Carburundum, also known as silicon carbide, stands as a cornerstone material in numerous industrial applications worldwide. Its exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance make it indispensable for sectors ranging from abrasives and refractories to electronics and automotive manufacturing. For international B2B buyers, especially those operating in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key hubs like Kenya and the UAE—understanding the complexities of sourcing carburundum is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and operational excellence.
This guide delivers a comprehensive roadmap to the global carburundum market, meticulously covering:
Equipped with this knowledge, B2B buyers can strategically navigate supplier selection, optimize procurement terms, and mitigate risks associated with international trade. Whether expanding operations or seeking cost-effective alternatives, this guide empowers you to make informed, confident sourcing decisions that align with your business objectives and regional market realities.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brown Carburundum | High purity, dense crystalline structure, dark brown color | Industrial grinding, cutting tools | Pros: Durable, cost-effective; Cons: Less heat resistant than black variant |
| Black Carburundum | High hardness, superior heat resistance, black granular form | Heavy-duty abrasive blasting, polishing | Pros: High wear resistance, excellent thermal stability; Cons: Higher cost, brittle under impact |
| Green Carburundum | Enhanced toughness, mixed crystalline phases, greenish tint | Precision grinding, finishing operations | Pros: Balances hardness and toughness; Cons: Limited availability, moderate price |
| White Carburundum | High purity, fine grain size, white crystalline appearance | Fine polishing, semiconductor industry | Pros: Produces fine finishes, chemically inert; Cons: Lower mechanical strength, premium price |
| Electrolytic Carburundum | Manufactured via electrochemical process, uniform particle size | High-precision machining, advanced abrasives | Pros: Consistent quality, tailored particle size; Cons: Higher production cost, niche applications |
Brown Carburundum is widely recognized for its robust crystalline structure and affordability. Its dense, dark brown granules make it ideal for industrial grinding and cutting applications where cost-efficiency and durability are prioritized. For B2B buyers, especially in manufacturing hubs across Africa and South America, this variant offers a balance of performance and price. However, it is less heat resistant than black carburundum, which should be considered for high-temperature processes.
Black Carburundum stands out due to its exceptional hardness and thermal stability, making it suitable for abrasive blasting and polishing heavy-duty materials. Its granular black form delivers superior wear resistance, favored in Middle Eastern and European heavy industries requiring long-lasting abrasives. The trade-off is a higher price point and brittleness under sudden mechanical impacts, necessitating careful handling and storage.
Green Carburundum offers a unique combination of toughness and hardness, with a distinctive greenish tint resulting from mixed crystalline phases. It is highly valued in precision grinding and finishing tasks where both durability and surface quality are critical. Buyers in precision engineering sectors, such as automotive and aerospace industries in the UAE and Europe, benefit from its balanced properties, though it may come at a moderate premium due to limited production.
White Carburundum is characterized by its fine grain size and chemical inertness, making it the preferred choice for fine polishing and delicate semiconductor manufacturing. Its white crystalline appearance indicates high purity. B2B buyers targeting high-tech and electronics sectors should note its premium pricing and comparatively lower mechanical strength, which limits its use to non-abrasive or light abrasion applications.
Electrolytic Carburundum is produced through an electrochemical process that ensures uniform particle size and high purity. This type is favored for high-precision machining and advanced abrasive tools, where consistency and tailored abrasive qualities are essential. While it commands a higher price and serves niche markets, buyers in technologically advanced regions like Europe and the Middle East will find this variant indispensable for specialized manufacturing needs.
Related Video: The Genius Behind Bach's Goldberg Variations: CANONS
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of carburundum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Metalworking | Abrasive grinding wheels and cutting tools | Enhances precision and durability in metal shaping and finishing | Quality grade, grit size, and consistent supply for continuous production |
| Construction & Building Materials | Surface grinding and polishing of concrete and stone | Improves surface finish and extends lifespan of construction elements | Abrasive hardness, bonding type, and compatibility with machinery |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Component surface finishing and deburring | Increases component longevity and performance | Abrasive form, thermal stability, and compliance with industry standards |
| Electronics & Semiconductor | Precision lapping and polishing of semiconductor wafers | Ensures ultra-smooth surfaces for optimal device performance | Purity level, particle size uniformity, and contamination control |
| Energy & Mining | Wear-resistant coatings and cutting tools for mining equipment | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs in harsh environments | Abrasion resistance, toughness, and local regulatory compliance |
Manufacturing & Metalworking
Carburundum is extensively used in abrasive grinding wheels and cutting tools within manufacturing and metalworking sectors. It provides the hardness and sharpness required to efficiently shape and finish metals, ensuring high precision and surface quality. For B2B buyers in regions such as Europe and the Middle East, sourcing carburundum with consistent grit size and industrial-grade quality is crucial to maintain uninterrupted production cycles and meet stringent quality standards.
Construction & Building Materials
In construction, carburundum abrasives are vital for grinding and polishing concrete, stone, and tiles. This application improves the aesthetic appeal and durability of building materials, directly impacting project longevity and client satisfaction. Buyers from Africa and South America should prioritize abrasives with appropriate hardness and bonding materials compatible with their local machinery, ensuring optimal performance in diverse environmental conditions.
Automotive & Aerospace
The automotive and aerospace industries rely on carburundum for surface finishing and deburring of critical components. This ensures smooth surfaces that enhance mechanical performance and reduce wear. International buyers, particularly from technologically advanced markets like Europe and the UAE, must focus on abrasives that offer thermal stability and meet rigorous industry standards to guarantee safety and reliability in high-stress applications.
Electronics & Semiconductor
Precision lapping and polishing of semiconductor wafers require ultra-fine carburundum abrasives. These ensure defect-free, ultra-smooth surfaces essential for semiconductor performance. B2B buyers in emerging electronics hubs across Africa and South America should source high-purity carburundum with tightly controlled particle size distribution and contamination levels to meet the demanding specifications of semiconductor manufacturing.
Energy & Mining
Carburundum’s wear resistance makes it ideal for coatings and cutting tools used in mining equipment, where abrasion and harsh conditions prevail. This application significantly reduces equipment downtime and maintenance costs. Buyers in mining-intensive regions such as Africa and the Middle East must consider abrasion resistance and toughness, alongside compliance with local environmental and safety regulations, to maximize operational efficiency and sustainability.
Related Video: From Waste to Wonder: The Surprising Uses of Carbon Dioxide
When selecting materials for carburundum applications, international B2B buyers must carefully evaluate the performance characteristics, cost implications, and regional compliance standards relevant to their specific markets. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in carburundum production, focusing on their suitability for diverse industrial environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties: Silicon carbide is the primary material for carburundum products, known for its exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, and outstanding resistance to thermal shock. It withstands high temperatures up to 1600°C and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance against acidic and alkaline media.
Pros & Cons: SiC offers superior durability and wear resistance, making it ideal for abrasive environments. However, it is relatively brittle and can be costly to manufacture due to complex sintering processes. Its hardness can lead to challenges in machining and shaping.
Impact on Application: SiC is widely used in cutting, grinding, and abrasive tools. Its chemical inertness makes it suitable for handling aggressive chemicals, which is critical in oil refining and chemical processing sectors common in the Middle East and Europe.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Kenya and UAE should ensure SiC materials comply with ASTM C799 or DIN EN standards for abrasive products. European buyers often require adherence to REACH regulations for chemical safety. Availability from suppliers with ISO 9001 certification is preferred to guarantee consistent quality.
Key Properties: Boron carbide is one of the hardest materials after diamond and SiC, with excellent neutron absorption properties and high resistance to wear and corrosion. It performs well under extreme pressures and temperatures around 2200°C.
Pros & Cons: B4C provides superior abrasion resistance and is lighter than SiC, which benefits applications requiring weight reduction. However, it is more expensive and less widely available, with more complex manufacturing requirements.
Impact on Application: Ideal for ballistic armor, nuclear applications, and high-performance abrasives. Its resistance to chemical attack suits industries in South America and Africa where harsh environmental conditions prevail.
Considerations for International Buyers: Importers should verify compliance with ASTM B622 for boron carbide powders. Due to high costs, buyers from emerging markets may prioritize suppliers offering volume discounts. Certification of origin and export documentation is critical for customs clearance in regions like the Middle East.
Key Properties: Aluminum oxide, or alumina, is a widely used abrasive material with good hardness, thermal stability up to 1750°C, and excellent chemical resistance. It is less brittle than SiC and offers good electrical insulation.
Pros & Cons: Alumina is cost-effective and easier to manufacture and machine compared to SiC and B4C. However, it has lower thermal conductivity and slightly inferior wear resistance, limiting its use in extremely abrasive or high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in grinding wheels, sandpapers, and refractory linings. Its versatility makes it popular in European manufacturing and South American mining industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with ISO 11146 for abrasive grains and ensure materials meet local environmental standards. Alumina’s lower cost and availability make it attractive for African markets with budget constraints.
Key Properties: Zirconium carbide offers high melting points (~3550°C), excellent hardness, and good chemical stability, particularly in reducing environments. It has superior thermal shock resistance compared to other carbides.
Pros & Cons: ZrC’s high temperature tolerance and chemical inertness make it valuable for specialized carburundum applications. However, it is expensive and less commonly stocked, which may lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Used in aerospace, nuclear reactors, and high-performance cutting tools where extreme conditions are encountered. Its niche applications are more prevalent in technologically advanced markets such as Europe and the UAE.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM B777 for zirconium carbide powders is essential. Buyers should consider supplier reliability and logistical factors, especially when sourcing from distant manufacturers to Africa or South America.
| Material | Typical Use Case for carburundum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide | Abrasive tools, chemical processing | High hardness and thermal shock resistance | Brittle and costly manufacturing | High |
| Boron Carbide | Ballistic armor, nuclear, high abrasion | Exceptional hardness and light weight | High cost and limited availability | High |
| Aluminum Oxide | Grinding wheels, refractory linings | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower wear resistance and thermal conductivity | Low |
| Zirconium Carbide | Aerospace, nuclear, extreme condition tools | Superior high-temperature stability | Expensive and less available | High |
Carburundum, commonly known as silicon carbide, is a highly durable abrasive material widely used in industrial applications such as grinding, cutting, and polishing. Understanding its manufacturing process is crucial for B2B buyers to evaluate supplier capabilities and product quality.
The production begins with sourcing high-purity raw materials—primarily silica sand and petroleum coke. These are carefully proportioned to ensure the correct stoichiometric balance for silicon carbide synthesis. In some cases, additives like sawdust or salt may be introduced to control grain size and purity.
The predominant manufacturing technique for carburundum is the Acheson process, a high-temperature electric resistance heating method.
After cooling, the blocks are broken down into smaller pieces.
For certain applications, carburundum particles are bonded with resins, ceramics, or metals to form grinding wheels, cutting tools, or refractory products.
Final finishing includes:
Robust QA/QC protocols are essential to maintain product reliability, especially for international B2B buyers sourcing carburundum from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
International buyers must perform due diligence to mitigate risks and ensure product quality.
By leveraging these insights, B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can secure high-quality carburundum products that meet their specific operational needs and regulatory requirements.
When sourcing carburundum (silicon carbide) for industrial applications, it is essential to dissect the cost components that collectively determine the final pricing. Key cost elements include:
Several dynamic factors influence the pricing landscape for carburundum, which buyers must carefully evaluate:
For buyers in Africa (e.g., Kenya), South America, the Middle East (e.g., UAE), and Europe, the following strategies can optimize sourcing costs and mitigate risks:
All pricing information discussed is indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, currency fluctuations, and supplier negotiations. Buyers should request updated quotations and conduct comprehensive due diligence to ensure accurate budgeting.
By thoroughly analyzing these cost components and influencing factors, international B2B buyers can make informed procurement decisions, achieving cost-efficiency without compromising quality or delivery timelines.
Understanding the core technical properties of carburundum is essential for buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to ensure optimal product performance and compatibility with their applications.
Material Grade
Carburundum (silicon carbide) comes in various grades, distinguished by purity and particle size. Higher purity grades offer superior hardness and thermal conductivity, critical for demanding industrial uses such as abrasives and refractories. Selecting the appropriate grade affects durability and efficiency, directly impacting operational costs.
Particle Size and Distribution
The granulometry of carburundum determines its abrasive action and surface finish. Fine particles provide smooth finishes, while coarser sizes are suited for heavy-duty grinding. Buyers must specify particle size ranges to match their manufacturing or processing requirements.
Hardness (Mohs Scale)
Carburundum is known for its high hardness, typically around 9-9.5 on the Mohs scale. This hardness ensures excellent wear resistance and longevity in cutting, grinding, and polishing applications. Understanding this helps buyers predict lifespan and maintenance intervals.
Thermal Stability and Conductivity
Its ability to withstand high temperatures without degradation makes carburundum ideal for high-heat industrial processes. Good thermal conductivity also aids in heat dissipation during abrasive operations, preventing tool overheating.
Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
For precision applications, such as in mechanical seals or electronic substrates, tight dimensional tolerances are critical. Buyers should verify the supplier’s capability to meet specified tolerances, ensuring seamless integration into their production lines.
Chemical Resistance
Carburundum resists corrosion from acids and alkalis, which is vital for chemical processing industries. This property ensures longevity and reduces replacement frequency in harsh environments.
Navigating the global B2B marketplace requires familiarity with common industry terms. These facilitate clearer communication and smoother transactions for buyers in regions like Kenya, UAE, Brazil, or Germany.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce parts or materials (like carburundum) used in another company’s final product. Buyers working with OEMs often require specific material certifications or custom grades to meet their product standards.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. MOQs can vary widely, influencing inventory management and budgeting. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan purchases to balance cost efficiency with storage capacity.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal inquiry sent by buyers to suppliers asking for pricing, availability, and terms for a specific carburundum product. A detailed RFQ accelerates the sourcing process and helps secure competitive pricing.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining the responsibilities and risks between buyers and sellers during shipping. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free on Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Clear agreement on Incoterms prevents misunderstandings related to shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery responsibilities.
Lead Time
The period between placing an order and receiving the product. Lead times affect production schedules and inventory planning. Buyers should negotiate realistic lead times, especially when importing carburundum from distant suppliers.
Batch Number / Lot Number
Identifies a specific production run of carburundum, crucial for quality control and traceability. Buyers can track product consistency and manage recalls if necessary.
By mastering these technical specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and establish reliable supply chains for carburundum tailored to their industrial needs.
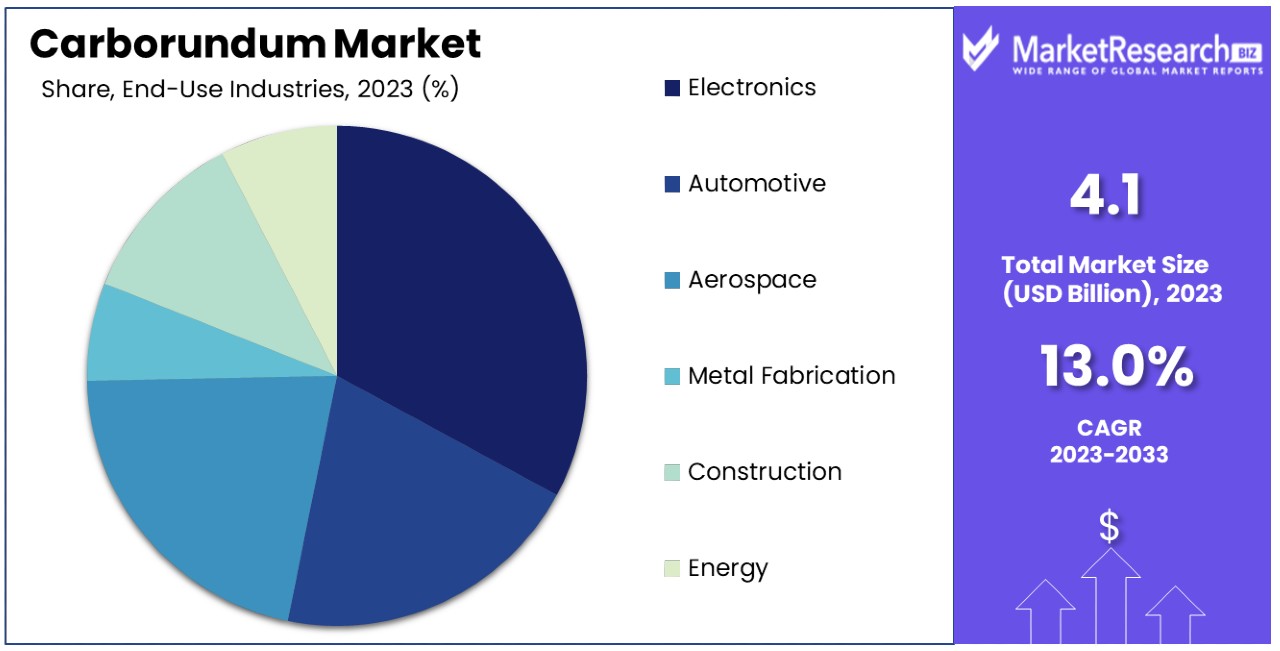
The global carburundum market, essential for industrial abrasives, refractories, and cutting tools, is experiencing robust demand fueled by rapid industrialization and infrastructure growth across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Countries like Kenya and the UAE are witnessing expanding manufacturing and construction sectors, driving demand for high-quality carburundum products. Key market drivers include the rising need for durable materials in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and metal fabrication industries.
Emerging sourcing trends emphasize digital procurement platforms and supply chain transparency, enabling buyers to access competitive pricing and verified quality from global suppliers. Buyers in these regions increasingly prefer suppliers who offer customizable solutions tailored to specific industrial applications, such as precision grinding or high-temperature resistance. Strategic sourcing is also influenced by geopolitical factors and logistics capabilities, with proximity to manufacturing hubs in Russia, China, and Europe playing a significant role in supplier selection.
Technological advancements in carburundum production, including improved sintering techniques and enhanced purity grades, are enhancing product performance and lifespan. Buyers should monitor innovations such as nano-structured carburundum powders, which offer superior abrasion resistance, to maintain a competitive edge. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 tools like IoT-enabled quality tracking and AI-driven demand forecasting is reshaping how B2B buyers manage inventory and supplier relationships.
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in carburundum procurement as industrial buyers prioritize reducing environmental footprints and aligning with global green standards. The production of carburundum involves high-energy processes and raw material extraction that can impact ecosystems. Therefore, international buyers are increasingly demanding suppliers who demonstrate commitment to eco-friendly manufacturing practices, such as energy-efficient kiln operations and waste minimization.
Ethical sourcing is critical, especially for buyers in regions with growing regulatory scrutiny like the European Union. Transparency in the supply chain ensures compliance with labor laws and responsible mining practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), REACH compliance, and conflict-free mineral sourcing are becoming prerequisites for partnership. Suppliers offering carburundum products with verifiable carbon-neutral footprints or those utilizing recycled feedstock materials are favored, aligning with corporate sustainability goals.
For B2B buyers, engaging with suppliers who proactively disclose sustainability metrics and invest in lifecycle assessments can mitigate risks and enhance brand reputation. Collaborations that support circular economy initiatives—like reclaiming and recycling spent abrasive materials—are gaining traction. Prioritizing sustainability in sourcing decisions not only future-proofs supply chains but also meets the evolving expectations of end customers and regulatory bodies.
Carburundum, or silicon carbide, was first synthesized in the late 19th century as a revolutionary abrasive material, replacing natural stones with a superior synthetic alternative. Its development marked a significant milestone in industrial manufacturing, enabling higher precision and efficiency in cutting and grinding operations. Over the decades, advancements in crystal growth and sintering methods have refined carburundum’s properties, expanding its applications beyond abrasives to include semiconductors and high-temperature ceramics.
For B2B buyers today, understanding this evolution highlights the material’s proven reliability and ongoing innovation potential. The historical trajectory from rudimentary abrasive grains to advanced engineered materials underscores the importance of sourcing from suppliers who invest in research and technological upgrades. This ensures access to carburundum products that meet contemporary industrial demands for performance and sustainability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Is customization of carburundum products feasible for international buyers, and how should I approach this?
Customization is often possible, especially for specialized industrial applications. Communicate your technical requirements clearly, including grain size, hardness, and bonding type. Provide detailed specifications or drawings if available. Work closely with suppliers who offer R&D support or tailored manufacturing. Be aware that customization may affect lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs). Establish clear agreements on quality standards and testing protocols for customized batches to avoid misalignment and ensure the final product meets your operational needs.
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for carburundum when sourcing internationally?
MOQs vary widely depending on the supplier’s scale and product type but generally range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons. Lead times typically span 4 to 8 weeks, influenced by production schedules, customization complexity, and shipping logistics. Buyers in Africa, South America, or the Middle East should factor in additional time for customs clearance and inland transport. Negotiating flexible MOQs with suppliers can be possible, especially when establishing long-term partnerships. Always confirm lead times and MOQs upfront to align your procurement planning and inventory management.
What payment terms are commonly accepted in international carburundum trade, and how can I mitigate financial risks?
Common payment terms include letters of credit (LC), telegraphic transfers (T/T), and documentary collections. LCs offer strong protection by ensuring payment only upon meeting agreed shipment conditions. T/T payments may require partial upfront deposits with balance upon delivery. To mitigate risks, conduct due diligence on supplier credibility, use escrow services when feasible, and request proforma invoices detailing terms. Negotiating staggered payments tied to production milestones or inspection approvals can also safeguard your investment, especially when dealing with new or untested suppliers in emerging markets.
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I expect from reputable carburundum suppliers?
Reputable suppliers typically provide quality assurance through standardized testing such as hardness, grain size distribution, and purity levels. Certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management are common indicators of consistent manufacturing practices. Suppliers may also offer material safety data sheets (MSDS) and compliance with international standards such as ASTM or EN norms. Request third-party inspection reports or lab test certificates to verify product conformity. For critical applications, consider engaging independent inspection agencies to validate batch quality before shipment.
How can I optimize logistics and shipping when importing carburundum to countries like Kenya, UAE, or Brazil?
Plan shipments by consolidating orders to reduce freight costs and ensure full container loads where possible. Choose reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling abrasive materials and knowledgeable about customs procedures in your destination country. Understand import regulations, duties, and required documentation such as certificates of origin and quality compliance. Utilize tracking systems for real-time visibility, and prepare for potential delays by building buffer time into your supply chain. Collaborate with suppliers to package carburundum securely to prevent contamination or damage during transit.
What are the best practices for resolving disputes or quality issues with international carburundum suppliers?
Address disputes promptly by documenting all communications, contracts, and product specifications. Use clearly defined contractual terms on quality standards, inspection rights, and penalties for non-compliance. Engage in open dialogue to seek amicable resolutions such as product replacement, discounts, or refunds. If disputes escalate, consider mediation or arbitration under internationally recognized frameworks like ICC rules. Maintaining a strong relationship with your supplier can facilitate smoother conflict resolution. Additionally, pre-shipment inspections and clear acceptance criteria help minimize disagreements.
How can B2B buyers ensure compliance with environmental and safety regulations when sourcing carburundum internationally?
Ensure suppliers comply with local and international environmental laws by verifying certifications like ISO 14001 and adherence to REACH or RoHS standards where applicable. Request documentation on safe handling, storage, and disposal of carburundum products. Evaluate the supplier’s commitment to sustainable sourcing and responsible manufacturing practices. For buyers in regulated markets such as the EU or UAE, confirm that imported products meet all safety and environmental standards to avoid legal penalties. Partnering with eco-conscious suppliers can also enhance your company’s corporate social responsibility profile.
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic sourcing of carburundum presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers to optimize supply chains, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating supplier reliability, geographic advantages, and compliance with international standards. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging regional trade agreements and understanding local market dynamics can unlock competitive pricing and timely delivery.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Value of Strategic Sourcing:
Looking ahead, the carburundum market is poised for innovation driven by demand in high-precision industries such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers from emerging and mature markets alike should proactively engage in supplier development programs and invest in digital procurement tools for enhanced transparency and agility.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Actionable Insight: International buyers—whether in Kenya, UAE, Brazil, or Germany—are encouraged to deepen their market intelligence, foster strategic partnerships, and embrace sustainable sourcing practices to secure a resilient and future-ready carburundum supply chain.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina