Guide to Types Of Alumina
In today’s interconnected global marketplace, selecting the right type of alumina is crucial for manufacturers and suppliers aiming to optimize product performance, cost-efficiency, and supply chain resilience. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Turkey and Nigeria—understanding the nuances of different alumina varieties can significantly impact operational success and competitive advantage.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international buyers with the critical knowledge needed to navigate the complex alumina landscape. It covers essential topics such as the various types of alumina, their specific material properties, manufacturing processes, quality control standards, and the leading suppliers worldwide. Additionally, it offers insights into market dynamics, pricing trends, and strategic sourcing considerations tailored to diverse regional needs.
By providing detailed, actionable information, this guide aims to facilitate smarter sourcing decisions—whether you're seeking high-purity alumina for advanced ceramics or cost-effective options for large-scale industrial applications. With a clear understanding of the market, quality benchmarks, and supplier options, B2B buyers can mitigate risks, negotiate effectively, and build resilient supply chains in a competitive global environment.
Ultimately, this resource positions you to make informed, strategic choices in alumina procurement—ensuring your business stays ahead in the evolving international market landscape.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcined Alumina | Fully calcined at high temperatures, resulting in high purity and hardness | Refractory materials, abrasives, ceramics | Pros: Consistent quality, high purity, excellent wear resistance. Cons: Higher cost, energy-intensive production. |
| Tabular Alumina | Sintered at high temperatures, forming dense, large, tabular crystals | Refractory linings, kiln furniture | Pros: Superior thermal stability, low porosity. Cons: More expensive, limited supply options. |
| Reactive Alumina | Fine, high surface area, highly reactive, often used in chemical applications | Catalysts, fillers, chemical processing | Pros: Enhanced reactivity, excellent chemical stability. Cons: Less suitable for structural uses, higher handling costs. |
| White Alumina | Purity-focused, low iron content, bright white appearance | Optical ceramics, electronics, precision components | Pros: High purity, aesthetic appeal, minimal coloration. Cons: Generally more expensive, limited mechanical strength. |
| Brown Alumina | Contains residual impurities like iron and silica, darker color | General abrasives, low-cost refractory uses | Pros: Cost-effective, readily available. Cons: Lower purity, limited high-performance applications. |
Calcined alumina is produced by heating bauxite at high temperatures (around 1000°C to 1600°C), which removes chemically bound water and enhances material hardness and purity. It is widely used in refractory linings, abrasives, and ceramic manufacturing due to its consistent quality and excellent wear resistance. For B2B buyers, calcined alumina offers reliability but comes with higher procurement costs, often justified by its durability and performance. Suppliers should emphasize quality certifications and consistent supply chain capabilities to mitigate risks associated with fluctuating prices.
Tabular alumina is characterized by its dense, crystalline structure formed during high-temperature sintering, resulting in large, flat, tabular crystals. Its superior thermal stability makes it ideal for kiln furniture, refractory linings, and other high-temperature industrial applications. Buyers benefit from its low porosity and long service life, but should be prepared for premium pricing and potential supply limitations. When sourcing, consider the supplier’s sintering process, quality control measures, and ability to meet volume demands, especially for large-scale projects.
Reactive alumina features a fine particle size and high surface area, making it highly reactive and suitable for chemical applications like catalysts and fillers. It is ideal for industries requiring high chemical stability and reactivity, such as chemical processing and advanced composites. B2B buyers should evaluate the purity levels and reactivity specifications closely, as these influence performance and processing costs. Due to its specialized nature, reactive alumina often commands a premium price, and supply stability can vary based on regional production capacities.
White alumina is produced with high purity levels, often through specific refining processes that reduce impurities like iron and silica. Its bright white appearance and high purity make it suitable for optical ceramics, electronics, and precision components where aesthetic and functional quality are critical. Buyers should consider the balance between cost and purity; high-purity white alumina tends to be more expensive but offers superior performance in sensitive applications. Suppliers should demonstrate strict quality control and traceability to ensure product consistency.
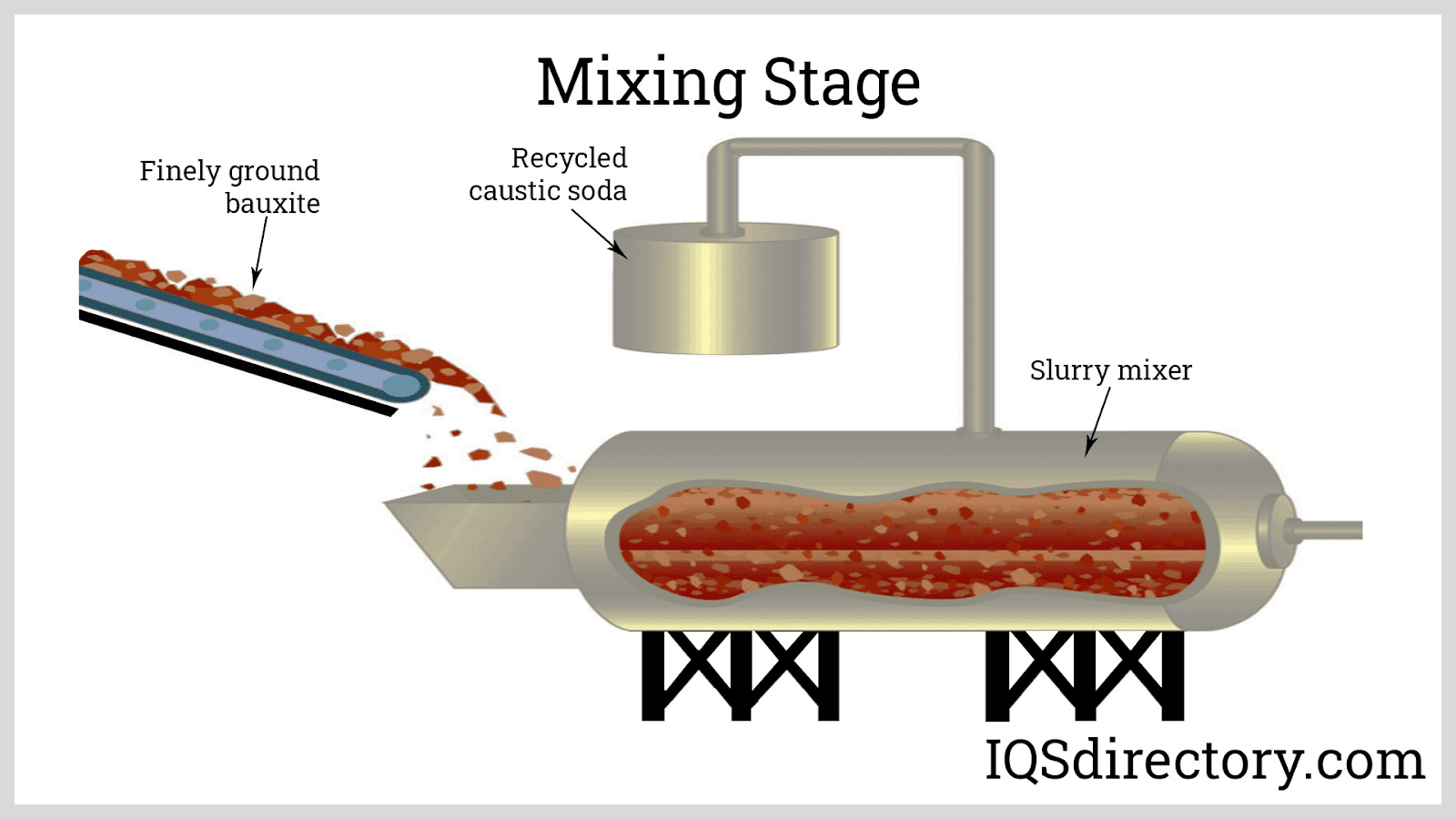
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Brown alumina contains residual impurities such as iron oxides and silica, giving it a darker color. It is primarily used in cost-sensitive applications like general abrasives, low-cost refractory linings, and construction materials. For B2B buyers, brown alumina offers a readily available and economical option, but its lower purity limits its use in high-end or high-performance applications. When sourcing, consider supplier reputation, impurity levels, and whether the material meets specific industry standards for abrasiveness and durability.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of alumina | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramics & Refractories | High-purity alumina for advanced ceramic components | Enhanced thermal stability, wear resistance, and product longevity | Consistent quality, high purity levels, reliable supply chains, and certification standards |
| Abrasives & Polishing | Alumina grit and powders for cutting and finishing tools | Superior abrasive performance, durability, and efficiency | Particle size precision, bulk availability, cost competitiveness, and safety standards |
| Electronics & Dielectrics | Alumina substrates for electronic components | Excellent electrical insulation, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength | Purity levels, defect-free material, compliance with industry standards, and traceability |
| Water Treatment & Filtration | Activated alumina for contaminant removal | Effective removal of fluoride, arsenic, and other impurities, ensuring water safety | Certification for potable water, chemical stability, supply consistency, and cost-effectiveness |
| Aerospace & Defense | Specialized alumina ceramics for components | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability | Customization options, stringent quality controls, and adherence to international standards |
High-purity alumina is essential in manufacturing advanced ceramics and refractory linings for high-temperature industrial processes. It provides exceptional thermal stability, mechanical strength, and wear resistance, making it ideal for kiln linings, crucibles, and ceramic parts used in industries such as metallurgy, glass, and cement. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America where industrial infrastructure is expanding, sourcing high-quality alumina ensures durability and reduces maintenance costs. Consistency in purity and supply reliability are critical to prevent production delays and meet stringent industry standards.
Alumina grit and powders are widely used in abrasive tools for cutting, grinding, and polishing across various manufacturing sectors. Their hardness and durability enable efficient material removal and surface finishing, essential for industries like automotive, machinery, and construction. Buyers from emerging markets such as Turkey or Nigeria require abrasives that combine cost-effectiveness with high performance. Sourcing considerations include particle size uniformity, bulk availability, and adherence to safety and environmental standards, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing operational risks.
Alumina substrates serve as insulating platforms in electronic devices, including semiconductors, LEDs, and sensors. They provide excellent electrical insulation, high thermal conductivity, and mechanical robustness, crucial for reliable electronic performance. International B2B buyers, especially from Europe and the Middle East, seek defect-free, high-purity alumina to meet strict industry certifications and quality benchmarks. Reliable sourcing with traceability, consistent purity, and compliance with international standards ensures the performance and longevity of electronic components, vital for competitive manufacturing.
Activated alumina is a key material in water purification systems, effectively removing fluoride, arsenic, and other harmful contaminants. Its chemical stability, high surface area, and regenerability make it a cost-effective solution for municipal, industrial, and rural water treatment projects. Buyers from regions like Nigeria or South America prioritize certified, safe, and reliable supply chains to ensure water safety standards are met. Sourcing considerations include compliance with health regulations, chemical stability over multiple cycles, and availability of bulk quantities at competitive prices.
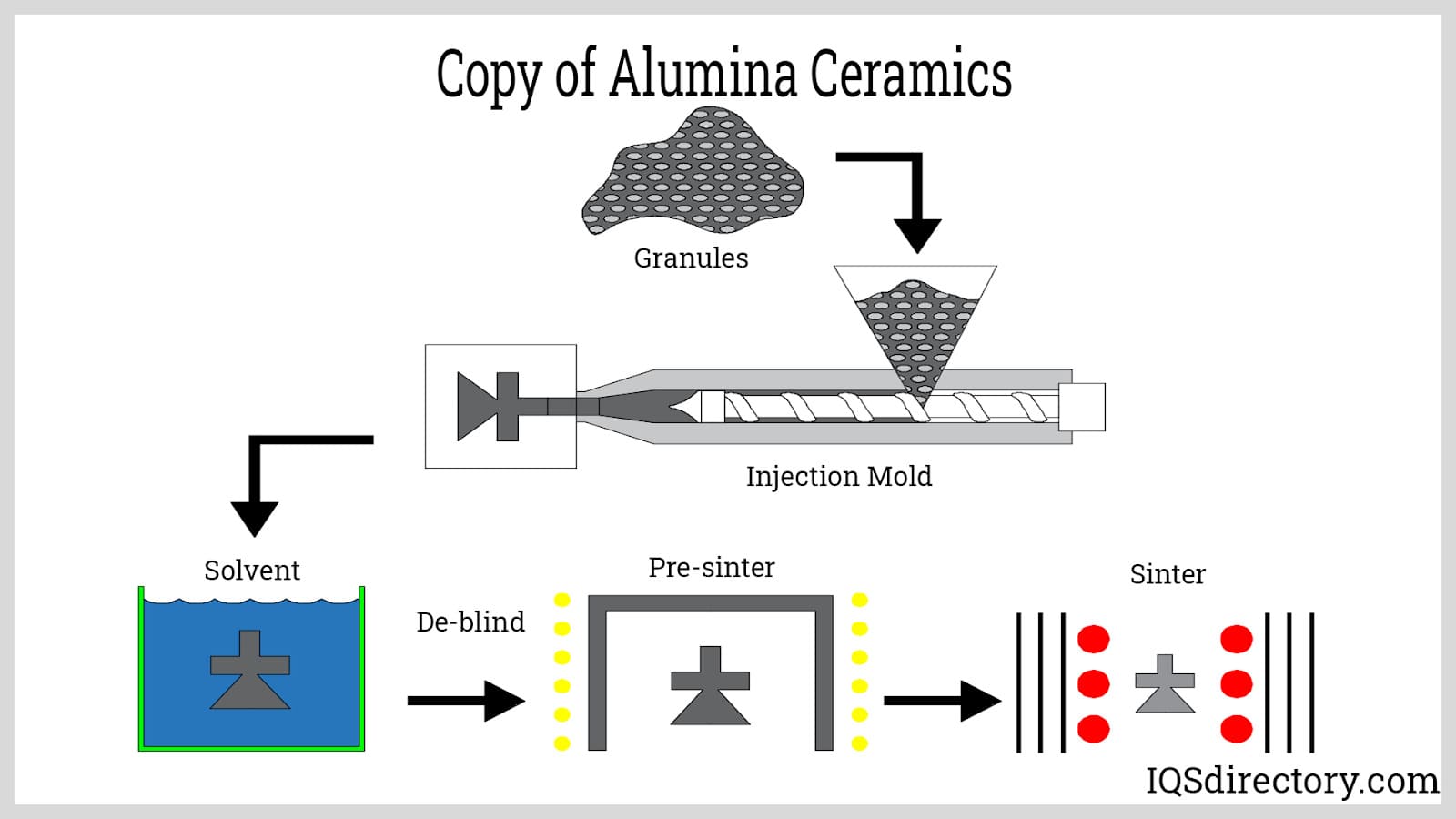
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Specialized alumina ceramics are employed in aerospace and defense applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. These ceramics are used in turbine blades, missile components, and protective armor. International B2B buyers require customization, rigorous quality controls, and adherence to international aerospace standards. Ensuring supply chain resilience, consistent quality, and access to advanced manufacturing capabilities is vital for buyers in Europe, Turkey, and other regions aiming to meet stringent industry specifications.
When selecting alumina materials for industrial applications, B2B buyers must consider key properties such as thermal stability, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and manufacturing complexity. The choice of alumina type directly influences product performance, longevity, and compliance with international standards. Below is an in-depth analysis of three prevalent alumina types—white fused alumina, tabular alumina, and reactive alumina—focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and considerations for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties:
White fused alumina is produced by melting high-purity alumina in electric arc furnaces, resulting in a dense, hard, and chemically inert material. It exhibits excellent thermal stability up to approximately 2000°C and offers high wear resistance, making it suitable for abrasive applications. Its chemical inertness ensures compatibility with various media, including acids and alkalis.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: High hardness and durability; excellent thermal and chemical stability; consistent quality; suitable for high-temperature environments.
- Cons: Relatively high cost due to energy-intensive manufacturing; limited porosity may restrict certain filtration applications; manufacturing complexity may lead to supply chain variability.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for abrasive tools, refractory linings, and wear-resistant components. Its inertness makes it suitable for corrosive media in chemical processing equipment.
International Buyer Considerations:
European standards such as EN and ASTM are widely recognized, facilitating compliance. Buyers from Africa and South America should verify supplier certifications aligning with ISO standards. The high cost may be a concern for large-volume projects, but quality consistency is critical for high-performance applications.
Key Properties:
Produced through calcining alumina hydrate at high temperatures (~1750°C), tabular alumina features a crystalline, plate-like structure. It offers superior corrosion resistance, excellent thermal stability, and high mechanical strength. Its low porosity enhances its resistance to chemical attack.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Excellent corrosion and alkali resistance; high thermal stability; good mechanical strength; lower impurity levels.
- Cons: Higher manufacturing costs; potential brittleness if not processed properly; limited availability in some regions.
Impact on Application:
Widely used in refractory linings, kiln furniture, and high-temperature insulation. Its resistance to aggressive media makes it suitable for chemical and petrochemical industries.
International Buyer Considerations:
Compliance with ASTM C799 and DIN 51004 standards is common. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with certifications aligned to these standards. The higher cost is offset by its durability and long-term performance, especially in corrosive environments.
Key Properties:
Reactive alumina is characterized by its high surface area and porosity, making it highly reactive and suitable for chemical applications. It is produced by controlled calcination, resulting in a material that can be easily processed into various forms.
Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Cost-effective; high reactivity; excellent for chemical catalysts and adsorbents; adaptable for different processing methods.
- Cons: Lower mechanical strength; less suitable for high-wear applications; limited thermal stability compared to fused alumina.
Impact on Application:
Primarily used in catalyst supports, adsorbents, and as a raw material for specialty ceramics. Its reactivity makes it ideal for applications requiring chemical interaction.
International Buyer Considerations:
Standards such as JIS and ASTM are relevant for reactive alumina. Buyers should ensure supplier compliance with regional certifications and verify batch consistency. Cost advantages are significant for large-volume chemical processing projects, but mechanical limitations should be considered for structural uses.
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of alumina | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Fused Alumina | Abrasives, refractory linings, wear-resistant components | High hardness, thermal stability, chemical inertness | High cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Tabular Alumina | Refractory linings, kiln furniture, chemical-resistant linings | Excellent corrosion resistance, high thermal stability | Higher manufacturing cost, potential brittleness | High |
| Reactive Alumina | Catalyst supports, adsorbents, specialty ceramics | Cost-effective, high reactivity, versatile processing | Lower mechanical strength, limited thermal stability | Low |
This comprehensive analysis equips international B2B buyers with critical insights into alumina selection, emphasizing the importance of aligning material properties with specific application needs and regional standards. By understanding the trade-offs between cost, performance, and compliance, buyers from diverse regions can make informed procurement decisions that optimize both quality and value.
The manufacturing of alumina (aluminum oxide) involves several well-established stages, each tailored to produce specific types with distinct properties. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to assess quality, consistency, and supplier reliability.
1. Material Preparation
The process begins with bauxite ore, which is refined to extract alumina via the Bayer process. This involves crushing the ore, digesting it with sodium hydroxide at high temperatures, and then precipitating alumina hydrate. For specialty aluminas like reactive or sintering grades, additional chemical modifications or purification steps may be incorporated to enhance purity and specific characteristics.
2. Calcination and Densification
The alumina hydrate is then calcined at controlled high temperatures (typically 1000-1600°C) to produce alumina powders with desired phase compositions. Variations in calcination temperature influence properties like porosity, particle size, and surface area, critical for applications such as refractories, ceramics, or abrasives.
3. Forming Techniques
Depending on the final application, alumina powders undergo forming processes such as pressing, extrusion, or slip casting. For high-density ceramics, hot pressing or isostatic pressing are common, ensuring uniformity and optimal mechanical properties. For abrasive or refractory products, granular or pelletized forms are prepared through pelletizing or granulation.
4. Sintering and Finishing
The shaped alumina components are sintered at elevated temperatures to achieve the desired density and structural integrity. Post-sintering treatments may include grinding, polishing, or surface coatings to meet strict dimensional tolerances and surface quality standards. Advanced manufacturing may also involve hot isostatic pressing (HIP) to eliminate porosity and improve strength.
Rigorous quality control is essential to meet international standards and ensure product reliability for diverse industrial applications.
1. International Standards & Certifications
Most reputable alumina manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001 quality management systems, ensuring consistent process control and product quality. Industry-specific standards such as CE (European Conformity), API (American Petroleum Institute), and ASTM provide specific test criteria for alumina's physical, chemical, and mechanical properties.
2. QC Checkpoints Throughout Production
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials, especially bauxite and chemical reagents, are tested for purity, particle size distribution, and contaminants before processing.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During calcination, forming, and sintering, parameters like temperature, pressure, and moisture are closely monitored. Sampling and testing ensure process stability and product uniformity.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished alumina products undergo comprehensive testing, including density measurements, hardness tests, phase analysis, and surface inspections.
3. Testing Methods
Standard testing methods include X-ray diffraction (XRD) for phase purity, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for microstructure analysis, laser diffraction for particle size distribution, and chemical titration for purity levels. Mechanical testing such as flexural strength or hardness assessments verifies suitability for demanding applications.
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality is vital to mitigate risks and ensure product performance.
1. Supplier Certifications and Documentation
Request copies of ISO 9001 certificates, industry-specific certifications (CE, API, ASTM), and third-party inspection reports. Reputable suppliers will readily provide detailed certificates of analysis (CoA) and test reports for each batch.
2. Conduct Audits and Factory Visits
Arranging on-site audits or engaging third-party inspection agencies allows buyers to assess manufacturing facilities, quality control procedures, and lab capabilities. Focus on cleanliness, equipment calibration, and QC documentation practices.
3. Third-Party Inspection and Testing
Utilize independent inspection companies to perform pre-shipment inspections, sampling, and testing according to relevant standards. This step is especially crucial for regions with less mature regulatory oversight or for high-value transactions.
4. Sample Testing and Validation
Prior to large orders, request samples for independent testing aligned with your specific application requirements. This helps confirm that the product meets agreed specifications and quality expectations.
Different regions have varying levels of regulatory oversight and industry standards, which influence QC expectations:
Africa and South America: Suppliers may have less stringent local regulations but should still comply with international standards like ISO or ASTM. Buyers should emphasize third-party audits and testing to verify quality claims.
Middle East and Turkey: These regions often have a mix of local standards and international certifications. Ensuring the supplier holds recognized certifications and demonstrates a track record of quality is critical.
Europe: Suppliers are generally more regulated and certified under strict standards like CE and EN certifications. Buyers can leverage these certifications for assurance but should still perform due diligence through audits or third-party testing.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols enables B2B buyers to select reliable alumina suppliers capable of delivering consistent, high-quality products. Emphasizing certification verification, on-site audits, third-party testing, and clear documentation will mitigate risks and foster successful international trade relationships across diverse regions.
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure of alumina is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary components include:
Several factors shape alumina pricing in the international market:
Prices for alumina can range broadly depending on type, quality, and source. As of late 2023, typical prices are approximately:
These figures are indicative and subject to fluctuations based on raw material prices, regional factors, and market conditions. Buyers should conduct current market research and obtain multiple quotes for accurate budgeting.
By understanding these cost components and influencing factors, B2B buyers can develop more strategic procurement plans, negotiate effectively, and optimize their alumina sourcing for cost-efficiency and reliability.
Understanding the key technical specifications of alumina is essential for making informed purchasing decisions and ensuring the material meets application requirements.
1. Material Grade and Purity:
Alumina is classified by purity levels, typically ranging from 85% to over 99.99%. High-purity grades are crucial in electronics, aerospace, and medical applications, where impurities can affect performance. For industrial uses like abrasives or refractory materials, lower purity grades may suffice. B2B buyers should specify their required purity to ensure optimal functionality and compliance with industry standards.
2. Particle Size and Distribution:
Particle size influences the processing and end-use of alumina. Fine powders (sub-micron to a few microns) are used in ceramics and electronics, whereas coarser grades are suitable for abrasives or refractory bricks. Uniform particle distribution ensures consistent quality and performance, reducing waste and rework during manufacturing.
3. Tolerance and Density:
Tolerance refers to the permissible deviation in dimensions or weight, critical for precision applications. Density impacts the material’s mechanical strength and thermal properties. For example, high-density alumina offers superior hardness and wear resistance, vital in cutting tools or wear plates. Buyers should verify these specifications align with their product standards.
4. Grain Size and Microstructure:
Microstructure, including grain size, affects alumina’s strength, toughness, and transparency. Fine-grain alumina typically provides higher strength and better optical clarity, whereas larger grains may enhance thermal shock resistance. Accurate microstructural data helps in selecting the right grade for specific industrial applications.
5. Chemical Composition and Impurities:
Apart from alumina content, trace elements like silica, iron, or sodium can impact product performance, especially in electronics and optical components. Suppliers should provide detailed certificates of analysis to confirm impurity levels meet industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Familiarity with common industry terminology streamlines negotiations and ensures clear communication between international buyers and suppliers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
Refers to companies that produce alumina components or parts used in their own products. When sourcing alumina for OEM manufacturing, buyers should clarify specifications, certifications, and batch traceability to ensure quality control.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell per order. Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan procurement, especially in markets with fluctuating demand. Negotiating MOQ can also impact pricing and delivery schedules.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation):
A formal document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting price quotes, lead times, and technical details. An RFQ is essential for comparing offers, especially when sourcing from multiple regions like Africa, South America, or Europe.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
Standardized trade definitions published by the International Chamber of Commerce, specifying responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs. Common terms like FOB (Free on Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) influence cost structure and risk management.
5. Certification and Compliance Terms:
References to standards such as ISO, ASTM, or REACH indicate adherence to quality, safety, and environmental regulations. Buyers should verify that alumina shipments come with appropriate certifications to meet local import requirements.
6. Lead Time:
The period from order placement to delivery. Understanding lead times helps in planning production schedules and avoiding delays, especially when working with suppliers in diverse regions with varying logistics infrastructure.
Mastering these technical properties and trade terms enhances your ability to select the right alumina grades and negotiate effectively across international markets. Clear specifications and common industry jargon reduce misunderstandings, streamline procurement processes, and foster long-term supplier relationships in competitive global industries.
The global alumina market is driven by the expanding aluminum industry, which itself is propelled by sectors such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and packaging. Emerging economies, particularly in Africa, South America, and parts of the Middle East, are increasingly investing in local alumina processing and refining capacities to reduce reliance on imports and to stimulate economic growth. For B2B buyers from these regions, understanding regional production hubs—such as Guinea, Brazil, and Oman—is crucial, as these markets are becoming more self-sufficient and offer competitive sourcing options.
In recent years, technological advancements have significantly influenced sourcing trends. Innovations in refining processes, such as the development of more energy-efficient Bayer and sintering methods, have lowered production costs and environmental footprints. Additionally, the rise of integrated supply chains—where alumina producers are vertically integrated with bauxite mining—has enhanced supply stability and pricing transparency. For European buyers, especially in Turkey and Nigeria, there is a growing preference for direct trade relationships with primary producers to ensure quality and reduce intermediary costs.
Market dynamics are also shaped by geopolitical factors, trade policies, and environmental regulations. Countries with strategic reserves or refining capacity—like Australia, Brazil, and the Gulf countries—are positioning themselves as key global suppliers. For African and South American buyers, forming partnerships with regional producers can mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. Furthermore, the increasing focus on high-grade, specialty alumina types—such as tabular or reactive alumina—opens new opportunities for industries requiring specific performance characteristics, encouraging tailored sourcing strategies.
Sustainability is increasingly pivotal in the alumina supply chain, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer demand for ethically sourced materials. The environmental footprint of alumina production—particularly the energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions—has come under scrutiny, prompting producers worldwide to adopt greener technologies. For B2B buyers, especially those in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing from certified sustainable producers can provide a competitive advantage and ensure compliance with stringent environmental standards.
Ethical sourcing encompasses responsible bauxite mining, community engagement, and transparent supply chains. Certification schemes such as the Aluminum Stewardship Initiative (ASI) and ISO 14001 help verify sustainable practices, fostering trust and reducing reputational risks. For buyers in regions like Nigeria and Turkey, engaging with suppliers holding these certifications can facilitate access to premium markets and meet corporate sustainability commitments.
Furthermore, the development of 'green' alumina—produced using renewable energy sources or with lower carbon emissions—is gaining momentum. Investing in or sourcing from producers committed to environmental innovation not only aligns with global sustainability goals but can also lead to cost savings over time through energy efficiencies. Transparency in sourcing practices is critical; buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide detailed environmental impact disclosures and adhere to ethical labor standards, thereby supporting a responsible alumina supply chain.
The alumina sector has evolved from rudimentary extraction and refining practices to a highly sophisticated, globally interconnected industry. Initially centered around basic bauxite processing, technological innovations such as the Bayer process revolutionized alumina production in the early 20th century, enabling large-scale, cost-efficient manufacturing. Over time, increasing environmental awareness and resource management concerns prompted the adoption of cleaner, more sustainable technologies.
Today, the industry emphasizes not only efficiency but also sustainability and traceability. As global demand for aluminum surges—particularly in developing economies—so does the importance of diversified sourcing options and responsible supply chains. For B2B buyers from emerging markets like Nigeria and South America, understanding this evolution helps in assessing supplier reliability, technological capabilities, and environmental commitments, which are increasingly critical decision factors in sourcing alumina.
To ensure supplier credibility, start by checking their certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and industry-specific standards like ASTM or API. Request detailed product datasheets, test reports, and third-party QA certificates to confirm alumina purity, particle size, and other specifications. Conduct virtual audits or visit supplier facilities if possible, especially for high-volume orders. Engaging with reputable third-party inspection agencies before shipment can further mitigate risks. Building relationships with suppliers who have transparent quality processes and positive references from other international buyers enhances trust and reduces supply chain disruptions.
Identify your specific application requirements—whether it’s for ceramics, refractories, abrasives, or other uses. Key parameters include alumina purity levels, grain size, bulk density, and chemical composition. Consult technical datasheets and industry experts to match product specifications with your process needs. Suppliers often offer customization options such as calcined, tabular, or fused alumina, tailored to different performance criteria. Request sample testing and small trial orders to validate performance before committing to large-scale procurement, ensuring the alumina meets your operational standards.
MOQs vary depending on supplier size, alumina type, and packaging options but generally range from 10 to 25 metric tons for standard grades. Custom or specialized alumina may have higher MOQs. Lead times typically span from 2 to 8 weeks after order confirmation, influenced by raw material availability and production schedules. To optimize supply chain planning, negotiate flexible MOQs and lead times upfront, especially if you're a new buyer or sourcing for niche applications. Establish clear communication channels to monitor production progress and avoid delays.
Most suppliers prefer letters of credit (L/C), advance payments, or a combination of both, depending on your creditworthiness and order volume. For trusted partners, open account terms may be possible after establishing a solid relationship. Payment methods include wire transfers, bank drafts, and sometimes online payment platforms for smaller orders. Always clarify payment terms before signing contracts, and consider using escrow services or trade finance options to protect both parties. Ensuring transparent payment processes builds trust and facilitates smoother transactions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Reliable suppliers provide comprehensive QA documentation, including purity analysis, particle size distribution, bulk density, and moisture content. Certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), and industry-specific standards add credibility. For certain applications, certifications like REACH or RoHS compliance may be necessary. Request batch-specific test reports and inquire about their quality control procedures. Establish quality benchmarks in your contract to ensure consistent product performance and reduce risks of rejection or rework.
Partner with freight forwarders experienced in handling bulk mineral shipments and familiar with export/import regulations of your country. Consider multimodal transportation—sea freight is common for large volumes, while air freight may be suitable for urgent smaller orders. Negotiate FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) terms to clarify responsibility and cost-sharing. Consolidate shipments to reduce costs and ensure proper packaging to prevent damage during transit. Regularly review logistics providers’ performance and consider warehousing options near your end-market for better inventory management.
Establish clear contractual clauses covering quality standards, inspection rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms like arbitration or mediation. Maintain detailed records of orders, communications, and inspection reports to support claims if issues arise. Conduct pre-shipment inspections and request third-party testing if necessary. In case of disputes, engage in transparent dialogue with the supplier, referencing contractual terms and documented evidence. If unresolved, escalate through arbitration bodies or trade associations familiar with international mineral trade laws to seek fair resolution.
Focus on transparency, consistent product quality, and timely deliveries to foster trust. Regular communication, site visits, and feedback help strengthen partnerships. Negotiate favorable terms for future orders, such as volume discounts or flexible MOQs, based on mutual growth. Stay informed about supplier capacity, raw material sourcing, and market trends to anticipate supply chain shifts. Establishing a collaborative relationship reduces risks of disruptions and opens opportunities for customization, innovation, and better payment terms, ultimately securing a reliable supply chain for your business expansion.
Effective sourcing of alumina requires a nuanced understanding of the diverse types available and their specific applications across industries. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers is essential to ensure quality, consistency, and cost-efficiency. Diversifying sourcing channels and leveraging regional strengths—such as Nigeria’s bauxite reserves or Turkey’s refining capacity—can mitigate supply chain risks and optimize procurement.
In an evolving global landscape marked by fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical shifts, proactive sourcing strategies will be critical. Staying informed about technological advancements and market trends will enable buyers to adapt swiftly and secure competitive advantages. As demand for alumina grows in sectors like aerospace, electronics, and construction, aligning sourcing strategies with industry developments will become increasingly vital.
Moving forward, international buyers should prioritize building resilient supply networks, fostering transparency, and engaging in long-term collaborations. By doing so, they will position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities, reduce vulnerabilities, and sustain growth in a dynamic global alumina market. Strategic sourcing is not just a necessity but a key driver of competitive success in the evolving alumina landscape.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina