Guide to Preisentwicklung Silizium
In the rapidly evolving landscape of high-tech manufacturing and renewable energy, silicon remains a cornerstone material—its price development (Preisentwicklung Silizium) directly influences global supply chains and procurement strategies. For international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of silicon market trends is essential to optimize sourcing, manage costs, and mitigate risks amid fluctuating prices.
This comprehensive guide explores every critical facet of Preisentwicklung Silizium—from the various types and material qualities to manufacturing standards and quality control processes. It also delves into the key global suppliers, pricing dynamics, and market drivers shaping current and future trends. Equipped with this knowledge, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives, whether they’re sourcing for semiconductor production, solar panels, or other high-demand applications.
By providing actionable insights into market fluctuations, cost factors, and supplier landscapes, this guide empowers B2B buyers—especially those in emerging markets and regions with growing industrial needs—to navigate the complexities of the global silicon market confidently. Whether you are sourcing from established suppliers in Europe or exploring emerging opportunities in Africa and South America, understanding Preisentwicklung Silizium is fundamental to maintaining competitiveness and ensuring supply chain resilience in an unpredictable market environment.
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polished Silicon (Czochralski) | High purity, crystalline structure, uniform grain size | Semiconductor manufacturing, solar cells | High quality; reliable for high-performance needs but costly and supply-sensitive |
| Metallurgical Grade Silicon | Lower purity, irregular crystalline structure, cost-effective | Aluminum alloys, silicones, construction | Cost-efficient; suitable for bulk applications but less suitable for sensitive tech |
| Amorphous Silicon | Non-crystalline, thin-film form, flexible deposition | Thin-film solar panels, displays | Flexible and easy to deposit; lower efficiency but good for niche markets |
| Silicon Wafers (Mono/Poly) | Sliced from crystalline ingots, either monocrystalline or polycrystalline | Solar panels, microelectronics | Monocrystalline offers high efficiency; polycrystalline is cheaper, trade-offs in performance |
| Recycled Silicon | Reprocessed from industrial waste or scrap | Eco-friendly electronics, secondary markets | Cost-effective and sustainable; quality varies, requiring careful supplier vetting |
Polished Silicon (Czochralski) is the gold standard for high-purity applications, especially in the semiconductor industry. Its crystalline uniformity ensures consistent electrical properties, making it ideal for advanced electronics and photovoltaic cells. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with verified purity standards and consistent supply chains, particularly in regions like South Africa or Nigeria where import dependencies are high. The main challenge is its high cost and limited availability, which necessitates strategic procurement planning.
Metallurgical Grade Silicon is characterized by its lower purity but significantly reduced cost, making it suitable for large-scale, less sensitive applications such as aluminum alloy production or silicones. For B2B buyers in emerging markets, this variation offers a cost-effective solution for industrial uses, but they must ensure supplier transparency regarding quality standards to avoid costly rework or product failures.
Amorphous Silicon is distinguished by its non-crystalline structure, allowing for flexible, thin-film deposition on various substrates. Its applications in solar panels and displays make it attractive for niche markets where flexibility and ease of manufacturing are priorities. Buyers should consider the efficiency trade-offs and establish reliable supply channels, especially as demand for flexible electronics increases globally.
Silicon Wafers (Mono/Poly) are sliced from large crystalline ingots, with monocrystalline wafers offering higher efficiency but at a premium price. Polycrystalline wafers are cheaper but slightly less efficient, making them suitable for cost-sensitive projects. B2B procurement strategies should focus on quality certifications and supplier reliability to ensure consistent performance, particularly for solar panel manufacturers or microelectronics firms.
Recycled Silicon emphasizes sustainability, derived from industrial waste or scrap silicon. Its growing acceptance aligns with global green initiatives, especially in Europe and environmentally conscious markets in South America. Buyers need to scrutinize supplier credentials and testing reports to ensure recycled material meets technical specifications, balancing cost savings with quality assurance.
When sourcing silicon types, buyers should evaluate purity levels, supply chain stability, and certification standards. Regions like Africa and South America may face import restrictions or higher logistics costs, so establishing local or regional suppliers can mitigate risks. Additionally, understanding the specific application requirements—such as electrical performance, flexibility, or cost constraints—will guide the optimal silicon type selection. Strategic partnerships with reputable suppliers and thorough quality assurance processes are essential for securing reliable, cost-effective silicon tailored to regional market demands.
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of preisentwicklung silizium | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Fabrication of integrated circuits (ICs) and microchips | Enables high-performance, energy-efficient devices; critical for innovation | Purity levels, supply chain stability, compliance with international standards |
| Renewable Energy | Solar panel manufacturing (photovoltaic cells) | Enhances efficiency and durability of solar modules; supports sustainable energy goals | Quality consistency, cost competitiveness, reliable sourcing channels |
| Automotive Industry | Power electronics and sensor components | Improves vehicle efficiency, safety, and autonomous capabilities | Material reliability, certification standards, regional import regulations |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Structural silicon-based materials (e.g., silica) | Provides durable, high-strength construction materials; supports infrastructure resilience | Quality assurance, regional availability, adherence to building codes |
| Healthcare & Medical Devices | Silicon-based sensors and diagnostic equipment | Ensures high sensitivity and reliability in medical diagnostics | Biocompatibility, regulatory approvals, consistent supply for critical applications |
Preisentwicklung Silizium is fundamental in the production of semiconductors, which form the backbone of electronic devices worldwide. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing high-purity silicon for integrated circuits ensures the manufacturing of reliable, high-performance chips. These chips power everything from consumer electronics to industrial automation. The key challenges include ensuring supply chain stability and compliance with international purity standards, especially for regions with developing manufacturing infrastructure.
Silicon's role in solar panel manufacturing is pivotal for the global shift toward renewable energy. B2B buyers involved in solar project development seek high-quality silicon to produce efficient photovoltaic cells. This application demands materials with consistent purity and performance to maximize energy conversion efficiency and panel lifespan. International buyers must prioritize suppliers with proven quality control, cost-effective logistics, and certifications aligning with regional standards to mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In the automotive sector, silicon-based components are increasingly essential for power electronics, sensors, and autonomous vehicle systems. For B2B buyers, especially in regions like South Africa or Brazil, sourcing silicon with reliable electrical properties and compliance with automotive standards is critical. These components enhance vehicle safety, efficiency, and connectivity. Buyers should focus on suppliers offering certified materials that meet regional regulatory requirements and can support just-in-time delivery to keep pace with automotive production cycles.
Silicon-derived materials, such as silica, are integral to modern construction—used in concrete, glass, and insulation. For infrastructure projects across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing high-quality silica ensures durability, structural integrity, and energy efficiency. Buyers need to verify supplier certifications, regional availability, and adherence to local building codes. Securing consistent supply chains minimizes project delays and ensures compliance with evolving safety standards.
Silicon’s unique properties make it ideal for medical sensors, diagnostic equipment, and implantable devices. For international B2B buyers in healthcare, sourcing high-purity silicon is vital for device reliability, biocompatibility, and regulatory approval. Especially in emerging markets, establishing relationships with certified suppliers that can provide consistent, high-quality materials ensures that medical devices meet stringent safety standards and are available for critical healthcare applications without interruption.
When selecting materials for applications involving Preisentwicklung Silizium, especially in a B2B context, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial. This ensures optimal performance, cost efficiency, and compliance with international standards across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Properties:
Silicon Carbide is renowned for its exceptional thermal stability, high-temperature resistance (up to 1600°C), and excellent chemical inertness. It also offers high hardness and good electrical conductivity, making it suitable for high-performance electronic and semiconductor applications.
Pros & Cons:
* Pros:*
- Outstanding thermal and chemical stability enhances durability in harsh environments.
- High corrosion resistance, especially against acids and alkalis.
- Good electrical properties for specialized electronic components.
Impact on Application:
Silicon Carbide's resistance to extreme conditions makes it ideal for high-temperature processing equipment and specialized electronic components in demanding environments.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should verify supplier compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. Additionally, sourcing from regions with established SiC manufacturing capabilities can reduce costs and ensure quality consistency.
Key Properties:
Quartz, or fused silica, offers excellent thermal stability (up to 1200°C), high optical transparency, and low thermal expansion. It is highly resistant to chemical corrosion, especially against acids and alkalis.
Pros & Cons:
* Pros:*
- Superior chemical inertness and optical clarity.
- Relatively straightforward manufacturing processes, leading to moderate costs.
- Good thermal shock resistance when properly processed.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for optical sensors, crucibles, and laboratory equipment, where chemical purity and transparency are critical.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers should ensure compliance with regional standards such as JIS or DIN. For regions like Nigeria or South Africa, sourcing from established suppliers with ISO certifications can mitigate risks related to quality and purity.
Key Properties:
Alumina is a ceramic material known for its high hardness, good thermal stability (up to 1700°C), and excellent electrical insulation properties. It also exhibits good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
* Pros:*
- Cost-effective compared to SiC and quartz.
- Easy to machine and shape into complex components.
- Suitable for electrical insulation and wear-resistant applications.
Impact on Application:
Widely used in insulators, wear parts, and substrates for electronic components, especially where electrical insulation is required.
International Buyer Considerations:
European and Middle Eastern buyers should look for alumina products conforming to DIN or ASTM standards. Regional suppliers with ISO certifications can offer consistent quality suitable for critical applications.
| Material | Typical Use Case for preisentwicklung silizium | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High-temperature electronic components, harsh environment equipment | Exceptional thermal and chemical stability | High manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Quartz (Fused Silica) | Optical sensors, laboratory crucibles | Excellent chemical inertness and optical clarity | Brittle and fragile | Medium |
| Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) | Electrical insulators, wear-resistant parts | Cost-effective, easy to machine | Moderate thermal shock resistance | Medium |
This comprehensive understanding of material properties, advantages, and limitations enables international B2B buyers to make informed decisions aligned with their specific application needs, regional standards, and budget constraints. Ensuring compliance with local and international standards while optimizing for durability and cost can significantly enhance project success and supply chain resilience.
The production of Preisentwicklung Silizium (price development silicon) involves a series of complex, high-precision manufacturing stages designed to meet the stringent demands of global industries such as electronics, renewable energy, and automotive sectors. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes is crucial to ensuring product quality, compliance, and supply chain resilience.
Manufacturing begins with the sourcing of high-purity silicon feedstock, typically derived from quartz or silica sand. The raw material undergoes initial purification through processes like hydrothermal treatment or carbothermic reduction, where silicon dioxide is reduced with carbon to produce metallurgical-grade silicon (MG-Si). Ensuring the raw material's purity and consistency is vital, as impurities can affect the final product's performance.
The next stage involves refining MG-Si into electronic-grade silicon (EG-Si) or solar-grade silicon, depending on application requirements. Techniques such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), zone refining, and distillation are employed to remove trace contaminants. These processes are conducted in controlled environments to prevent recontamination, adhering to international standards like ISO 9001 for quality management.
High-purity silicon is then shaped into ingots through methods like Czochralski (CZ) process or float zone (FZ) technique. These methods involve melting the silicon and carefully pulling or zone refining to produce single-crystal or polycrystalline silicon ingots. Precision in temperature control and process parameters is essential to achieve uniform crystal quality, impacting downstream manufacturing.
Ingot slicing produces wafers, which are subsequently polished to achieve flatness and surface smoothness critical for semiconductor applications. The wafer production process includes lapping, etching, and chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP). Consistent quality control during these steps ensures minimal defects, which is paramount for high-performance applications.
For specialized applications like sensors or photovoltaic modules, wafers are assembled into larger units or integrated into devices. Finishing processes may include coating, doping, or metalization. Each step requires meticulous process control to meet industry-specific standards.
Quality assurance (QA) is integral throughout the manufacturing lifecycle to ensure product reliability, compliance, and performance. International and industry-specific standards guide these QA processes, and B2B buyers should verify adherence at every stage.
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality is paramount to mitigate risks and ensure consistent supply.
A comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for Preisentwicklung Silizium enables B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. Emphasizing rigorous supplier evaluation, adherence to international standards, and transparent testing protocols will mitigate risks and foster long-term, reliable partnerships across diverse regions. By implementing proactive verification strategies, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can confidently integrate high-quality silicon into their supply chains, ensuring competitiveness and compliance in their respective markets.
Understanding the comprehensive cost framework is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their silizium procurement. The primary cost components include:
Several factors influence silizium pricing, often leading to fluctuations that B2B buyers must navigate:
To optimize costs and mitigate risks, consider these actionable strategies:
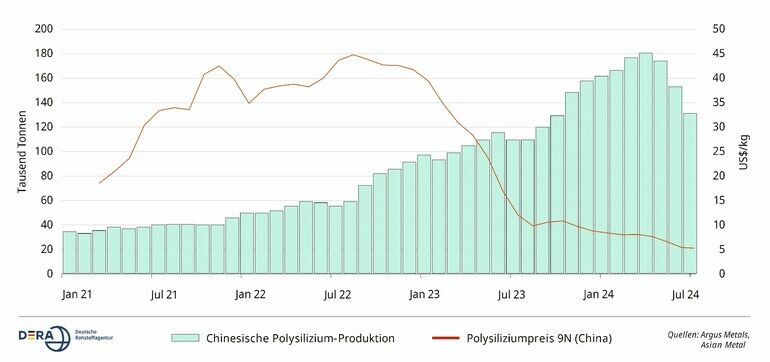
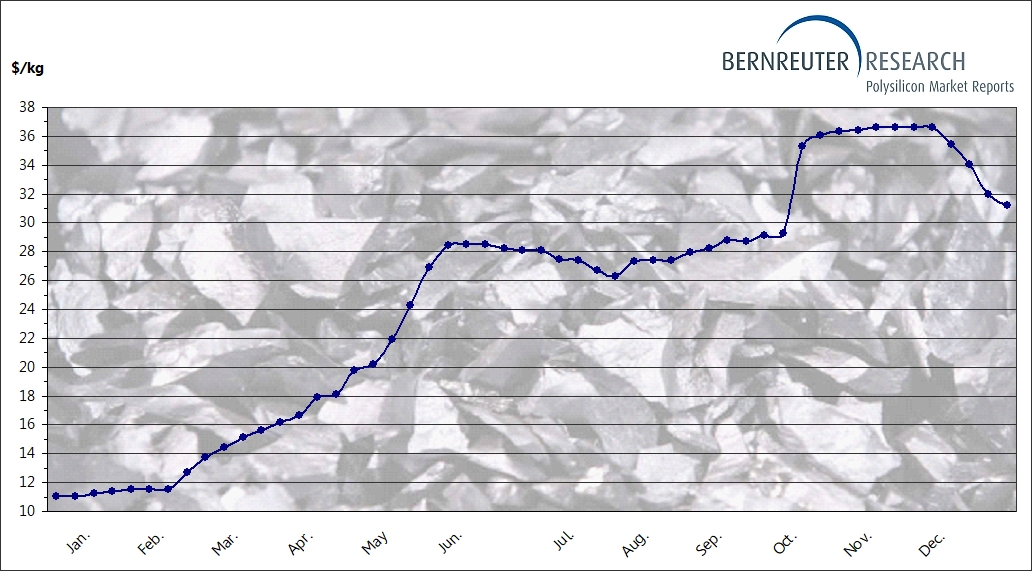
Price estimates for silizium sourcing are highly variable and depend on specific grades, quantities, and market conditions at the time of purchase. As of the latest data, prices for high-purity electronic-grade silizium can range approximately from $10 to $20 per kilogram for large-volume orders, whereas metallurgical-grade silizium typically costs between $3 and $6 per kilogram. Buyers should conduct thorough supplier due diligence and request updated quotes tailored to their precise specifications and logistics needs.
By understanding these cost components and influencing factors, international B2B buyers can better strategize their sourcing approach, negotiate effectively, and optimize their total procurement costs in the evolving silizium market.
Understanding the technical specifications of silicon is essential for international buyers to ensure they receive the right material for their specific applications. Here are the key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Silicon is classified into various grades based on purity and intended use. The most common for industrial applications is solar-grade silicon (around 99.9999% purity) and electronic-grade silicon (99.9999999% purity). Higher purity grades are crucial for semiconductor manufacturing, while slightly lower grades may suffice for photovoltaic or industrial purposes. Confirming the grade ensures compatibility with your manufacturing process and performance expectations.
2. Purity Level
Purity directly impacts the efficiency and quality of end products. Higher purity silicon reduces defects and improves electrical performance. For example, solar-grade silicon typically contains less than 50 parts per million (ppm) of impurities, whereas electronic-grade silicon often has impurities below 1 ppm. Buyers should specify the required purity level and verify it through certification.
3. Tolerance and Size Specifications
Silicon is supplied in various forms—ingots, wafers, powders, or chunks. Tolerance specifications define allowable deviations in dimensions, weight, and shape. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.1 mm for wafers) are critical for precision manufacturing. Buyers should specify size, shape, and tolerance standards to prevent costly adjustments or rejections.
4. Impurity Content and Trace Elements
Impurities such as iron, aluminum, or boron can adversely affect silicon's performance. Industry standards often specify maximum allowable impurity levels. Understanding impurity content is vital, especially for high-tech applications, to ensure the material meets quality and safety requirements.
5. Mechanical and Chemical Properties
Properties like density, hardness, and chemical stability influence processing and application performance. For instance, silicon's chemical stability ensures durability, while mechanical properties affect handling and fabrication. Buyers should review these properties if they plan to integrate silicon into complex manufacturing workflows.
Familiarity with industry-specific terms helps streamline negotiations and ensures clear communication with suppliers. Here are key jargon and concepts:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce silicon materials or components for other manufacturers. Understanding whether a supplier is an OEM or a distributor influences purchasing decisions, quality assurance, and pricing.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. For high-value silicon, MOQs can be significant. Buyers should negotiate to balance cost efficiency with inventory needs, especially in regions with fluctuating demand like Africa or South America.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers request price and delivery details from multiple suppliers. An RFQ helps compare offers and ensures transparency. Preparing detailed specifications increases the likelihood of accurate quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs. Common Incoterms include FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). Understanding these terms ensures clarity on costs and liabilities during transit, especially important for international transactions.
5. Certification and Compliance Standards
Terms like ISO, RoHS, and REACH specify quality, environmental, and safety standards. Ensuring suppliers provide relevant certifications reduces risks related to regulatory compliance, especially critical for buyers in regulated markets like Europe and the Middle East.
6. Lead Time
The period from order placement to delivery. Longer lead times may impact project timelines, so understanding and negotiating lead times with suppliers ensures supply chain reliability.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed purchasing decisions, negotiate effectively, and establish reliable supply chains for silicon materials. Clear specifications and industry terminology are vital for minimizing risks and ensuring quality in international transactions.
The global silicon market, particularly for preisentwicklung silizium (price development in silicon), is driven by the rapid expansion of renewable energy, semiconductor manufacturing, and electronics industries. Key drivers include increasing demand for photovoltaic (solar) panels, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics, all of which rely heavily on high-quality silicon. Emerging B2B sourcing trends reflect a shift towards diversified supply chains, with a growing emphasis on securing reliable, cost-effective sources from regions outside traditional markets like China and the United States.
For international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Countries such as Nigeria and South Africa are exploring local or regional processing capabilities to reduce dependency on imports and mitigate supply chain disruptions. Meanwhile, Middle Eastern nations leverage their strategic geographic position and investments in technological infrastructure to become regional hubs for silicon sourcing.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors, tariffs, and trade policies, which can cause price volatility. Currently, prices are affected by supply chain constraints, environmental regulations, and technological advancements that favor higher purity and efficiency in silicon production. Buyers should monitor these trends closely, engaging with multiple suppliers and exploring long-term contracts to hedge against price fluctuations.
Furthermore, technological innovations like metallurgical-grade silicon improvements and the development of alternative materials are shaping future supply and demand. For B2B buyers, aligning sourcing strategies with these trends—such as investing in regional supply chains or forming strategic partnerships—can provide competitive advantages and ensure supply security.
Sustainability is increasingly central to the silicon supply chain, driven by environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and consumer expectations. The extraction and processing of silicon, especially in regions with lax environmental oversight, can have significant ecological impacts, including land degradation, water usage, and chemical pollution.
For international buyers, prioritizing ethically sourced silicon involves verifying supply chains against recognized environmental standards and certifications. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or responsible sourcing standards (e.g., RCS) are vital benchmarks. 'Green' silicon—produced with reduced carbon emissions and minimal ecological footprint—gains importance as companies aim to meet sustainability commitments and reduce lifecycle emissions.
Implementing transparent supply chains is critical. This involves engaging with suppliers committed to ethical labor practices, environmental stewardship, and compliance with international standards. For example, some producers are investing in renewable energy-powered manufacturing facilities or recycling silicon scrap to minimize waste.
In addition, buyers should consider the use of eco-labels and third-party audits to validate claims of sustainability. These actions not only enhance corporate reputation but also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions due to environmental or social controversies. As sustainability regulations tighten worldwide, integrating green sourcing into procurement strategies will become a key differentiator and risk management tool.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The silicon market has evolved significantly over the past decades. Initially driven by basic electronic applications, it expanded rapidly with the rise of the semiconductor industry and renewable energy sectors. The 2000s saw China emerge as a dominant supplier, pushing prices downward but raising concerns about supply chain concentration and ethical sourcing.
In recent years, technological innovations and environmental considerations have reshaped the landscape. Advances in purification processes and recycling have improved supply sustainability, while geopolitical tensions have prompted diversification efforts. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential for strategic planning, risk mitigation, and aligning procurement with global sustainability trends. Recognizing the market's history helps contextualize current supply risks and opportunities, facilitating more resilient sourcing strategies in an increasingly complex global landscape.
To ensure supplier credibility, conduct thorough due diligence by checking their business licenses, certifications (ISO, industry-specific standards), and customer references. Review their track record in international trade, especially with clients from your region. Engage in direct communication to assess transparency and responsiveness. Consider requesting third-party audits or visiting their facilities if feasible. Partnering with suppliers who have a proven history of consistent quality and reliable delivery minimizes risks associated with fluctuating silicon prices and ensures a stable supply chain for your operations.
When seeking customized silicon, clearly define your specifications, including purity levels, form factors, and specific chemical compositions relevant to your industry (e.g., semiconductor, solar). Verify if the supplier has the technical capability and equipment to meet these requirements. Establish clear communication channels and request detailed samples or prototypes before bulk orders. Discuss lead times, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and costs associated with customization to ensure alignment with your project timelines and budget constraints.
MOQ and lead times depend on supplier size, production capacity, and product complexity. Larger suppliers often have higher MOQs but shorter lead times, while smaller or emerging suppliers may offer lower MOQs but longer production periods. Payment terms commonly range from 30% upfront with the balance before shipment to letter of credit arrangements. Negotiate flexible terms that suit your cash flow, and always clarify penalties for delays or cancellations. Building good relationships can help secure more favorable terms over time.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Prioritize suppliers with internationally recognized certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and industry-specific standards like ASTM or IEC for semiconductor-grade silicon. Request detailed test reports, certificates of analysis (COA), and quality assurance protocols. Suppliers should have traceability systems for raw materials and production processes. Conduct or commission independent testing if necessary. These measures ensure the silicon meets your specifications and reduces the risk of quality issues impacting your production.
Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with your destination region's import regulations and customs procedures. Opt for reliable shipping methods—sea freight for bulk shipments or air freight for urgent needs—considering cost, speed, and volume. Ensure all customs documentation, such as invoices, certificates, and import permits, are accurate and complete to prevent delays. Establish clear communication channels with suppliers and logistics providers to track shipments and address issues proactively, minimizing downtime and costs.
Maintain detailed documentation of all communications, contracts, and quality reports. In case of disputes, refer to contractual terms, including warranty clauses, penalty provisions, and dispute resolution mechanisms (e.g., arbitration, mediation). Engage a third-party inspector or lab to verify quality issues objectively. Negotiate in good faith to reach amicable solutions, such as replacement, refunds, or discounts. Building strong relationships and clear contractual agreements upfront can prevent many disputes and facilitate smoother resolution if issues arise.
Subscribe to industry reports, market analysis from reputable sources, and trade publications focused on raw materials and semiconductor markets. Participate in industry trade shows, webinars, and forums to network with suppliers and experts. Establish relationships with multiple suppliers to get diverse insights and avoid dependency on a single source. Use data analytics tools to monitor pricing trends and forecast future movements, enabling strategic procurement decisions that optimize costs and mitigate risks associated with price volatility.
Focus on transparent communication, consistent quality, and timely delivery. Invest in understanding your supplier’s production capabilities, market conditions, and challenges. Offer feedback and engage in collaborative planning to align your forecasts and reduce uncertainties. Consider establishing long-term contracts with favorable terms that include price stability clauses or volume discounts. Regular audits, supplier visits, and joint development initiatives foster trust and mutual growth, ensuring a resilient supply chain aligned with your international expansion and procurement goals.
Effective strategic sourcing remains critical for international B2B buyers navigating the volatile silizium price landscape. By diversifying supply sources, fostering strong supplier relationships, and leveraging data-driven market insights, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can mitigate risks and secure more favorable terms. Staying adaptable to market fluctuations and understanding geopolitical influences will further enhance procurement resilience.
Looking ahead, the silizium market is poised for continued evolution driven by technological advancements and increasing demand from sectors like renewable energy and electronics. Forward-thinking buyers should prioritize building flexible sourcing strategies, exploring emerging suppliers, and investing in supply chain transparency to capitalize on market opportunities.
Now is the time for international buyers to strengthen their strategic sourcing approaches—not only to manage costs effectively but also to secure a competitive edge in a dynamic global market. Proactive engagement and ongoing market analysis will be essential in navigating future price trends and ensuring sustainable supply chains in the years to come.
Tags: Black Silicon Carbide, White Fused Alumina, Brown Fused Alumina, Pink Fused Alumina, Black Fused Alumina