aerospace and automotive applications.
Thermal Conductivity
Aluminium oxide exhibits relatively low thermal conductivity compared to metals, making it an excellent insulator. This property is particularly important for applications requiring thermal management, such as in electronics and heat exchangers. B2B buyers should evaluate thermal conductivity to ensure their applications maintain operational efficiency.
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for navigating the procurement process effectively. Here are some essential terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are used as components in another company's products. For B2B buyers, partnering with reputable OEMs for aluminium oxide can ensure high-quality standards and reliable supply chains.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is vital for budget-conscious buyers, particularly small to medium-sized enterprises, as it affects overall purchasing costs and inventory management.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits pricing and terms from suppliers. It is an essential tool for B2B buyers to gather competitive pricing and assess supplier capabilities. Providing detailed specifications in an RFQ helps ensure accurate and comparable quotes.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, particularly when sourcing aluminium oxide globally.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time between placing an order and receiving the product. Buyers must consider lead times when planning production schedules to avoid delays. Clear communication with suppliers about lead times can enhance supply chain efficiency.
Certification Standards
Certification standards refer to the quality assurance processes that materials must undergo to meet industry regulations. Familiarity with relevant certification standards, such as ISO or ASTM, can help buyers ensure that the aluminium oxide they procure meets necessary safety and quality benchmarks.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding aluminium oxide, ultimately leading to better procurement outcomes and enhanced product performance.
The aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt (alumina melting point) sector is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction. Key global drivers include advancements in technology, rising urbanization in Africa and South America, and stringent regulations promoting the use of lightweight and durable materials. B2B buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe are particularly focused on high-performance materials that can withstand extreme conditions, thereby influencing sourcing strategies.
Emerging technologies such as automation and artificial intelligence are reshaping supply chain dynamics, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs. For international buyers, leveraging digital platforms to connect with suppliers and streamline procurement processes is becoming essential. The trend towards digitalization includes the use of Blockchain for traceability in sourcing alumina, which is particularly relevant for buyers concerned about the authenticity and quality of materials.
Furthermore, the shift towards localized sourcing is gaining traction. Buyers from regions like the UAE and Mexico are seeking to reduce lead times and transportation costs by collaborating with regional suppliers. This trend is compounded by geopolitical factors that influence trade policies and tariffs, necessitating a more agile and responsive supply chain approach.
Sustainability is no longer an optional consideration; it is a critical factor influencing sourcing decisions in the aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt sector. B2B buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact associated with aluminium production, including high energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. This awareness has led to a growing demand for sustainable and ethically sourced materials.
To address these concerns, suppliers are adopting 'green' certifications and practices. Buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to standards such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and that can provide materials sourced from recycled or sustainably managed sources. Additionally, the use of innovative processing technologies that reduce energy consumption during the production of alumina is becoming a key differentiator in the market.
Investing in suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance a company’s brand reputation and compliance with international regulations, particularly in Europe, where environmental standards are stringent. Ultimately, ethical sourcing not only contributes to environmental stewardship but can also lead to cost savings through improved efficiencies and waste reduction.
The history of aluminium oxide dates back to its discovery in the early 19th century, but its commercial significance surged in the mid-20th century as industries recognized its exceptional properties, such as high melting point and chemical stability. Initially, the primary use of alumina was in the production of aluminium metal, but its applications expanded significantly over the decades.
By the 1980s, advancements in processing techniques, such as the Bayer process, allowed for more efficient extraction and refinement of aluminium oxide. This set the stage for its use in various high-tech applications, including ceramics, abrasives, and catalysts. Today, the aluminiumoxid schmelzpunkt sector continues to evolve, driven by innovations in materials science and increasing demand for high-performance solutions across diverse industries. This evolution highlights the importance of staying informed about technological advancements and market shifts for B2B buyers seeking to remain competitive in their respective markets.
How do I determine the melting point of aluminum oxide (alumina) for my specific application?
To determine the melting point of aluminum oxide suitable for your application, refer to the technical data sheets provided by suppliers. Generally, aluminum oxide has a melting point around 2050°C (3722°F). However, the exact melting point can vary based on the specific grade and purity of alumina used. It’s advisable to consult with your supplier for detailed specifications and any factors that might influence melting characteristics, such as additives or processing methods.
What is the best grade of aluminum oxide for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, a high-purity aluminum oxide, often referred to as "alumina," is recommended. Grades such as 99.5% or higher purity alumina are suitable for environments that require resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress. Ensure that the supplier provides comprehensive data on thermal stability and mechanical properties to confirm the grade's suitability for your specific needs.
How can I effectively vet suppliers of aluminum oxide for international trade?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Request references and review their history in international trade, particularly in your target regions. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or industry-specific directories to find verified suppliers. Conduct due diligence by visiting their production facilities if possible, and request samples to assess product quality firsthand before making bulk orders.
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for aluminum oxide?
Minimum order quantities for aluminum oxide can vary significantly by supplier and region. Typically, MOQs range from 50 kg to several tons, depending on the supplier's business model and production capabilities. When negotiating, inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you're testing new applications or markets. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for trial orders or smaller businesses.
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aluminum oxide internationally?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include 30% upfront payment with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established buyers. Always confirm the payment methods accepted, such as letters of credit, PayPal, or bank transfers. It’s wise to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies.
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for aluminum oxide products?
To ensure quality assurance, request a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from your supplier, detailing the chemical composition and physical properties of the aluminum oxide. Implement a quality control process upon receipt, including visual inspections and laboratory testing if necessary. Establish clear specifications and communicate them with your supplier to ensure consistency in future orders.
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing aluminum oxide?
When importing aluminum oxide, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and import tariffs applicable in your country. Work with freight forwarders who have experience in handling industrial materials to navigate the logistics smoothly. Ensure that your supplier is aware of your preferred shipping arrangements and that all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, is prepared in advance.
How do I manage supply chain risks when sourcing aluminum oxide from different regions?
To manage supply chain risks, diversify your supplier base across different regions to avoid dependency on a single source. Establish long-term relationships with multiple suppliers to ensure continuity of supply. Conduct regular risk assessments, considering geopolitical factors, transportation issues, and market fluctuations. Additionally, keep a buffer stock of essential materials to mitigate disruptions during unforeseen events.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
In summary, understanding the melting point of aluminium oxide is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in industries such as ceramics, metallurgy, and electronics. The melting point influences material selection, processing techniques, and overall product performance. Strategic sourcing of aluminium oxide not only ensures quality and consistency but also optimizes supply chain efficiency, enabling companies to respond swiftly to market demands.
Investing in strategic sourcing for aluminium oxide can lead to significant cost savings and improved quality control. By establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers, companies can mitigate risks associated with price volatility and supply disruptions. This approach is particularly beneficial for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where local sourcing opportunities may vary greatly.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality aluminium oxide is expected to grow, driven by advancements in various industries. International B2B buyers should proactively seek out innovative suppliers who can provide not only competitive pricing but also insights into emerging trends and technologies. By doing so, they can position themselves as leaders in their respective markets. Engage with suppliers today to explore how strategic sourcing can enhance your operations and foster sustainable growth.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina